Coupling method of PLC optical branching device
A technology of optical splitter and optical waveguide, which is applied in the field of integrated optics, can solve the problems of increased chip R&D cost and R&D time, increased difficulty of chip design, and low production efficiency, so as to improve yield rate, optical performance, and R&D time Short, consistent effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
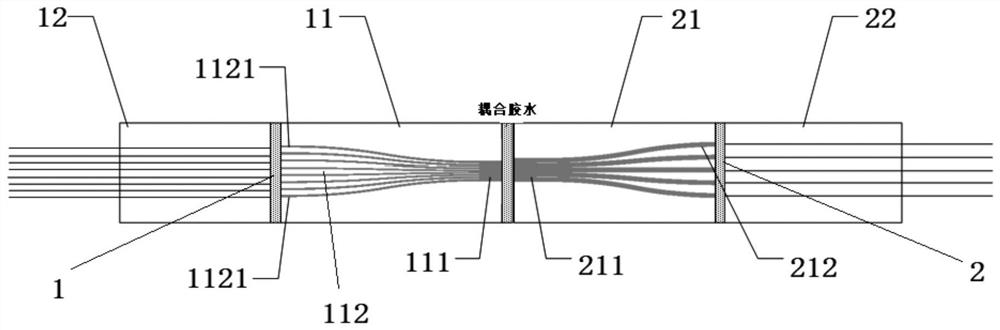
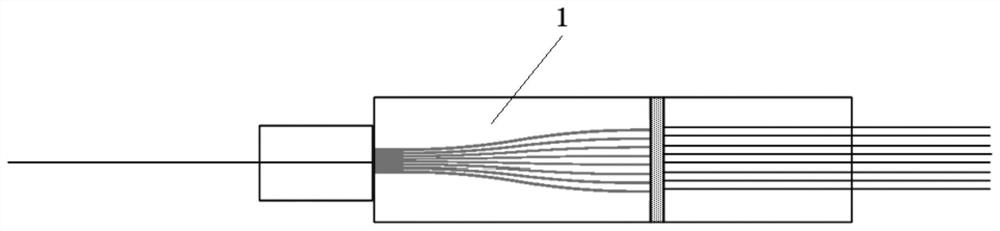
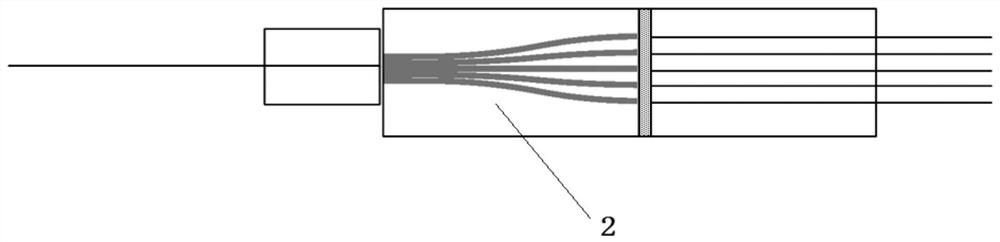
[0034] A coupling method for a PLC optical splitter, first coupling and bonding an optical splitter chip containing 1×2 with a 2-channel FA to form a 1×2 input component, and then combining an optical splitter chip containing 1×8 The chip is coupled with the 8-channel FA to form a 1×8 output component, and then the 1×2 input component and the 1×8 output component are collimated, coupled and bonded to each other to form a 2×8 optical splitter.
[0035] Among them, the width of the optical waveguide at the input end of the 1×2 optical splitter chip is 100 μm, and the width of the two optical waveguides at the output end is 50 μm;
[0036] The width of the optical waveguide at the input end of the 1×8 optical splitter chip is 400 μm, and the width of the eight optical waveguides at the output end is 50 μm;
[0037] In the process of collimation, coupling, and bonding of the 1×2 input component and the 1×8 output component of the PLC 2×8 optical splitter, first connect to the No. ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] A coupling method of a PLC optical splitter, first coupling and bonding an optical splitter chip containing 1×5 with a 5-channel FA to form a 1×5 input component, and then combining an optical splitter chip containing 1×32 The chip is coupled with the 32-channel FA to form a 1×32 output module, and then the 1×5 input module and the 1×32 output module are collimated, coupled and bonded to each other to form a 5×32 optical splitter.
[0040] Among them, the width of the optical waveguide at the input end of the 1×5 optical splitter chip is 100 μm, and the width of the five optical waveguides at the output end is 18 μm;
[0041] The width of the optical waveguide at the input end of the 1×32 optical splitter chip is 640 μm, and the width of the 32 optical waveguides at the output end is 10 μm;
[0042] In the process of collimation, coupling, and bonding of the 1×5 input component and the 1×32 output component of the PLC 5×32 optical splitter, first connect to the No. 1 po...
Embodiment 3
[0044] A coupling method of a PLC optical splitter, first coupling and bonding the optical splitter chip containing 1×16 with the FA of 16 channels to form a 1×16 input component, and then combining the optical splitter chip containing 1×12 The chip is coupled with the 12-channel FA to form a 1×12 output component, and then the 1×16 input component and the 1×12 output component are collimated, coupled and bonded to form a 16×12 optical splitter.
[0045] Among them, the width of the optical waveguide at the input end of the 1×16 optical splitter chip is 1600 μm, and the width of the 16 optical waveguides at the output end is 80 μm;
[0046] The width of the input optical waveguide of the 1×12 optical splitter chip is 1600 μm, and the width of the output, 12 optical waveguides is 130 μm respectively;
[0047]When the 1×16 input component and the 1×12 output component of the PLC 16×12 optical splitter are collimated, coupled, and bonded to each other, first connect to the No. 1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com