Derivative kit and method for separating citric acid and isocitric acid
A derivative reagent, the technology of isocitric acid, applied in the field of chemical analysis, can solve problems such as missed diagnosis, inability to separate citric acid and isocitric acid, and detection errors, so as to improve accuracy and sensitivity, facilitate subsequent analysis or detection, and achieve huge economic benefits. value effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Example 1 Derivatization of 2-picolylamine (PA)
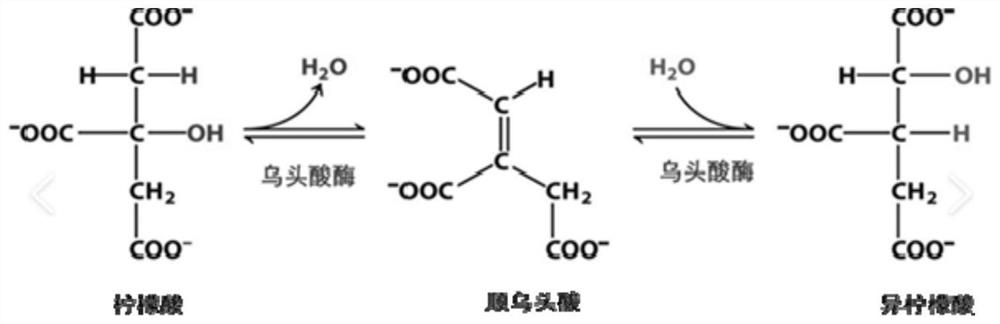
[0049] Isocitrate and citric acid are endogenous substances of isomers ( figure 1 ), which all contain carboxylic acids. The inventors therefore initially attempted to derivatize the carboxyl group.
[0050] First, use pyridine amino groups to react with carboxyl groups: 2-picolylamine (PA) is a commonly used derivatization reagent for reaction with carboxyl groups, with short derivatization time and simple pretreatment.
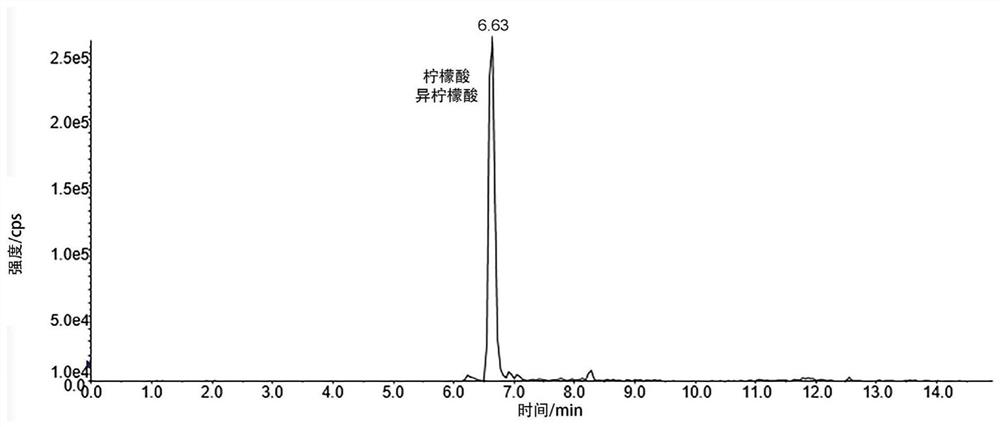
[0051] Derivation steps and conditions: Take 20 μL of urine samples from patients with urinary calculi, add 20 μL of isotope-labeled citric acid, blow dry with nitrogen at 60°C, add 200 μL of 10 mM triphenylphosphine (TPP), 200 μL of 2,2'-dithiodi Pyridine (DPDS), 200 μL 1g / L 2-aminomethylpyridine (PA), vortex for 3 minutes, stand at 60°C for 30 minutes, then add 200 μL 0.1% formic acid aqueous solution at room temperature for detection.
