Method for integrating yarrowia lipolytica genome based on non-homologous end-linking mechanism
A Yarrowia lipolytica, non-homologous technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of low homologous recombination efficiency and unrealizable application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
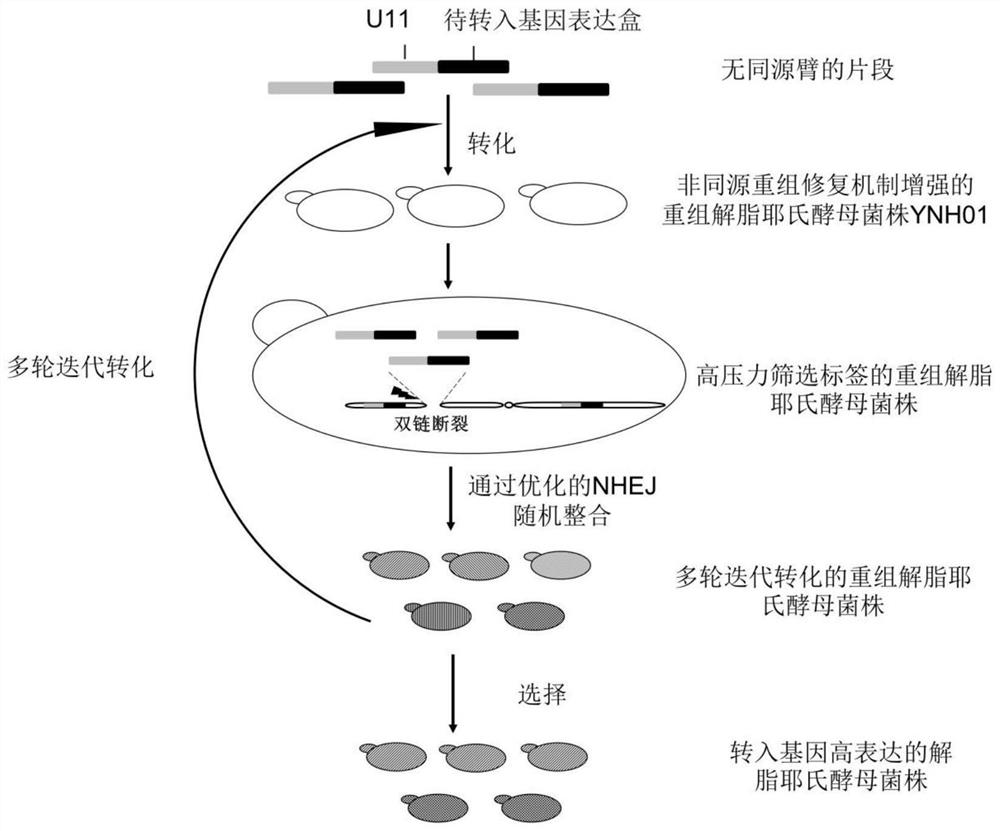
[0038] A method for Yarrowia lipolytica genome integration based on a non-homologous end-joining mechanism (see figure 1 ), including the following steps:
[0039] (1) Obtain the gene DL4 (SEQ ID NO.1) and XRCC4 (SEQ ID NO.3) derived from Yarrowia lipolytica CLIB122 from the NCBI database, the gene PAXX amino acid sequence derived from Homo sapiens, and artificially synthesize the PAXX gene (SEQ ID NO.3) through codon optimization NO.2), the expression cassettes of three genes were assembled simultaneously.
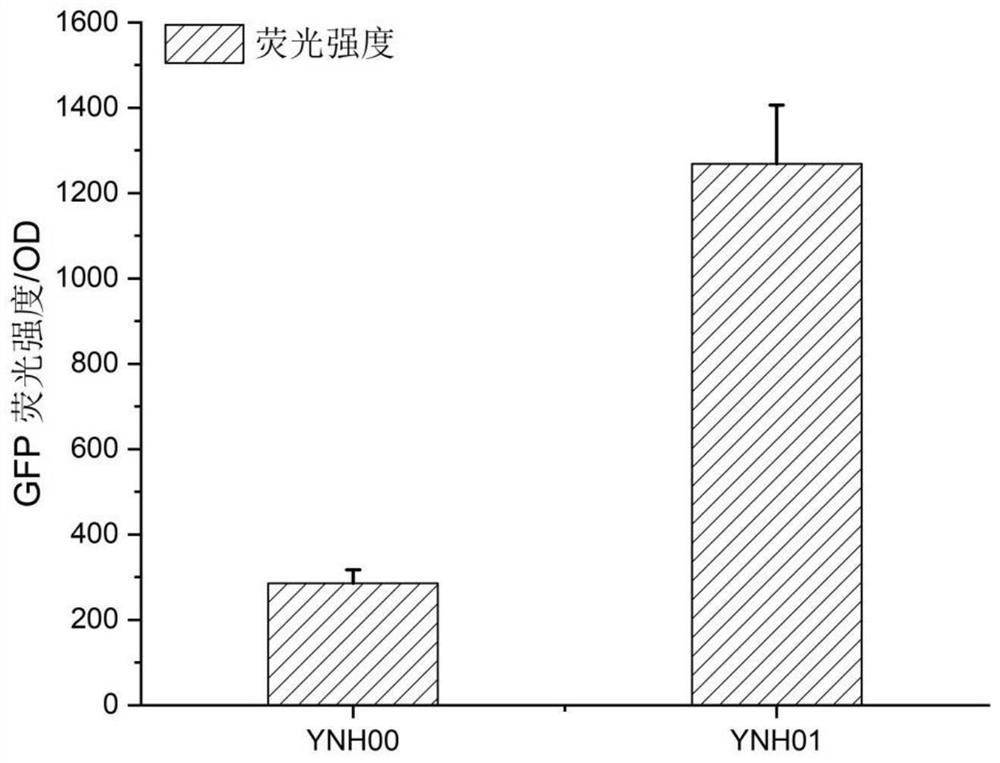
[0040] Through the method of homologous recombination, the DL4 gene expression cassette, the PAXX gene expression cassette and the XRCC4 gene expression cassette were integrated into the genomic rDNA site of Yarrowia lipolytica ATCC201249 strain, and the non-homologous recombination repair mechanism of Yarrowia lipolytica was enhanced The recombinant strain YNH01.
