Aortic root stent system
A stent system and aortic technology, which is applied in the direction of stents, blood vessels, and devices of human tubular structures, can solve the problems of small anchoring area, weak positioning, and easy displacement, so as to improve stability and increase the scope of application , the effect of not easy to shift
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
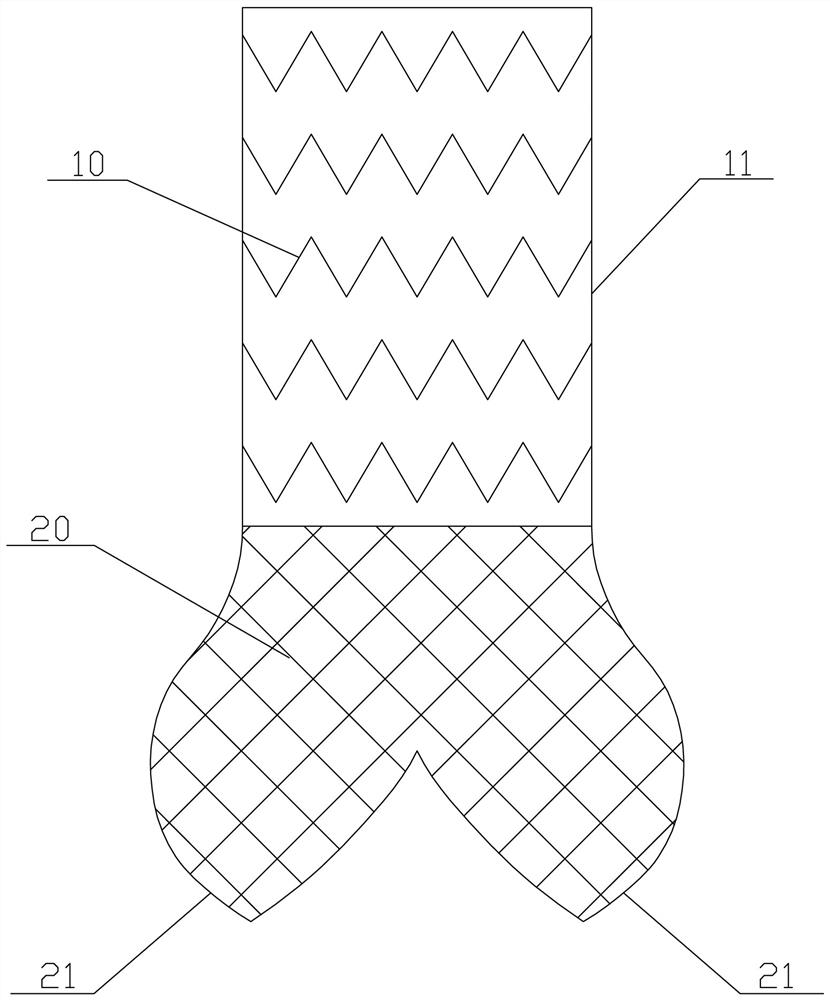
[0031] A kind of aortic root stent system, with reference to figure 1 and figure 2 , including an aortic stent 10 and a sinus anchor stent 20 . The aortic stent 10 is provided with a covering film 11, and the aortic stent 10 is correspondingly attached to the inner wall of the ascending aorta 1, and extends from the inner wall of the distal end of the ascending aorta 1 to the inner wall of the sinotubular junction 2. When a dissection occurs in a certain part of the ascending aorta 1, the corresponding part of the aortic stent 10 is provided with a film-11, and the surrounding part is also provided with a film-11 as an anchoring area, and the aortic stent 10 The other parts of the film can be provided with a film-11, and also can not be provided with a film-11.
[0032] refer to Figure 1 to Figure 3 The bottom of the proximal end of the aortic stent 10 is also fixed with a sinus anchoring stent 20 . The sinus anchoring stent 20 abuts against the inner wall of the aortic s...
