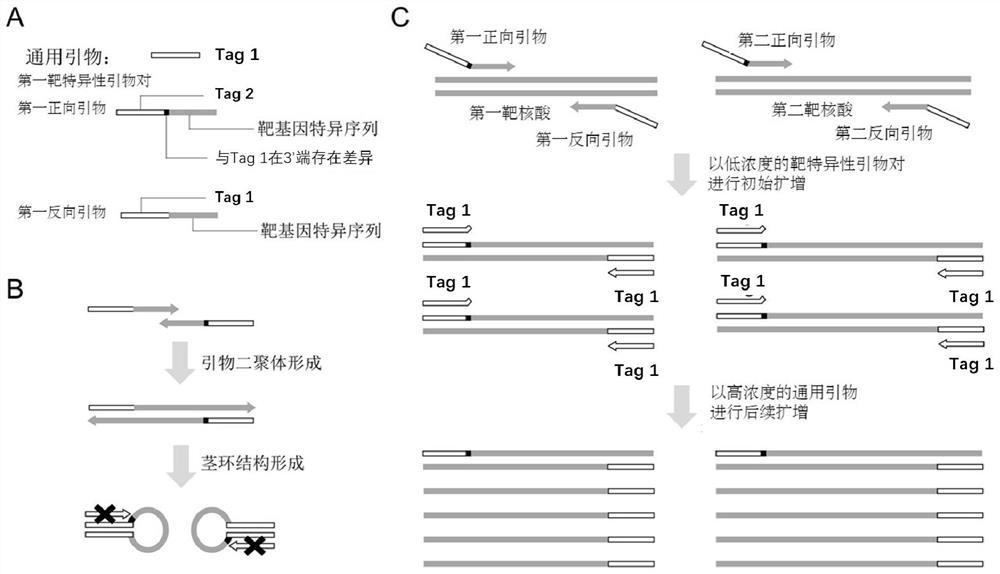
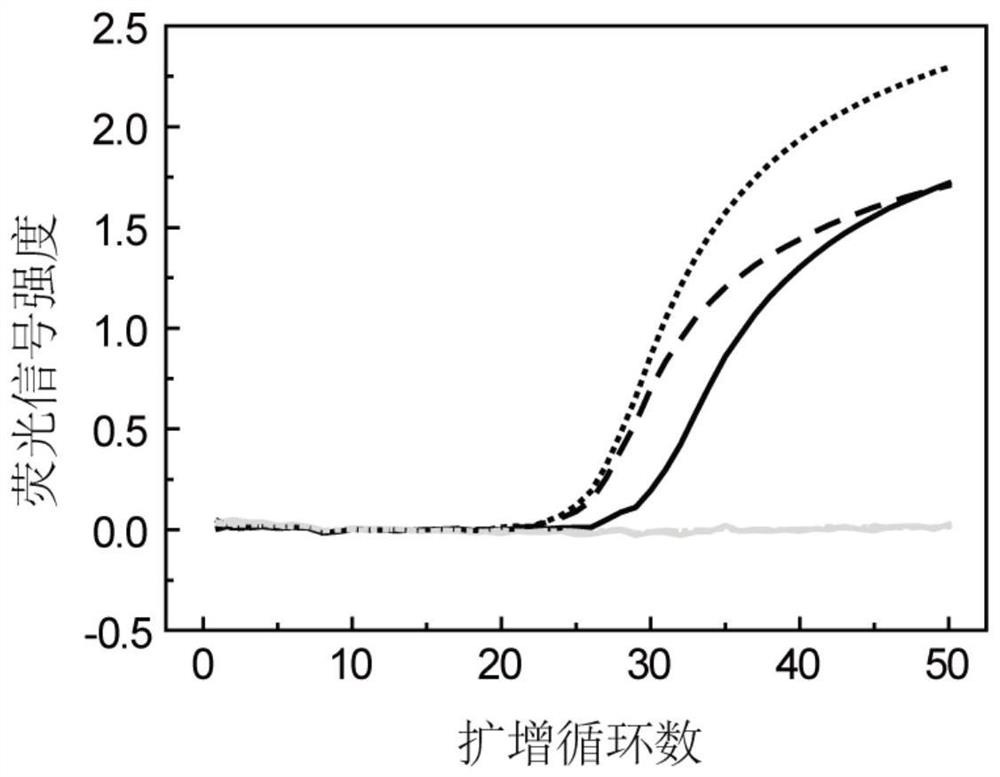
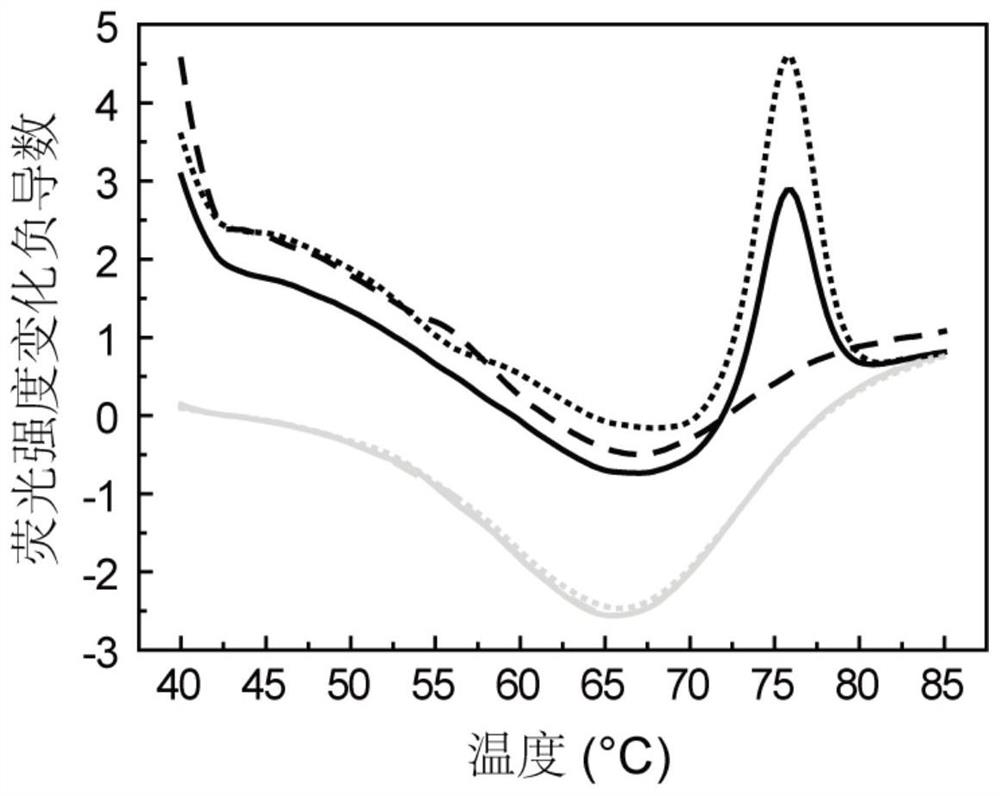
Method for asymmetrically amplifying target nucleic acid
A technology for target nucleic acid and nucleotide, applied in the field of asymmetric amplification of target nucleic acid, can solve problems such as application limitation and inability to produce single-stranded products, and achieve the effect of improving specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0163] In this example, the DNA fragment covering the gene polymorphism site rs2252992 on human chromosome 21 was used as the target nucleic acid to be amplified, and the HAND system, the common asymmetric PCR system and the system (primer set) of the present invention were investigated to produce a single The case of strand nucleic acid products. The sequences of the primers and probes used in this example are shown in Table 1. The instrument used in this example is SLAN96 real-time fluorescent PCR instrument (Xiamen Zhishan Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Xiamen).
[0164] In short, in this example, a 25 μL PCR reaction system was used for PCR amplification and melting curve analysis. The PCR reaction system included: 1×TaqPCR buffer (TaKaRa, Beijing), 5.0 mM MgCl 2 , 0.2mM dNTPs, 1UTaq DNA polymerase (TaKaRa, Beijing), 0.2μM rs2252992-P probe, 5μL human genomic DNA (rs2252992 genotype is A / A homozygous) or negative control (water) and primers; wherein,
[0165] (1) Add 0.03 μM r...
Embodiment 2
