Financial risk control method and device based on responsibility chain mode
A responsibility and risk control technology, applied in the field of financial risk control based on the chain of responsibility model, can solve problems such as bloated functions, complex implementation, and poor scalability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
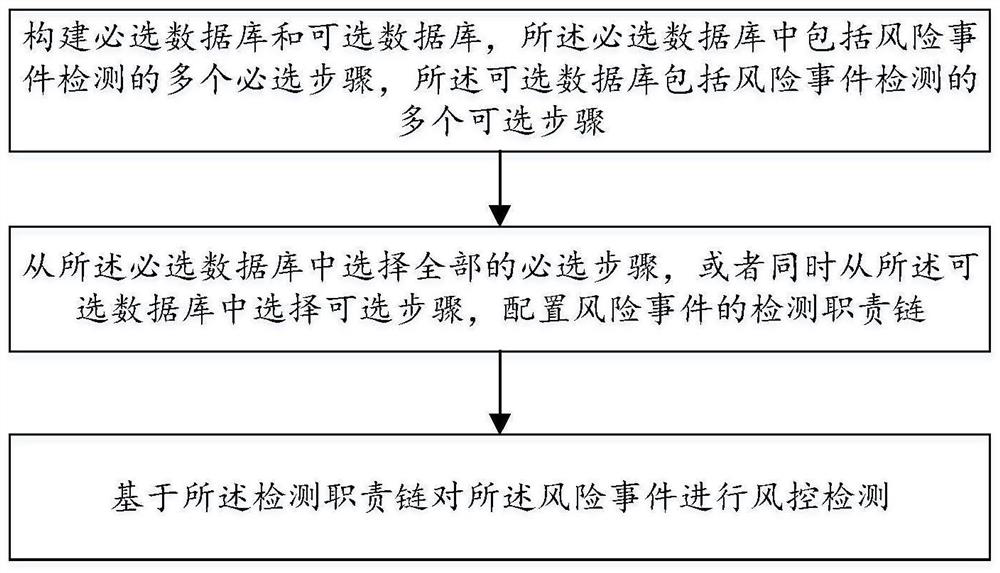
[0050] see figure 1 , this embodiment provides a financial risk control method based on the responsibility chain model, including:
[0051] Construct a mandatory database and an optional database, the mandatory database includes multiple mandatory steps for risk event detection, and the optional database includes multiple optional steps for risk event detection; select all mandatory steps from the mandatory database, Or select optional steps from the optional database at the same time, configure the detection responsibility chain of risk events; perform risk control detection on risk events based on the detection responsibility chain.
[0052] In the financial risk control method based on the chain of responsibility model provided in this embodiment, by constructing a mandatory database and an optional database, users can select mandatory steps and optional steps to configure the chain of responsibility for risk event detection according to the detection needs of risk events ...
Embodiment 2
[0075] This embodiment provides a financial risk control device based on the responsibility chain model, including:
[0076] A library building unit, configured to construct a mandatory database and an optional database, the mandatory database includes multiple mandatory steps for risk event detection, and the optional database includes multiple optional steps for risk event detection;
[0077] A configuration unit, configured to select all mandatory steps from the mandatory database, or select optional steps from the optional database at the same time, and configure the detection responsibility chain of risk events;
[0078] A detection unit, configured to perform risk control detection on the risk event based on the detection responsibility chain.
