Spatial similarity geological disaster prediction method based on feature subset coupling model
A technology for geological hazards and feature subsets, applied in prediction, character and pattern recognition, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as result interference, improvement of difficult model formulas, and improved robustness and accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
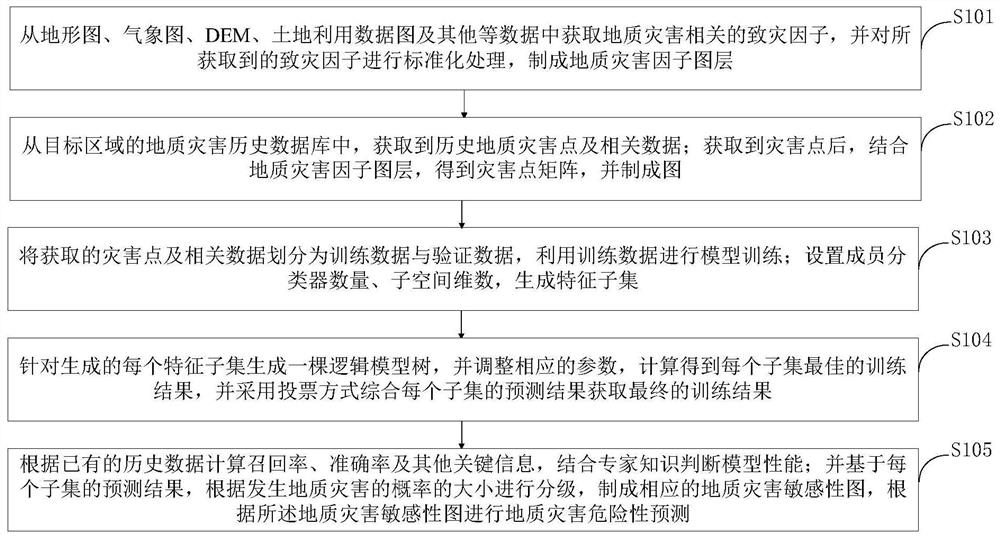
[0120] The prediction of geological hazards based on this model includes the following steps:
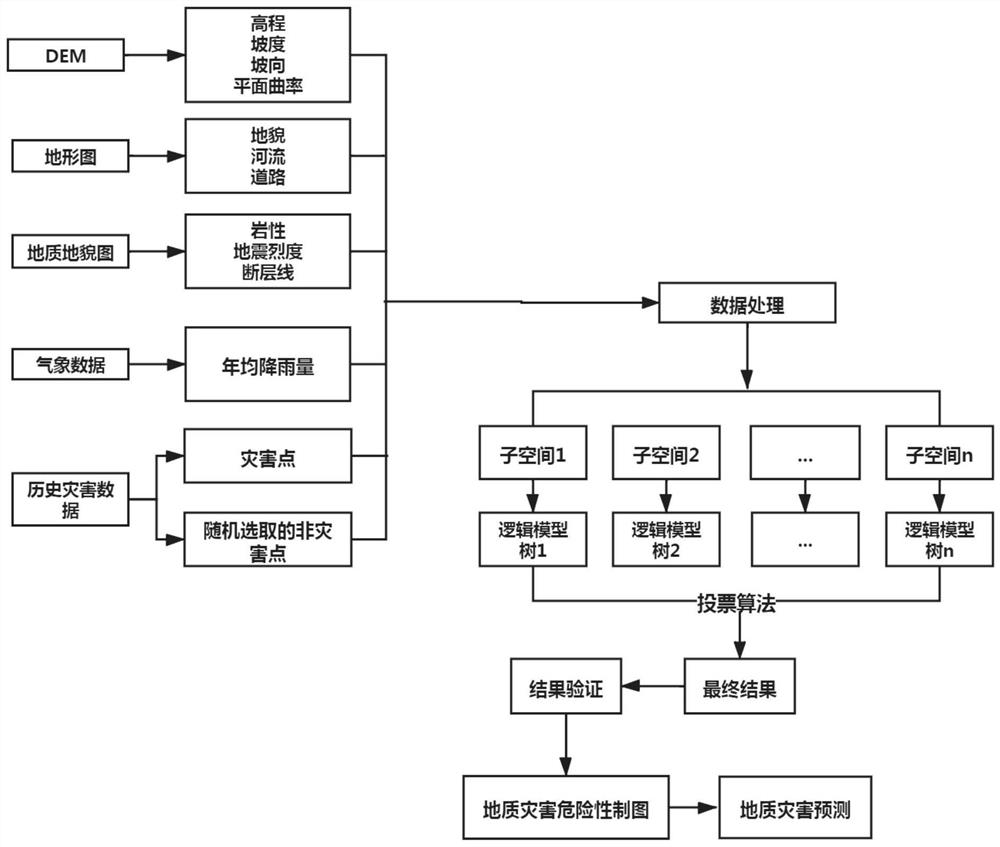
[0121] (1) Extraction of disaster factors, including obtaining disaster-causing factors related to geological hazards from data such as topographic maps, meteorological maps, DEM, and land use data maps, and standardizing the obtained disaster-causing factors to make corresponding layer.
[0122] (2) Acquisition of disaster points. From the historical database of geological disasters in the target area, historical geological disaster points are obtained, including key data such as occurrence time, location, and scope of influence. After obtaining the disaster points, combine the geological disasters in step 1 Factor layer, make a matrix of disaster points, and make a map.
[0123] (3) Make the disaster points obtained in step 2 into training data, set the number of member classifiers and subspace dimensions, and generate feature subsets;
[0124] (4) In each feature subset, genera...
Embodiment 2
[0128] The specific implementation method of the spatial similarity geological hazard prediction based on the feature subset coupling model is as follows:
[0129] (1) Extracting disaster factors. Specifically, Arcgis software can be used to extract key disaster-causing factors, such as slope, aspect, fault, average rainfall, water system, etc., from the topographic map, DEM, weather map, etc. of the target area , after extraction, each factor needs to be normalized. For continuous factors, the following formula can be used for processing:
[0130]
[0131] where μ is the mean of the factor and σ is the standard deviation of the factor. For discrete factors, such as aspect, values can be used instead of categories, such as 1 for true north. After normalization processing, continue to use Arcgis software for mapping to make a hazard map of the target area.
[0132] (2) Obtain the historical disaster data of the target area, select a sufficient number of disaster points t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com