Low-power-consumption scheduling method suitable for periodic dependency task of open type numerical control system
A technology that depends on tasks and numerical control systems. It is applied in general control systems, control/regulation systems, and program control. It can solve problems such as not considering task dependencies, and achieve the goals of improving local search capabilities, low energy consumption, and reducing system energy consumption. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0042] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
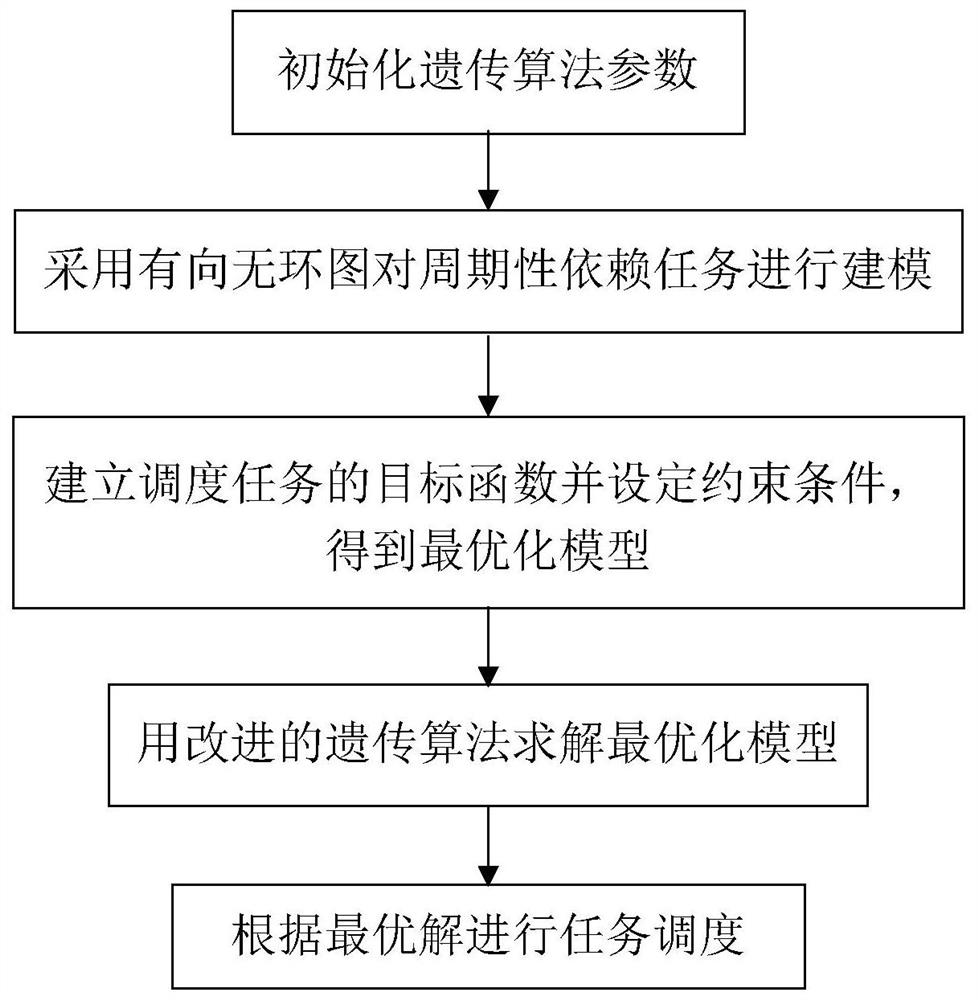
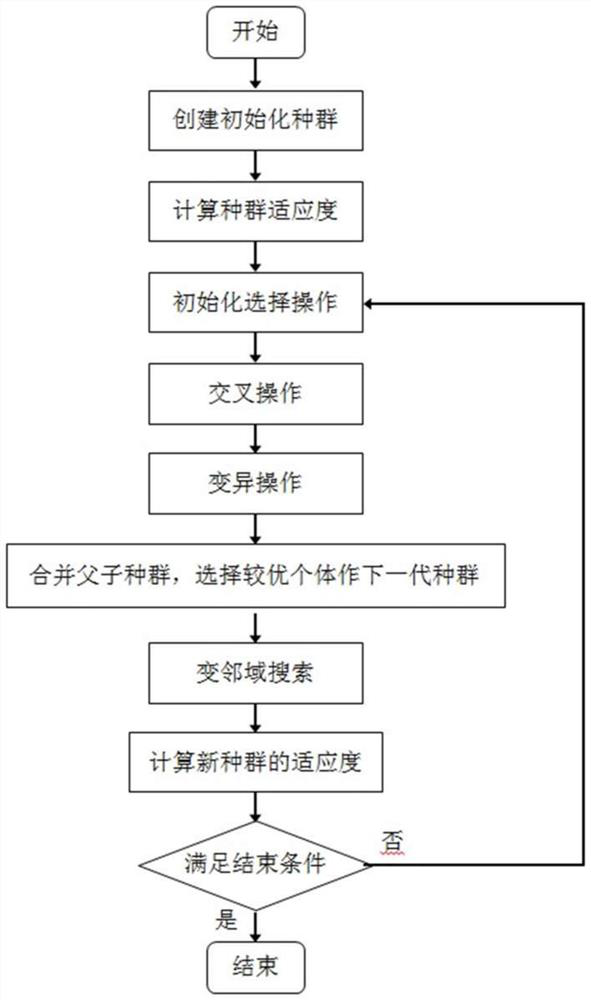
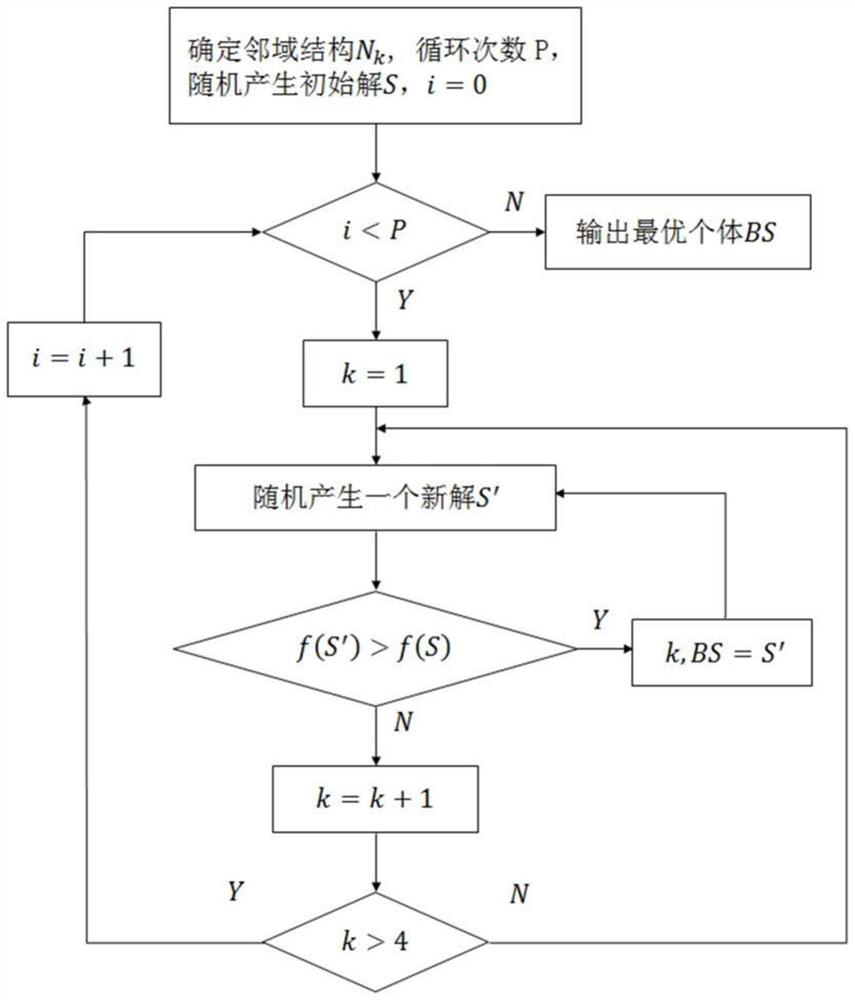
[0043] The invention provides a low-power scheduling method of an open numerical control system based on an improved genetic algorithm. Firstly, a directed acyclic graph is used to model periodic dependent tasks, and then the scheduling problem is formally described and abstracted as An optimization problem with some constraints. Aiming at the task-dependent topology, an initial solution generation method and a crossover operation that can maintain the task topology are proposed, and then a genetic algorithm is used to generate an approximate optimal solution, and a variable neighborhood search algorithm is used to expand the search range to find a local optimal solution. Realize the goal of fast task distribution and low power consumption on the multi-core processor system.
[0044] like figure 1 As shown, a low-power scheduling method suit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com