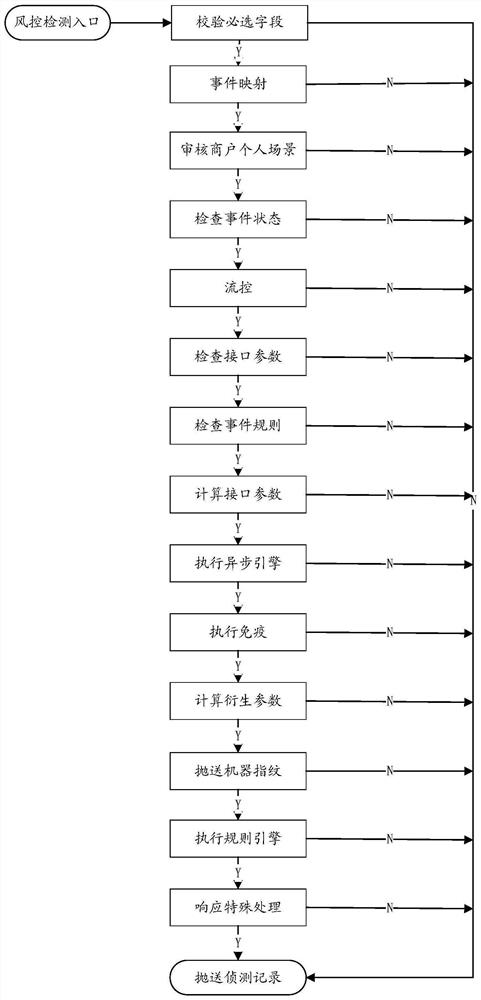
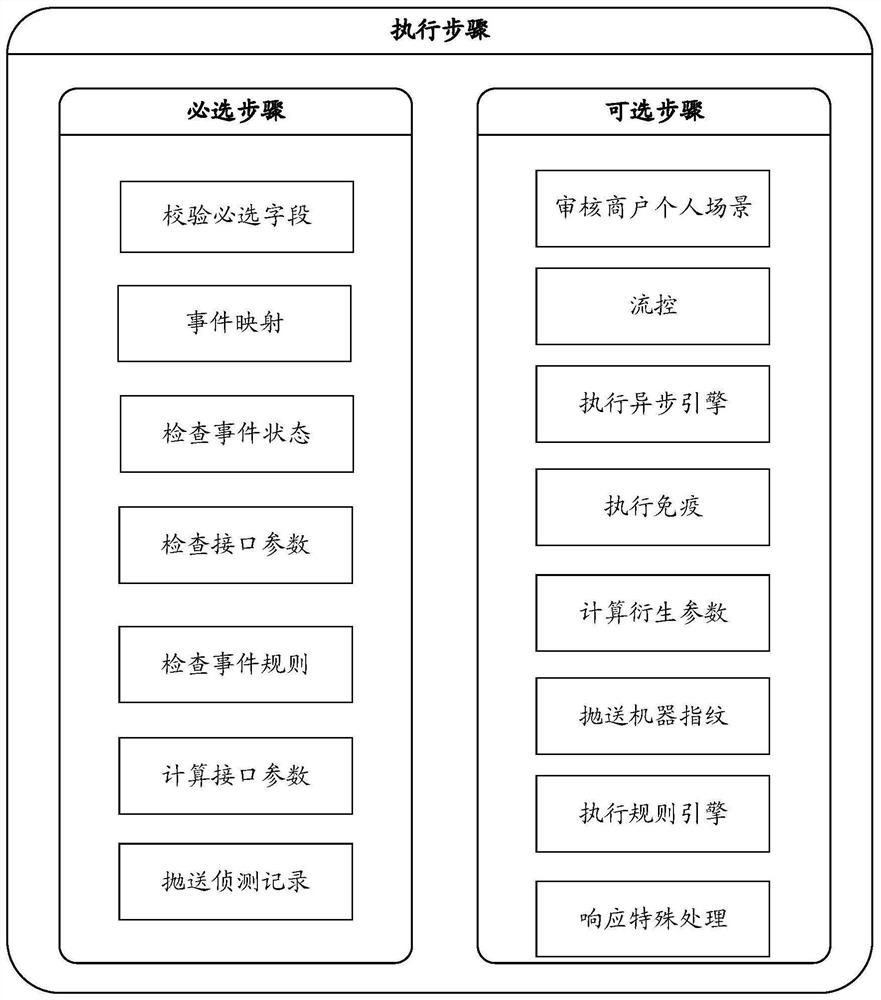
[0079] Preferably, the mandatory database includes the steps of checking required fields, event mapping, checking event status, checking interface parameters, checking event rules, calculating interface parameters, and throwing i...
Embodiment 3
[0083] This embodiment provides a computer-readable storage medium. A computer program is stored on the computer-readable storage medium. When the computer program is run by a processor, the above-mentioned steps of the financial risk control method based on the chain of responsibility mode are executed.
[0084] Compared with the prior art, the beneficial effect of the computer-readable storage medium provided by this embodiment is the same as the beneficial effect of the financial risk control method based on the chain of responsibility model provided by the above technical solution, and will not be repeated here.
[0085] Those of ordinary skill in the art can understand that all or part of the steps in the above-mentioned inventive method can be completed by instructing related hardware through a program. The above-mentioned program can be stored in a computer-readable storage medium. When the program is executed, it includes: For each step of the method in the above embodi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com