Quantitative analysis method for low-grade minerals containing light elements
A quantitative analysis, low-grade technology, applied in the analysis of materials, using wave/particle radiation for material analysis, measuring devices, etc., can solve problems such as inaccurate test results, impact of ore development and utilization, and lack of quantitative analysis of minerals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
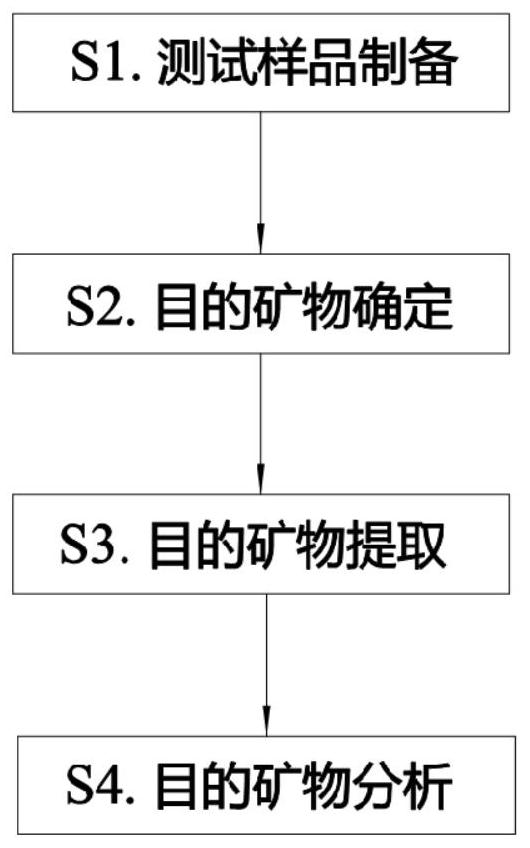
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0036] The following will further explain and describe the present invention through specific implementation modes. It should be understood that the purpose of the following implementation modes is to make the technical solution of the present invention clearer and easier to understand, and not to limit the protection scope of the claims.
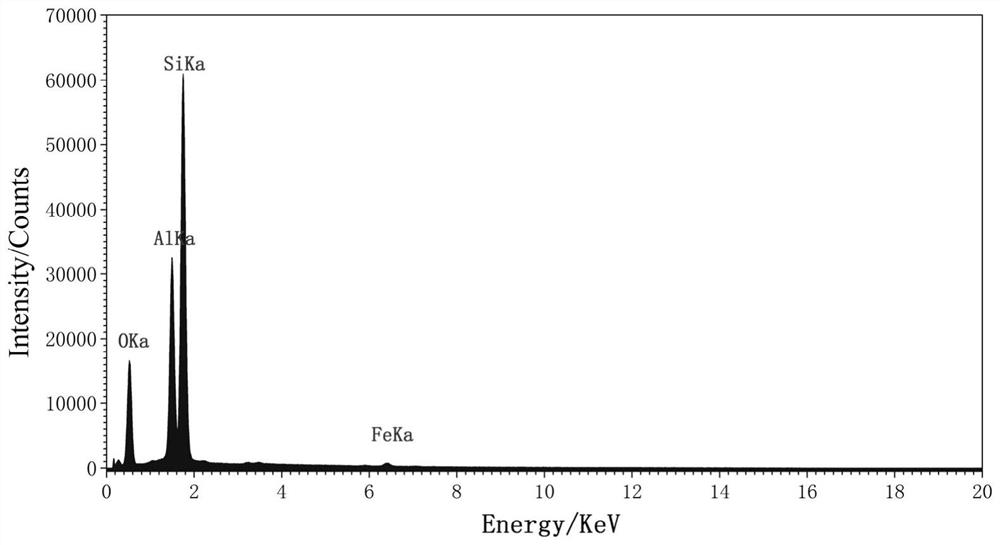
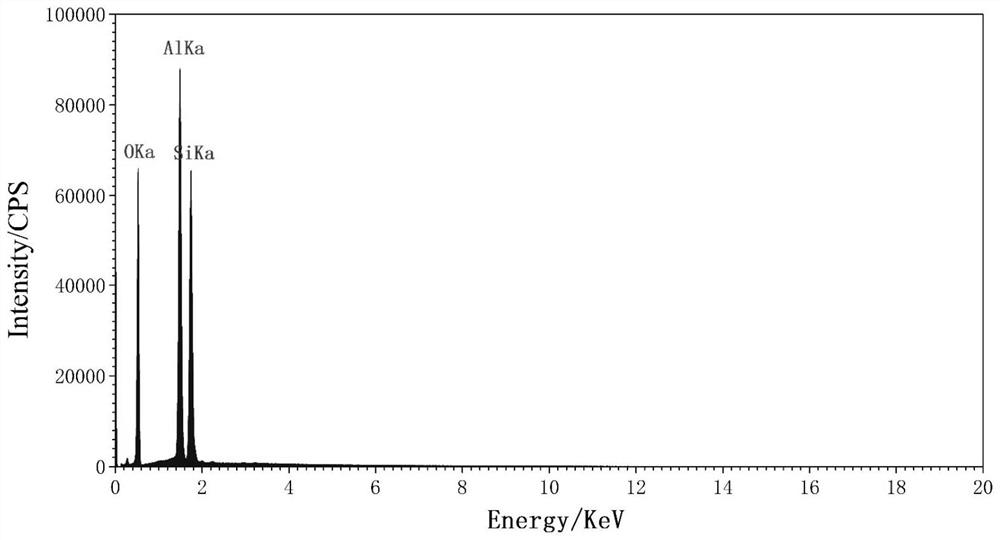
[0037] This example provides a joint quantitative determination method for low-grade lithium beryllium minerals in a lithium beryllium tantalum niobium polymetallic ore containing Li 2 O 1.59%, BeO 0.042%. The specific process is as follows:
[0038] In this embodiment, "-" means the following, for example -0.2mm means the particle size is not more than 0.2mm; "+" means the above, for example -0.2+0.1mm means the particle size is not more than 0.2mm and not less than 0.1mm.
[0039] (1) Crush the ore to -0.2mm, take about 200g of representative solid ore samples, and obtain four grades of products through screening and water analysis: -0.2...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com