Embodiment 2
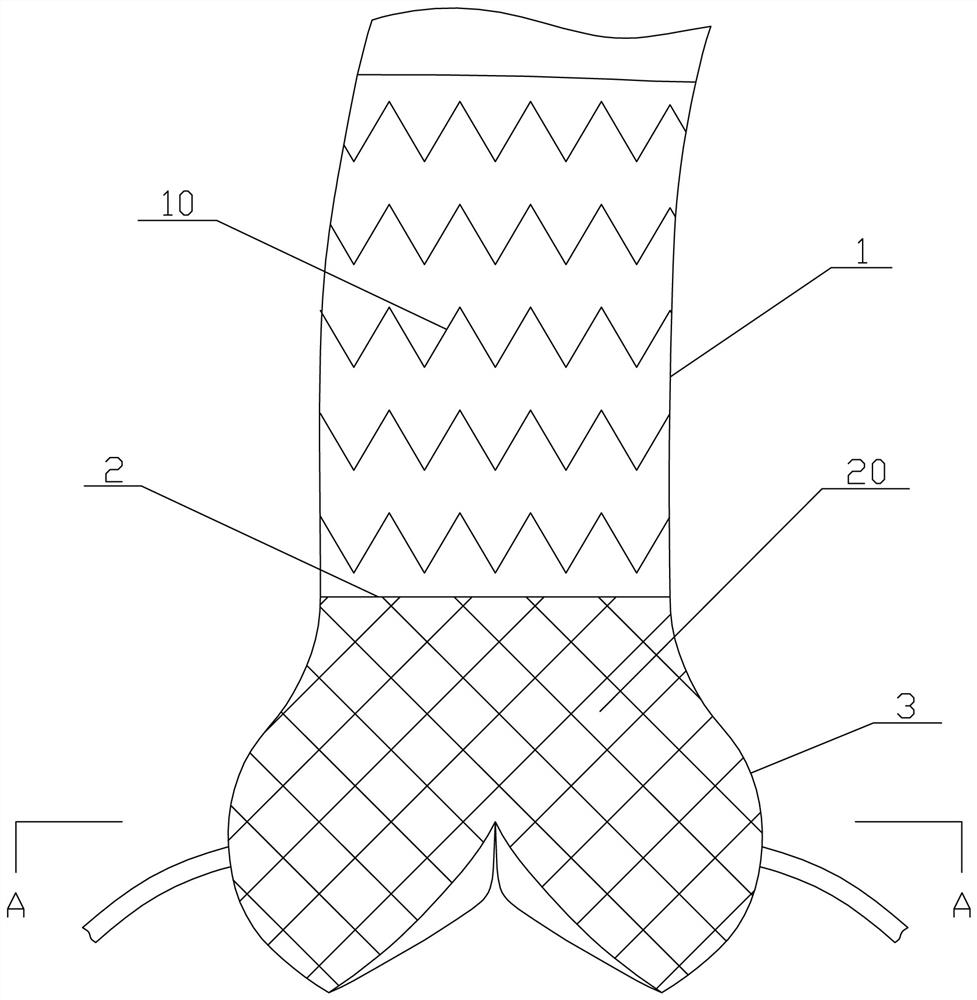
[0037] refer to Figure 4 and Figure 5 , the aortic root stent system of this embodiment also includes an aortic stent 10 and a sinus anchoring stent 20 . The aortic stent 10 is correspondingly attached to the inner wall of the ascending aorta 1 , and extends from the inner wall of the distal end of the ascending aorta 1 to the inner wall of the sinotubular junction 2 , and the aortic stent 10 is provided with a covering film 1 . The sinus anchoring stent 20 is correspondingly attached to the inner wall of the aortic sinus 3, and extends downward from the sinotubular junction 2, and the bottom of the sinus anchoring stent 20 forms several coronary valves that are correspondingly attached to the aortic sinus Stents 21, the outer peripheral surfaces of several coronal valve stents 21 form a garlic clove-like structure.
