Chain key exchange method, client, server and system
A technology of key exchange and server, which is applied in the field of server and system, client, and chain key exchange method, which can solve the problems that attackers cannot carry out eavesdropping man-in-the-middle attacks, cannot achieve cracking, security risks, etc., and reduce network security. Effects of resource consumption, increased attack difficulty, and leak prevention
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
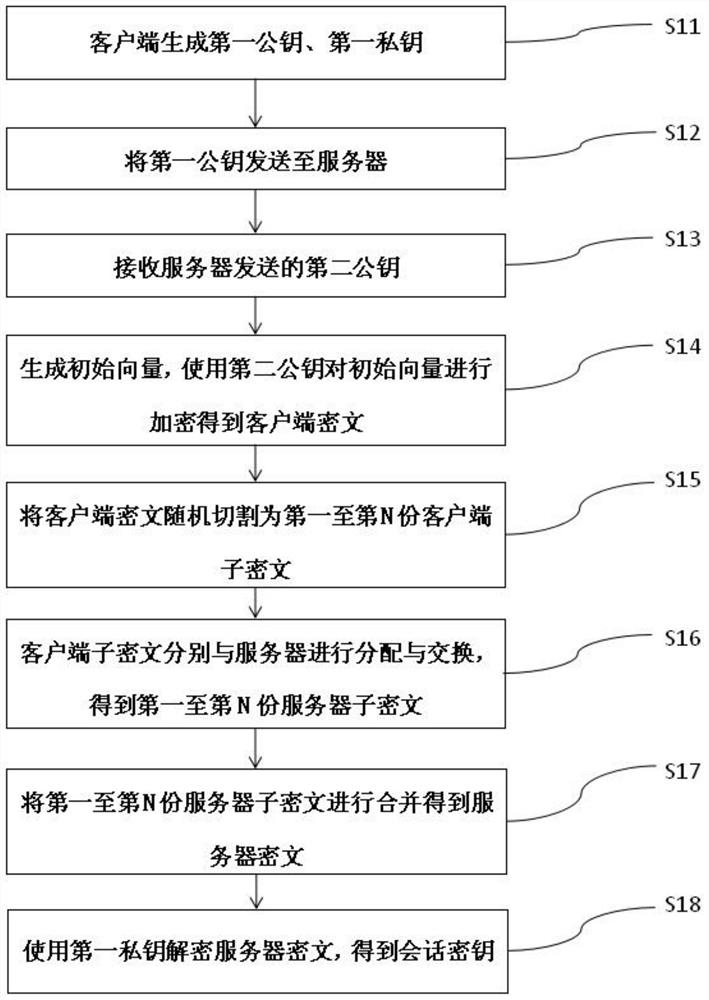
[0062] Please refer to the attached figure 1 And attached Figure 5 , Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a chain key exchange method, which is applicable to client 1, and the method includes:
[0063] Step S11: Client 1 generates a first public key and a first private key paired with the first public key.
[0064] Step S12: Send the first public key to the server 2.
[0065] Step S13: Receive the second public key sent by the server 2.
[0066] Step S14: Client 1 generates an initial vector, and then uses the second public key to encrypt the initial vector with an encryption algorithm to obtain the client ciphertext.
[0067] Step S15: Randomly cut the client ciphertext into N parts, and obtain the first to Nth client sub-ciphertexts, where N is the number negotiated by the communication parties; the data size of the N client sub-ciphertexts is uncertain of. Attackers cannot judge the number of ciphertext cuts by eavesdropping on the data, and therefore cannot...
