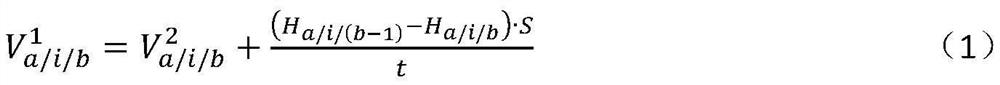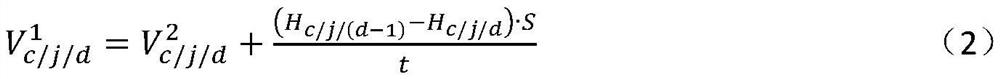Method for calculating theoretical inflow of secondary water supply tank
A technology of inflow water volume and calculation method, which is applied in general water supply conservation, calculation, water supply installation and other directions, and can solve the problems of residual chlorine concentration attenuation, outflow use, and difficulty in accurately controlling inlet flow.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
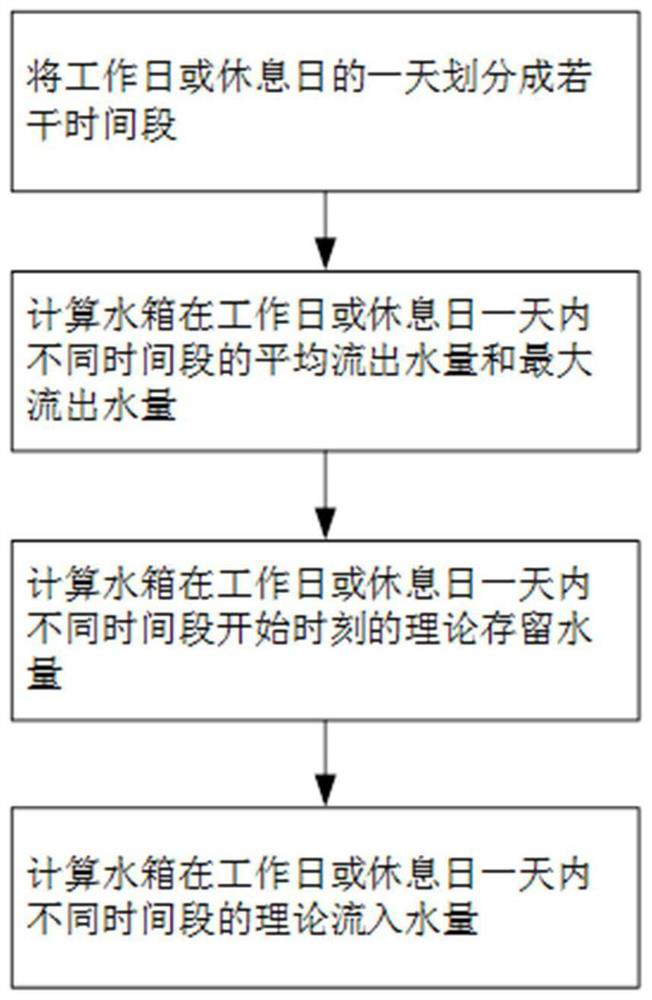
[0077] This embodiment provides a method for calculating the theoretical inflow of water in a secondary water supply tank, which includes the following steps:
[0078] Step 1. Divide a working day or a rest day into several time periods according to the water consumption of the water tank on the working day or rest day.
[0079] The specific method of dividing the time period in this step is: divide the working day into N 1 The duration of different time periods can be the same or different. Use i to represent the sequence number of different time periods in a working day; divide the rest day into N according to the peak and trough conditions of water use on the rest day. 2 The duration of different time periods can be the same or different. Use j to represent the sequence number of different time periods in a day on rest days.
[0080]Step 2. According to the outlet flow data of the water tank in different time periods in the last few days on working days or rest days, calcu...
Embodiment 2
[0130] In order to further confirm the accuracy, effectiveness and practicability of the method described in Example 1, the applicant now further describes the scheme of Example 1 in conjunction with specific actual data, as follows:
[0131] Step 1. Divide a working day or a rest day into several time periods according to the water consumption of the water tank on the working day or rest day.
[0132] In this step, it is set to divide the working day into the following 5 time periods, 0:00-7:59, 8:00-11:59, 12:00-15:59, 16:00-19:59, 20 :00-23:59, use i to indicate the sequence number of different time periods in a working day; divide a rest day into the following 3 time periods, 0:00-9:59, 10:00-16:59, 17: 00-23:59, use j to represent the sequential number of different time periods in a day on rest days.
[0133] Step 2. According to the outlet flow data of the water tank in different time periods in the last few days on working days or rest days, calculate the average outfl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com