Process for producing receiver substrate for semiconductor-on-insulator structure for radiofrequency applications and process for producing such structure
A technology of semiconductors and insulators, used in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, circuits, etc., and can solve problems such as breakdown voltage drop
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
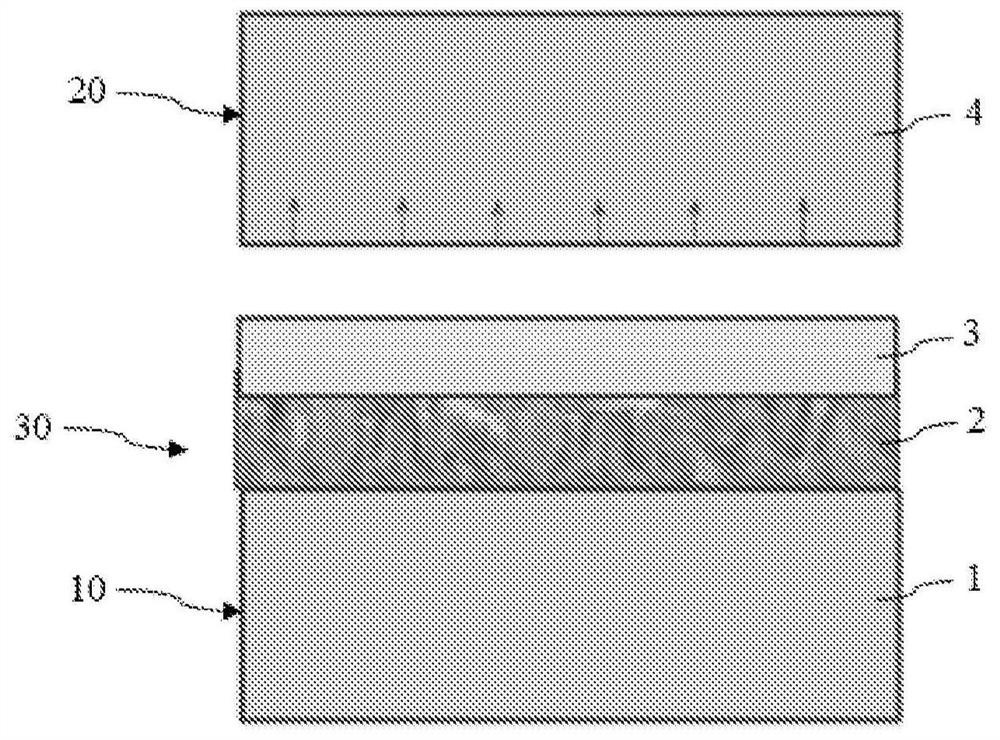
[0066] The invention relates to a method of manufacturing a receiver substrate (30) of a semiconductor-on-insulator structure for radio frequency applications, comprising the steps of:
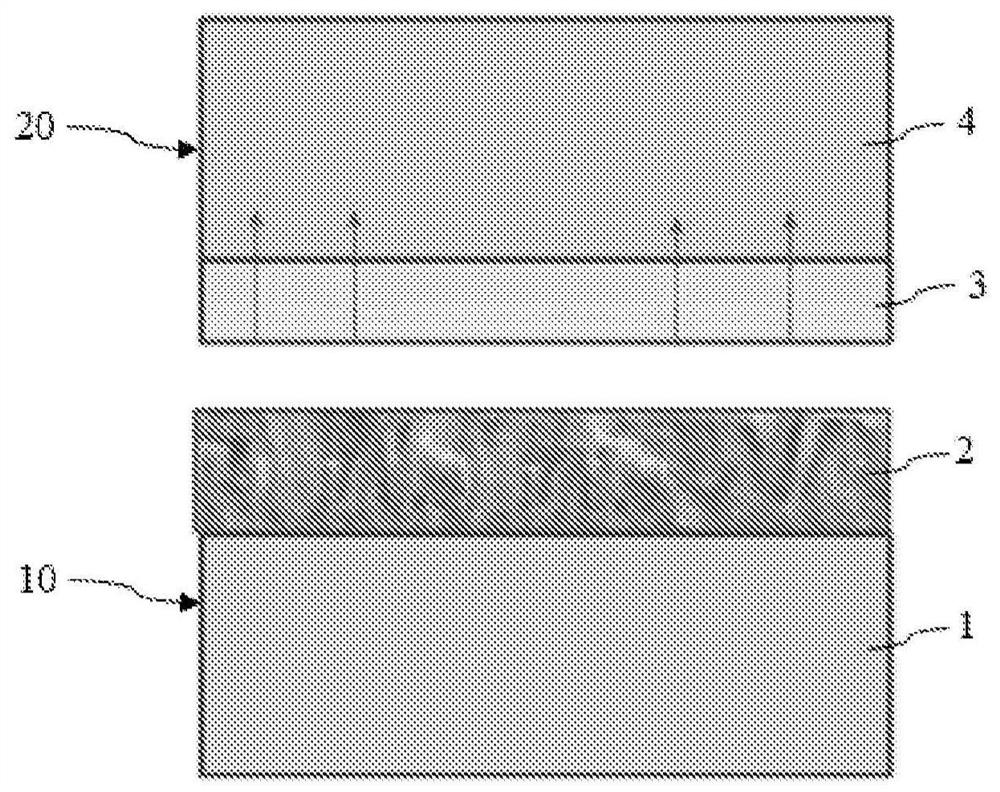
[0067] The method of the present invention is a reverse splicing method. refer to figure 2 , the method includes the step of providing