Embodiment 2
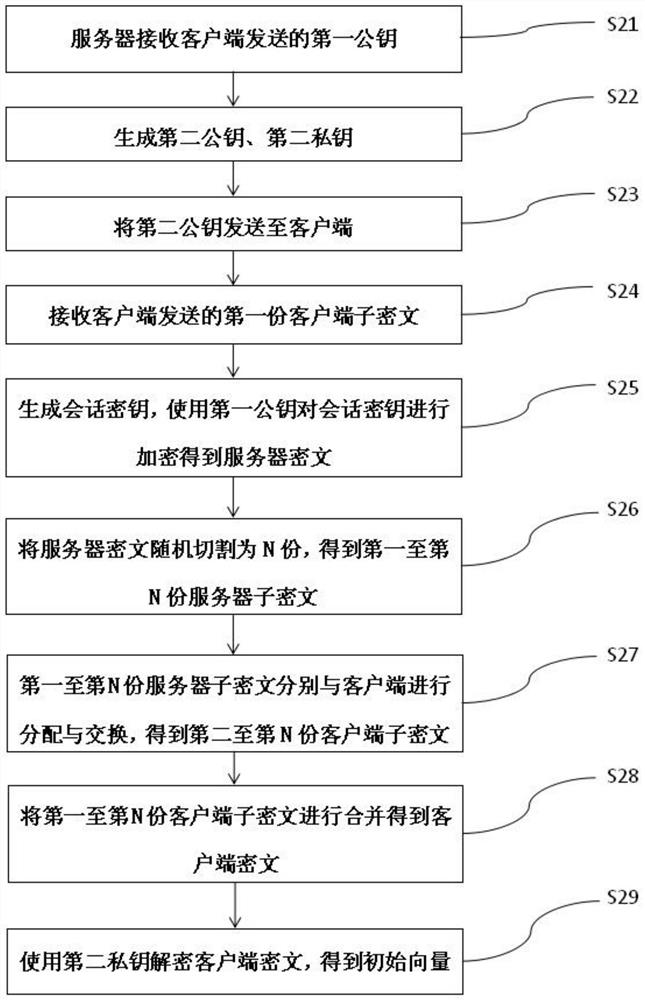
[0083] Please refer to the attached figure 2 And attached Figure 5 , Embodiment 2 of the present invention provides a method for exchanging chain keys, which is applicable to the server 2 and corresponds to the method in Embodiment 1 above. By way of example and not limitation, the methods include:
[0084] Step S21: the server 2 receives the first public key sent by the client 1.
[0085] Step S22: the server 2 generates a second public key and a second private key paired with the second public key.
[0086] Step S23: the server 2 sends the second public key to the client 1.
[0087] Step S24: Server 2 receives the first client sub-ciphertext sent by client 1.
[0088] Step S25: The server 2 generates a session key, and uses the first public key to encrypt the session key with an encryption algorithm to obtain server ciphertext.
[0089] Step S26: Randomly cut the server ciphertext into N parts to obtain the first to N th server sub-ciphertexts, where N is the number n...
Embodiment 3
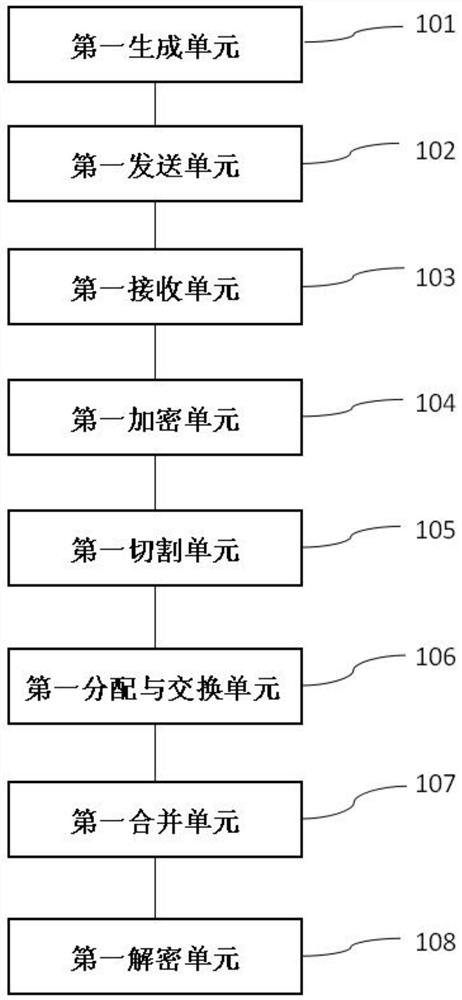
[0100] Please refer to the attached figure 1 , attached image 3 , attached Figure 5 , Embodiment 3 of the present invention provides a client 1, as an example but not a limitation, corresponding to the chain key exchange method provided in Embodiment 1 above, since the client 1 provided in the embodiment of the present application is the same as the above-mentioned The chain key exchange method provided in Embodiment 1 is corresponding, so the implementation of the aforementioned chain key exchange method is also applicable to a client 1 provided in this embodiment, so it is no longer used in this embodiment A detailed description. The client 1 includes:
[0101] A first generating unit 101, configured to generate an initial vector, a first public key, and a first private key paired with the first public key;
[0102] The first sending unit 102 is configured to send the first public key to the server 2;
[0103] The first receiving unit 103 is configured to receive the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com