Magnetic resonance K-space data correction method
A data correction and k-space technology, which is applied in the computer field, can solve the problems such as the lack of detailed description of the K-space data splicing method and the lack of detailed description of the magnetic resonance receiving gain difference and phase difference correction problem.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0042] In order to facilitate those skilled in the art to understand the technical content of the present invention, the content of the present invention will be further explained below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
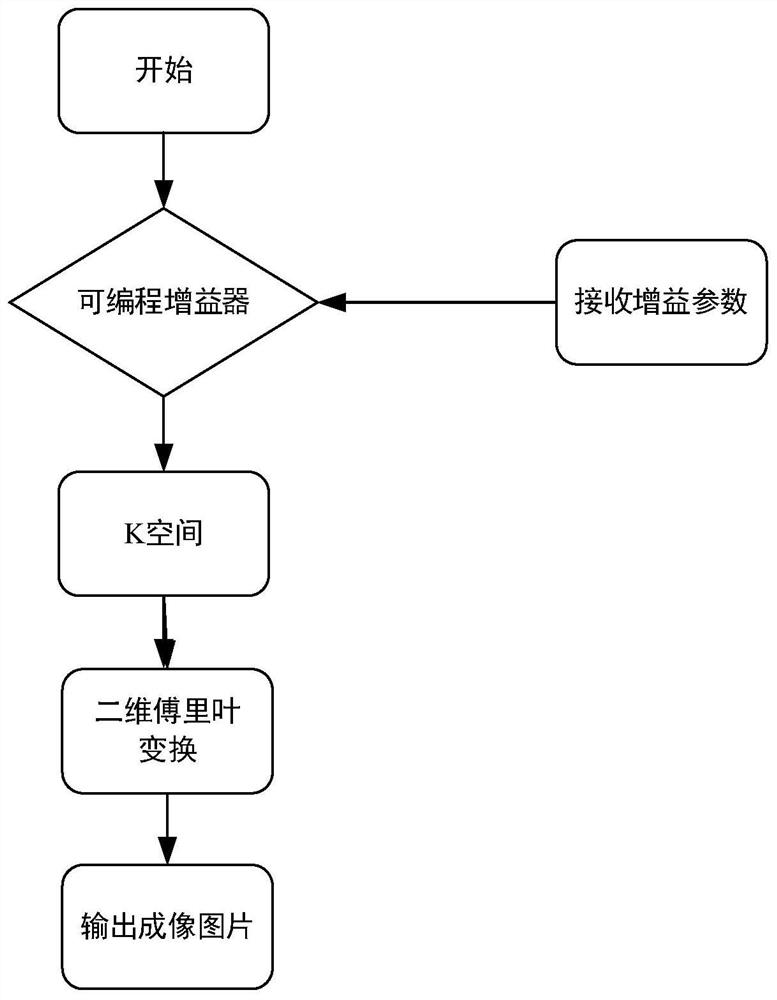
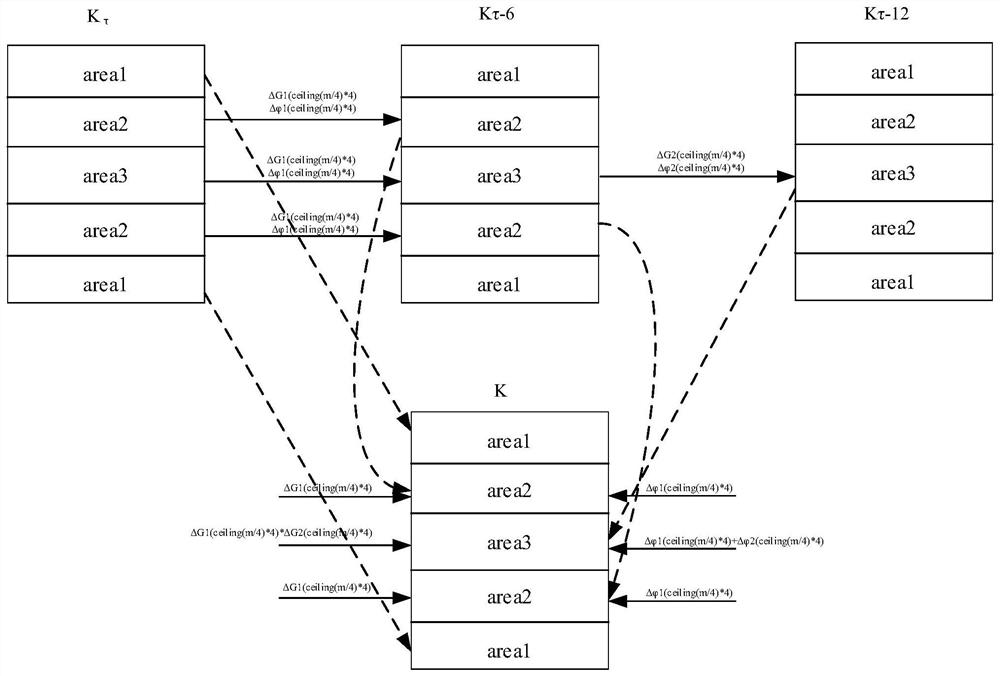
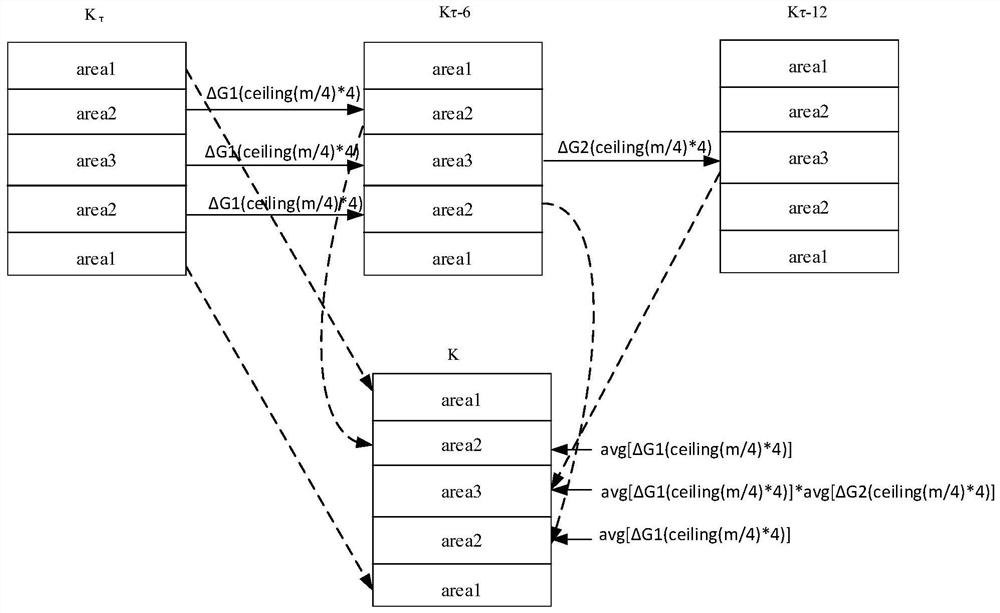
[0043] In the sequence scanning data acquisition, each receiving gain control parameter is adjusted once, then a sequence scanning is performed to obtain a set of K space raw data, and three sets of K with receiving gain parameters of τdB, τ-6dB and τ-12dB respectively Spatial data Kτ, Kτ-6, Kτ-12. By analyzing the gain difference and phase difference of these three sets of data, a data space of a spliced image is constructed, and an image can be obtained by Fourier transforming the spliced data space. The system execution process is as follows: figure 1 shown.
[0044] The invention proposes a method for splicing K-space data obtained under different receiving gain parameters into a piece of K-space data, and a method for normalizing the K-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com