[0041] Use YNH01 as the chassis to transfer the green fluorescent protein GFP gene expression cassette (S...
Embodiment 2
[0049] A method for Yarrowia lipolytica genome integration based on a non-homologous end joining mechanism, comprising the steps of:
[0050] (1) Preparation of the recombinant strain YNH01 with step (1) of Example 1;
[0051] (2) The construction method of the second high-pressure screening label strain, comprises the following steps:
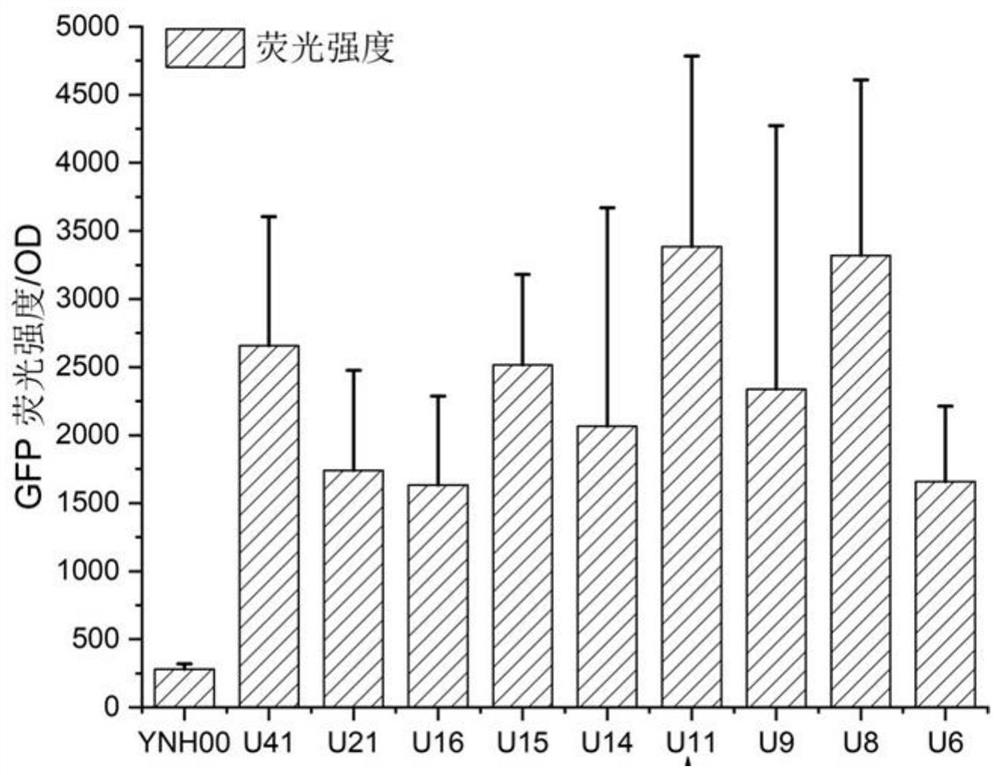
[0052] URA3 nutrition label U11 with promoter truncated to 11bp and lycopene synthesis gene CrtE (SEQ ID NO.5) expression cassette H0-LD01-CrtE-H1, lycopene synthesis gene CrtB (SEQ ID NO.6) expression cassette H1-LD02in-CrtB-H2 and lycopene synthesis gene CrtI (SEQ ID NO.7) expression box H2-LD03-CrtI-H3, 4 fragments are connected to obtain the connection fragment-2; the connection fragment-2 is transformed into a recombinant After the strain YNH01, the second high-pressure screening tag strain was obtained;
[0053] CrtE (SEQ ID NO.5), CrtB (SEQ ID NO.6) and CrtI (SEQ ID NO.7) are artificially synthesized from Erwinia Stawartii Pantoea ste...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com