[0177] In this example, the DNA fragment of the gene polymorphism site rs2252992 on human chromosome 21 was used as the target nucleic acid to be amplified, and the differences between the second universal sequence and the first universal sequence were investigated (that is, the second universal sequence The effect of different variant types of the sequence relative to the first universal sequence) on asymmetric amplification. The sequences of the primers and probes used in this embodiment are shown in Table 2, wherein the 3' terminal nucleotide of the universal primer (Tag primer) used is A; and 5 forward primers were designed, namely: The 3' terminal nucleotide of the second universal sequence of rs2252992-F-C is C, the 3' terminal nucleotide of the second universal sequence of rs2252992-F-G is G, and the 3' terminal nucleotide of the second universal sequence of rs2252992-F-T The acid is T, the 3' terminal nucleotide of the second universal sequence of rs2252992-F-A is A, a...
Embodiment 3
[0185] In this example, the genotyping of gene polymorphism sites rs2252992 and rs4816597 is taken as an example to illustrate that the system of the present invention can realize double and asymmetric amplification in a single reaction tube and be used for probe melting curve analysis. The sequences of primers and probes used in this example are shown in Table 3. The instrument used in this example is a SLAN 96 real-time fluorescent PCR instrument.
[0186] In short, in this example, a 25 μL PCR reaction system was used for PCR amplification and melting curve analysis, and the PCR reaction system included: 1×Taq PCR buffer, 5.0 mM MgCl 2 , 0.2 mM dNTPs, 1 U Taq DNA polymerase, 0.05 μM rs4816597-F, 0.05 μM rs4816597-R, 0.4 μM rs4816597-P, 0.04 μM rs2252992-F, 0.04 μM rs2252992-R, 0.4 μM rs2251.962-P Primers, 5 μL human genomic DNA or negative control (water). In this embodiment, four samples were detected (sample 1, 2, 3 and 4; each PCR reaction system detected a sample), wh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com