Tilting type free half-rotating flapping rotor aircraft
A flapping rotor and free technology, applied in the field of aircraft, can solve the problems of low efficiency, poor lift stability, and poor flight flexibility of flapping rotor aircraft, and achieve the effects of improving efficiency, improving stability, and maneuvering flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
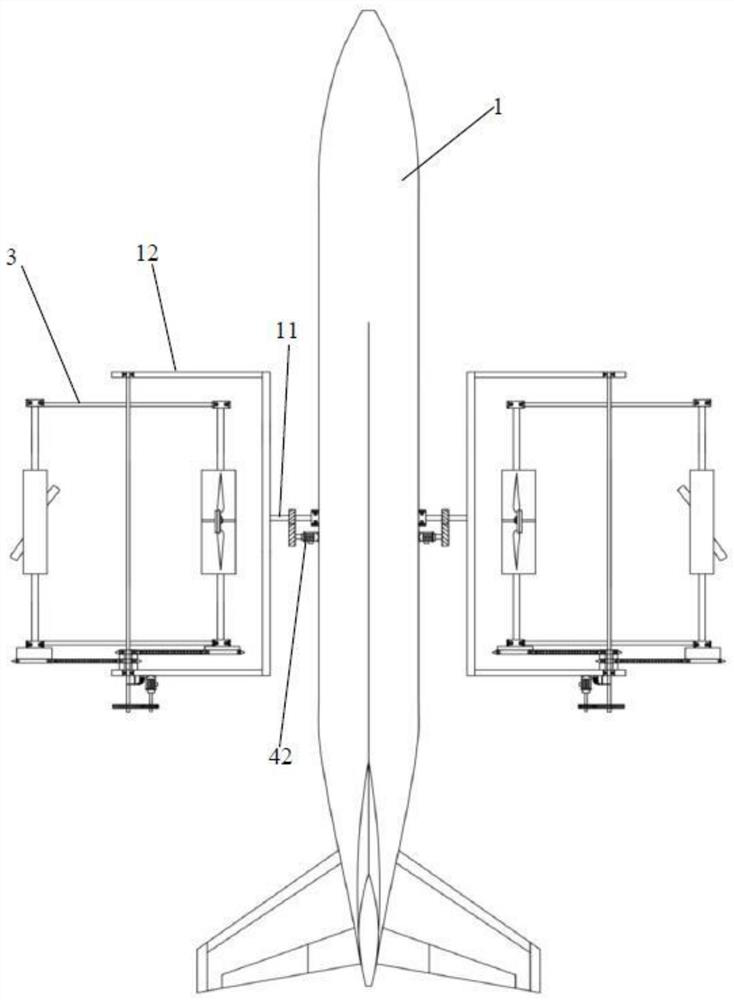
[0126] The embodiment of the present invention discloses a tilting free semi-rotating flapping rotor aircraft, comprising: a fuselage 1, a flapping rotor 3, an inclination adjustment device 42, a rotating shaft 11, a frame 12 and a controller;
[0127] Wherein, the tail portion of the fuselage 1 is provided with an empennage or a tail rotor, and the belly is provided with a landing gear, both sides of which are symmetrically connected to the rotating shaft 11 through bearing rotation, and the frame 12 is fixed on the rotating shaft 11;
[0128] The inclination adjustment device 42 is respectively connected to the fuselage 1 and the rotating shaft 11, and is electrically connected to the controller to drive the rotating shaft 11 to rotate and drive the frame 12 to tilt;
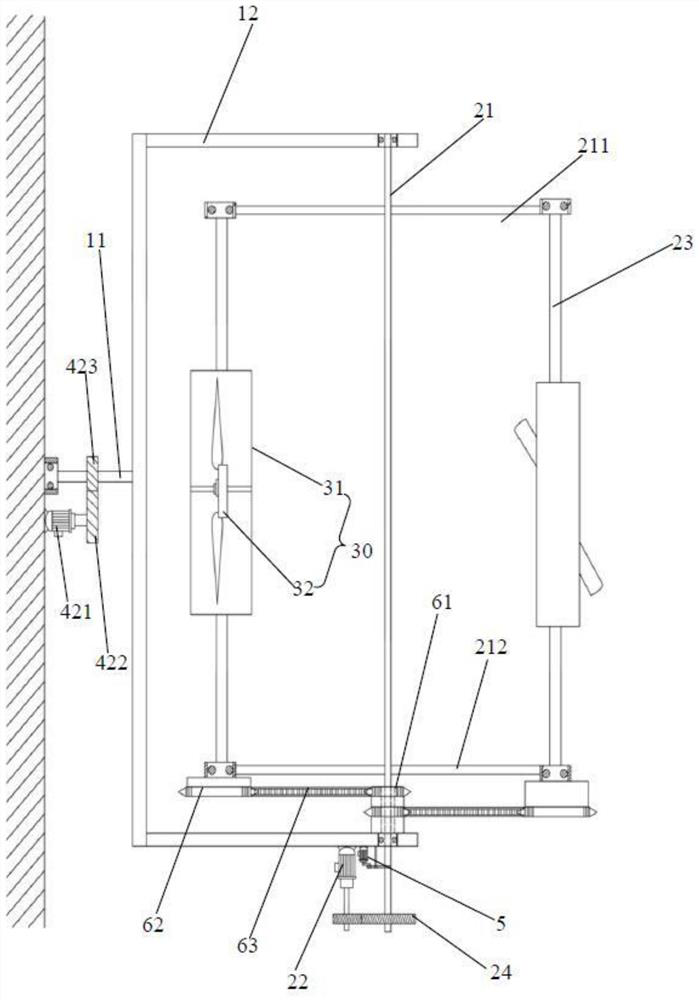
[0129] The flapping rotor 3 includes: a revolution main shaft 21, a revolution motor 22, a revolution transmission gear set 24, an autorotation transmission, an autorotation main shaft 23 and a rotor mechanism ...