[0038] The main difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that: the aortic stent 10 is a covered stent with a first covering 11 , while ...
Embodiment 3
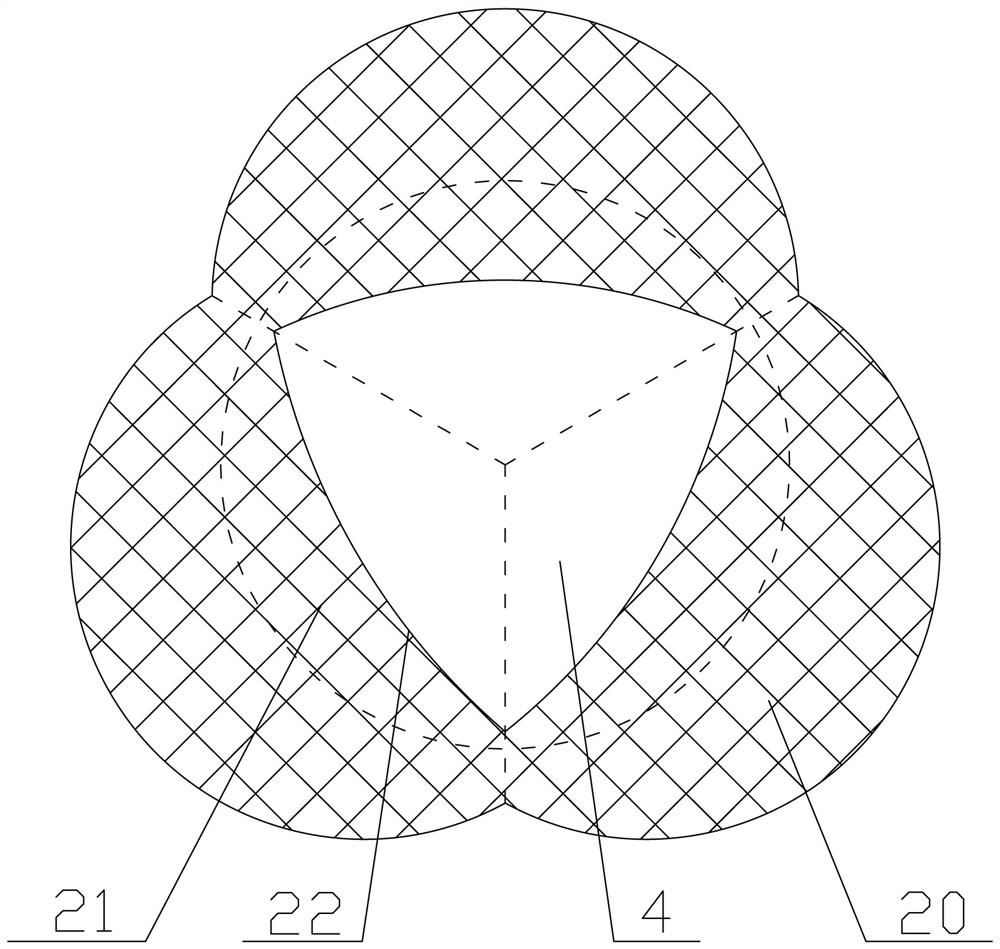
[0040] refer to Figure 6The aortic root stent system of this embodiment also includes an aortic stent 10 and a sinus anchoring stent 20. The bottom of the sinus anchoring stent 20 forms a plurality of corresponding coronary valve stents 21 attached to the aortic sinus. The main difference between the present embodiment and the second embodiment is that: when the dissection of the sinus lesion in the present embodiment occurs below the coronary artery ostium, therefore, the sinus anchoring stent 20 corresponding to the coronary artery ostium must be provided with an overlay Membrane 2 23, through-hole 24 corresponding to the opening of the coronary artery must be opened on the covering membrane 2 23, so as to ensure the normal supply of coronary artery blood flow.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com