Manufacturing process of motor stator core
A manufacturing process and stator core technology, which is applied in the field of manufacturing process of motor stator core, can solve the problems of difficult to control thickness difference, non-uniform thickness, and uneven thickness of stator core, so as to eliminate uneven thickness and uniform thickness. good effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Embodiment 1: A manufacturing process of a motor stator core, comprising the following process steps:
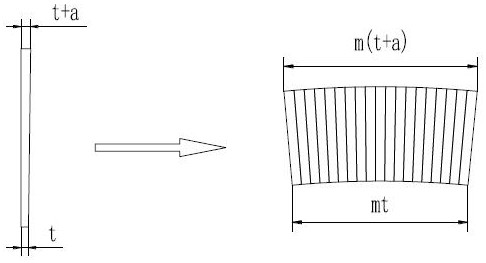
[0037] Pre-step: Detect the average thickness of the strip 1, and obtain the multiple relationship between the average thickness of the strip 1 and the thickness setting value of the stator core single block, so as to determine the stamping required to form a stator core single block The number of single stator core pieces;
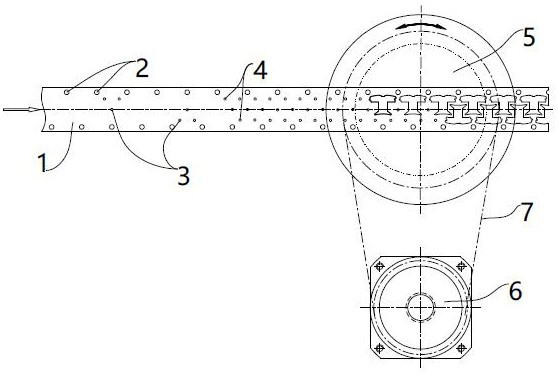
[0038] Step A, feeding: Take the strip material 1 and send it to the punching machine, so that the strip material 1 can continuously step forward and feed the material on the punching machine; There are 3 stations at the metering point, 4 stations at the punching point and blanking station. The schematic diagram of the stamping process line is as follows figure 1 shown;
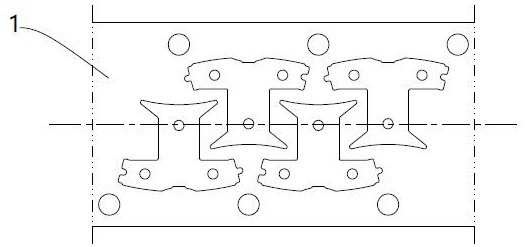
[0039] Step B, Punching the guiding hole 2: During the step forward feeding process of the strip 1, after each step, implement a punching of the guiding hole 2 on both sides o...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Embodiment 2: A manufacturing process of a motor stator core, comprising the following process steps:
[0058] Pre-step: Detect the average thickness of the strip 1, and obtain the multiple relationship between the average thickness of the strip 1 and the thickness setting value of the stator core single block, so as to determine the stamping required to form a stator core single block The number of single pieces of the stator core;
[0059] Step A, feeding: Take the strip material 1 and send it to the punching machine, so that the strip material 1 can continuously step forward and feed the material on the punching machine; There are 3 stations at the metering point, 4 stations at the punching point and blanking station. The schematic diagram of the stamping process line is as follows figure 1 shown;
[0060] Step B, Punching the guiding hole 2: During the step forward feeding process of the strip 1, after each step, implement a punching of the guiding hole 2 on both ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com