Embodiment 2
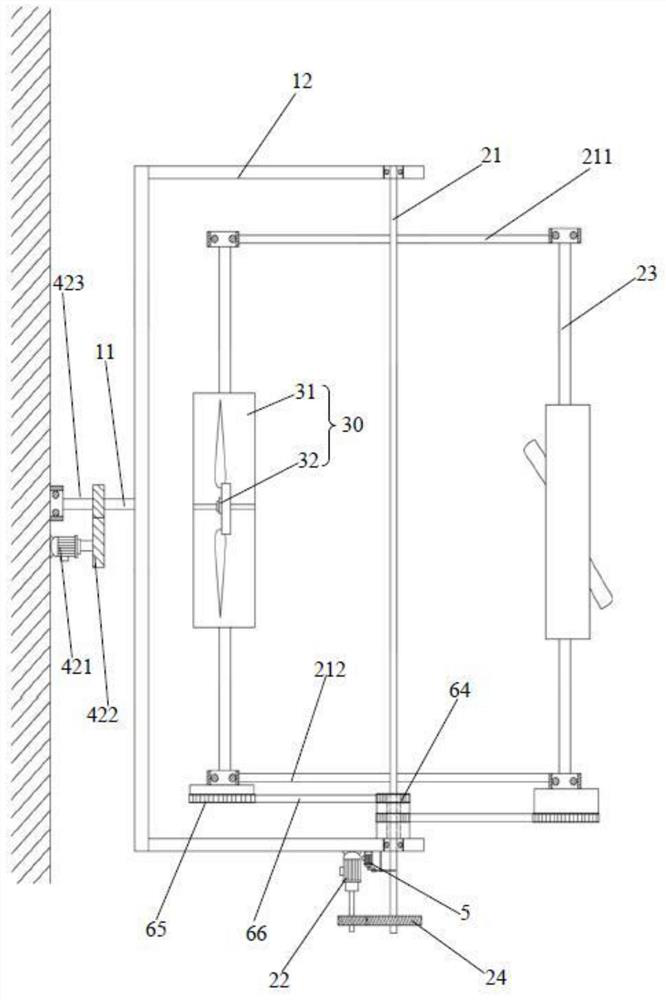
[0143] Embodiment 2 of the present invention is different from Embodiment 1 in that: the rotation transmission device is a synchronous belt transmission mechanism, and the synchronous belt transmission mechanism includes two identical central synchronous wheels 64, transmission synchronous wheels 65 and synchronous belts 66, and the central synchronous wheel 64 The diameter ratio with the transmission synchronous wheel 65 is 1:2;
[0144] The two central synchronous wheels 64 are all located between the rear pivot arm 212 and the frame 12, or between the front pivot arm 211 and the frame 12, and the end faces of the two central synchronous wheels 64 are parallel and fixed, and at the same time, one of the central synchronous The end face of wheel 64 is fixed with frame 12;
[0145] The centers of the two central synchronous wheels 64 are provided with a through hole with a diameter larger than that of the revolving main shaft 21 as a rotating space, and the shaft ends of the r...
Embodiment 3
[0148] Embodiment 3 of the present invention is different from Embodiment 1 in that: the rotation transmission device is a chain transmission mechanism, and the chain transmission mechanism includes two identical first driving bevel gears 67, second driven bevel gears 68 and torque transmission mechanisms;
[0149] The end surfaces of the two first driving bevel gears 67 are parallel and fixed, while the end surface of one of the first driving bevel gears 67 is fixed on the frame 12, and the centers of the two first driving bevel gears 67 are provided with a diameter larger than the revolving main shaft 21 The through hole is used as a turning space;
[0150] The two second driven bevel gears 68 are respectively fixed on the two self-rotating main shafts 23 in one-to-one correspondence, and the two first driving bevel gears 67 are connected to the two second driven bevel gears 68 in one-to-one correspondence through a torque transmission mechanism. .
[0151] The torque trans...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com