Single-beam three-degree-of-freedom heterodyne laser interferometer based on array detector
A laser interferometer and heterodyne interference technology, applied in the field of laser applications, can solve the problems of small angle measurement range, multi-axis periodic nonlinear coupling, difficult processing, etc. The effect of advantage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] Specific embodiments of the laser interferometer proposed by the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
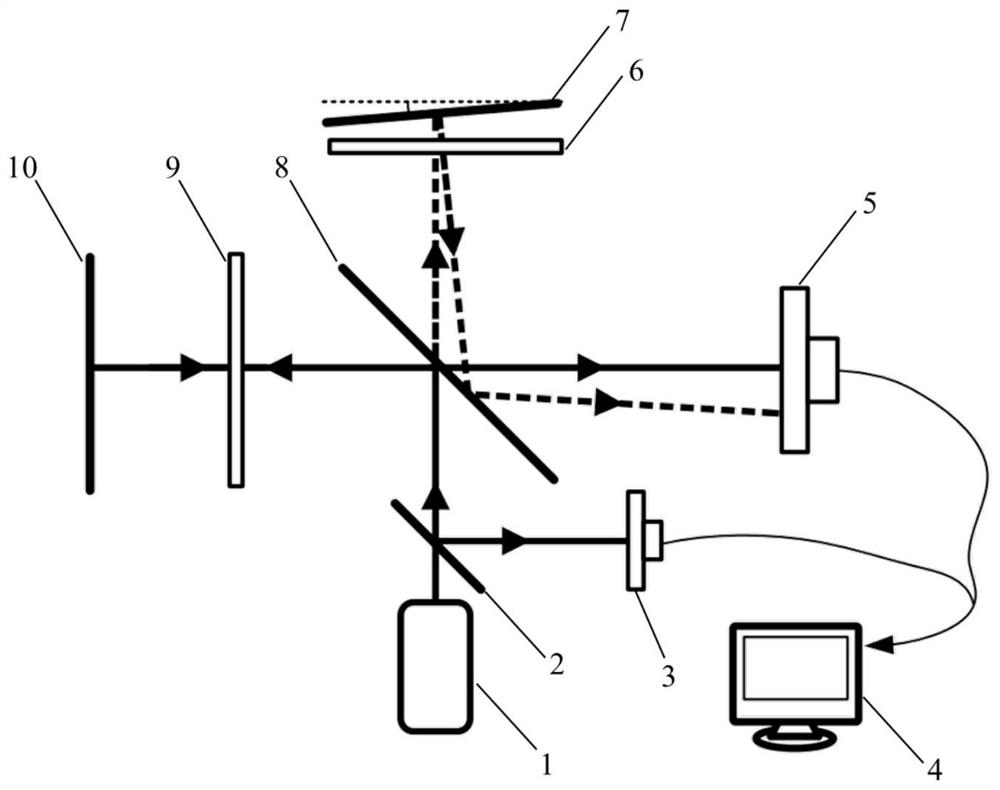
[0027] Such as figure 1The shown single-beam three-degree-of-freedom heterodyne laser interferometer based on array detectors includes a laser light source 1, a first beam splitter 2, a photoelectric receiver 3, a host computer 4, an array detector 5, and a second quadrant A wave plate 6, a fixed reference plane mirror 7, a second beam splitting surface 8, a first quarter wave plate 9, a movable target plane mirror 10; wherein the laser light source 1 provides coaxial transmission and has different frequencies The first input beam and the second input beam; the fixed reference plane mirror 7, the first splitting surface 2, the second quarter-wave plate 6, the first quarter-wave plate 9 and the movable target plane The mirror 10 forms a Michelson interference structure, and the first beam-splitting surface ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com