a semiconductor substrate 10 comprising a base substrate 1 made of a single crystal material and a charge-trapping layer 2 made of polysilicon disposed on the base substrate, followed by a pair of charges The trapping layer 2 is oxidized to form an oxide layer 3 disposed on said charge trapping layer.
[0068] The charge-trapping layer 2 may be formed by epitaxy on the base substrate 1, or alternatively deposited thereon by chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
[0069] The charge-trapping layer 2 is at least partially oxidized at a temperature comprised between 750°C and 875°C.
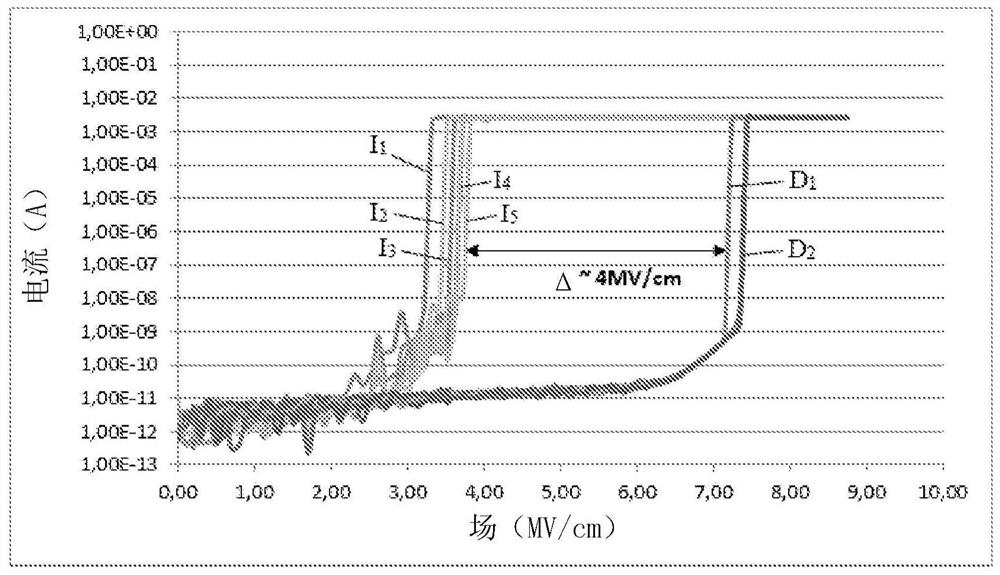
[0070] Such a method makes it possible to form, by reverse bonding, a receiver sub...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com