[0052] Chromatographic column conditions: ACE Excel-2 C18-PFP ...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Embodiment 2 Alcohol derivatization
[0058] In order to achieve the purpose of successfully separating citric acid and isocitric acid, the inventors tried a large number of new derivatives. Surprisingly, it has been found that derivatization with alcohols results in amplified differences in the hydroxyl positions of citric and isocitric acids.
[0059] Take n-butanol derivatization as an example:
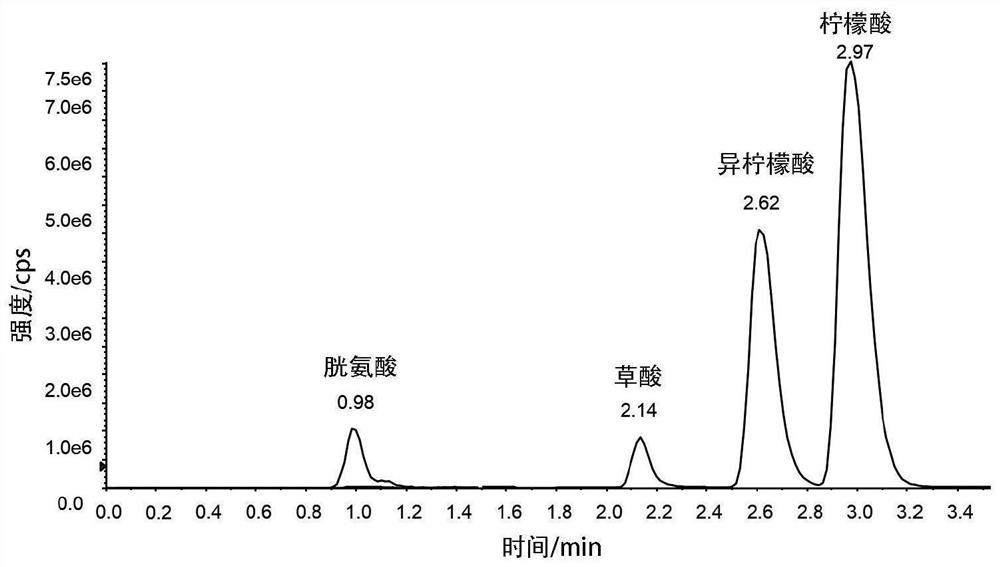
[0060] Derivatization steps and conditions: Take 20 μL of urine sample, add 20 μL of isotope-labeled citric acid, oxalic acid and cystine internal standards, blow dry at 60°C with nitrogen, add 100 μL of 3mol / L hydrochloric acid n-butanol solution, vortex for 3 minutes, Shake at 60°C for 20 minutes, centrifuge for 3 minutes, blow dry at 60°C with nitrogen, add 100 μL of methanol to redissolve, and wait for detection.
[0061] Chromatographic column conditions: ACE Excel-2 C18-PFP column (100×2.1mm, 2.6μm), column temperature 35°C.
[0062] Elution conditions: mobility A i...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Example 3 Application of Separation of Citric Acid and Isocitric Acid in Diagnosis of Urinary Calculi
[0070] (1) Preparation of standard solution.
[0071] (1) Preparation of internal standard solution: Accurately weigh citric acid-D with an analytical balance 4 , the internal standard was dissolved in pure water, and the internal standard stock solution with a concentration of 10 mg / mL was prepared.
[0072] (2) Standard product preparation: citric acid and isocitric acid were accurately weighed with an analytical balance, and each standard product was prepared into standard product mother solutions with concentrations of 10 mg / mL and 50 mg / mL with pure water, respectively.
[0073] (3) Internal standard stock solution: absorb 100 μL of internal standard stock solution, dilute to 1 mL with pure water, and dilute into an internal standard stock solution.
[0074] (4) Standard stock solution: Pipette 500 μL and 300 μL of citric acid and isocitric acid standard mother...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com