Patents
Literature
32 results about "Polarized light microscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polarized light microscopy can mean any of a number of optical microscopy techniques involving polarized light. Simple techniques include illumination of the sample with polarized light. Directly transmitted light can, optionally, be blocked with a polariser orientated at 90 degrees to the illumination. More complex microscopy techniques which take advantage of polarized light include differential interference contrast microscopy and interference reflection microscopy. Scientists will often use a device called a polarizing plate to convert natural light into polarized light.
Enhancing polarized light microscopy
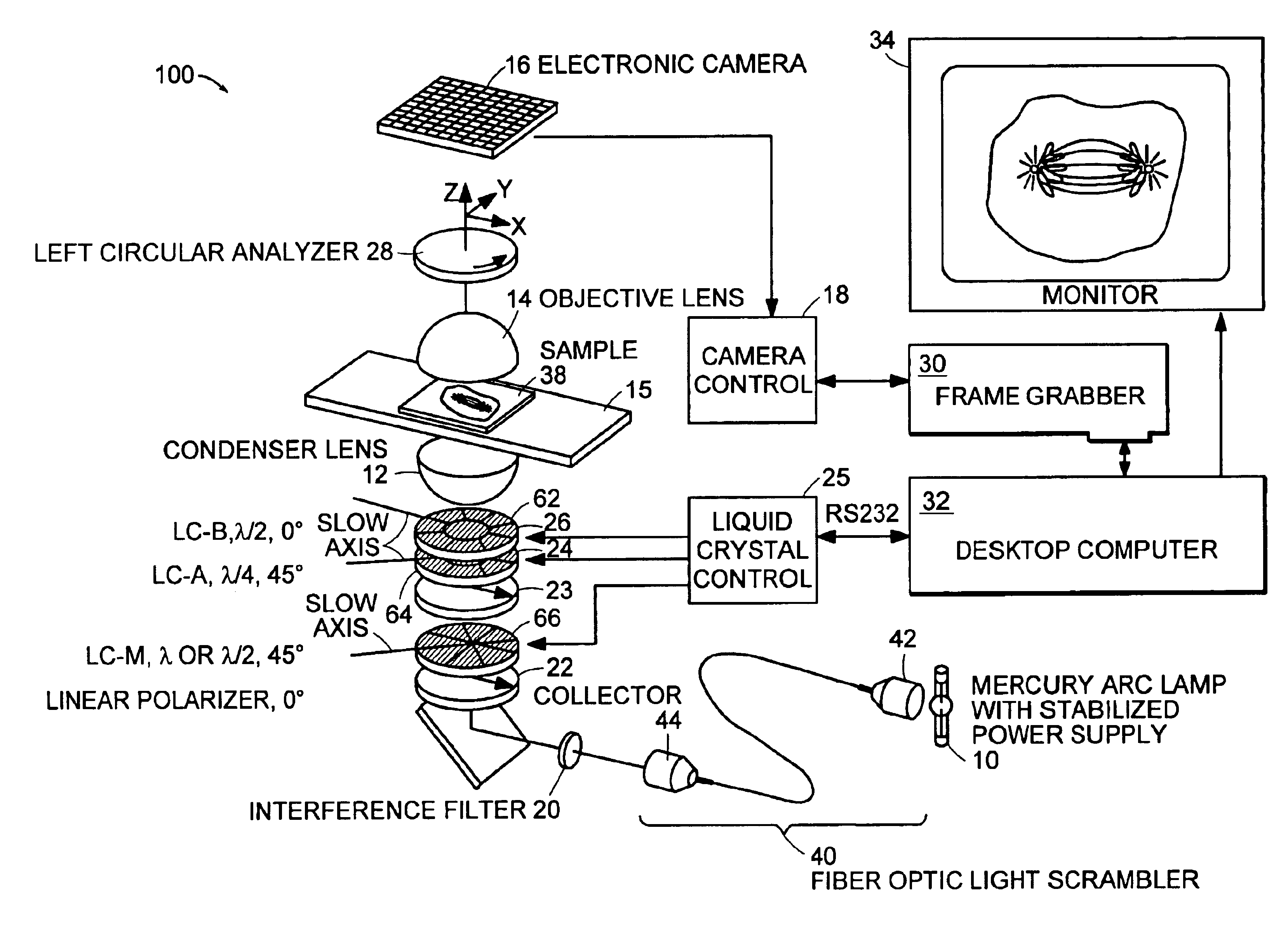
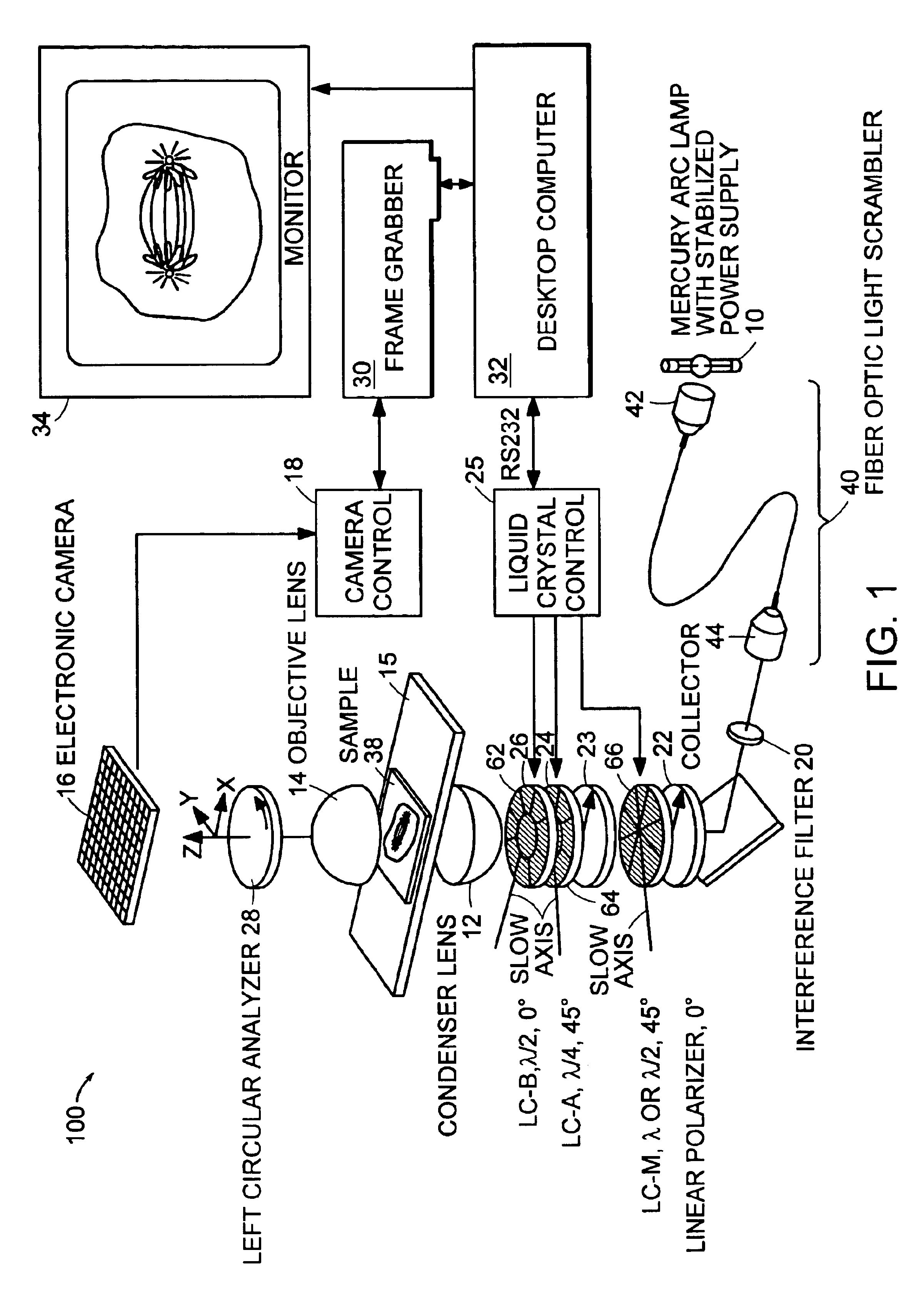
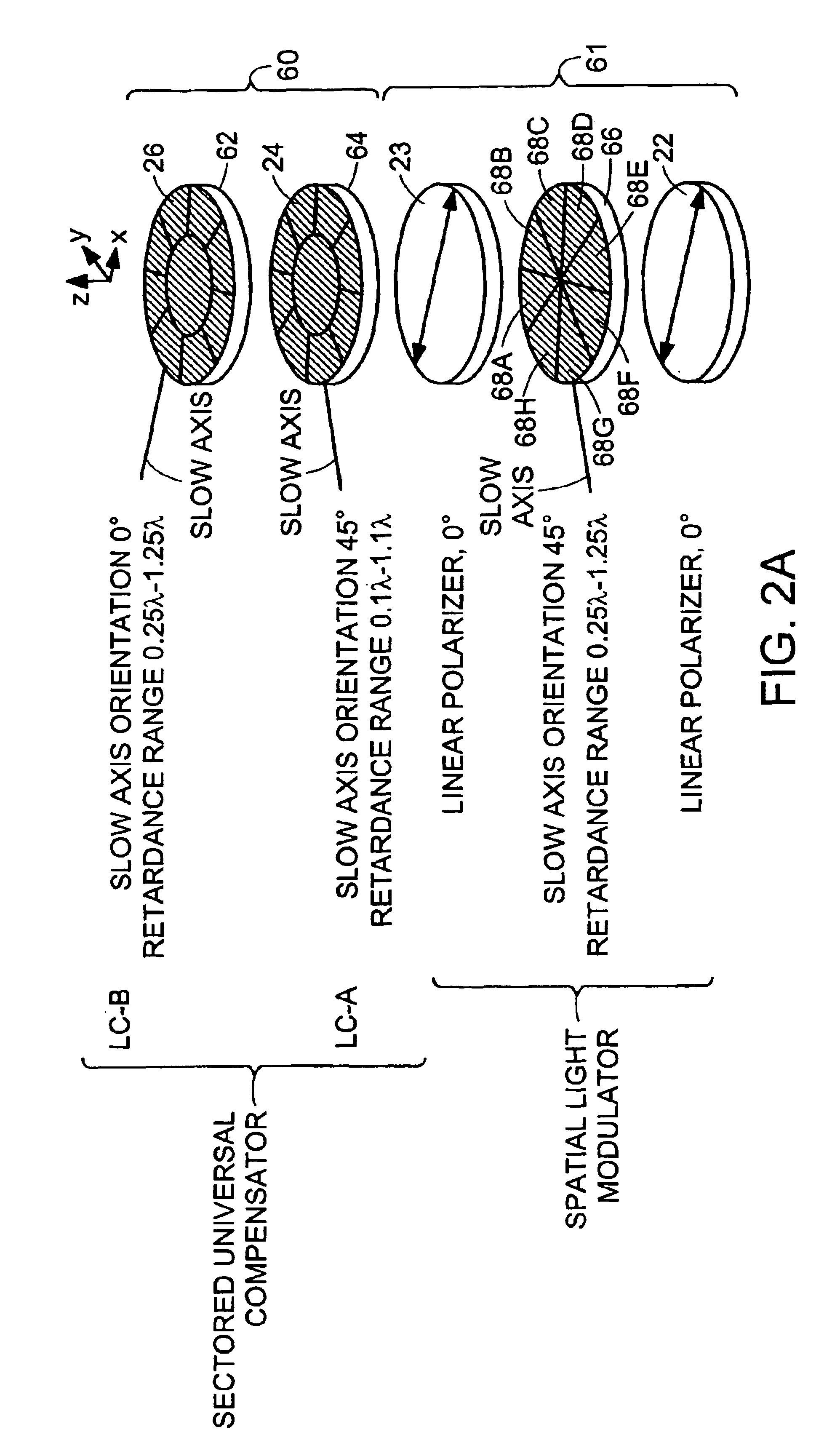
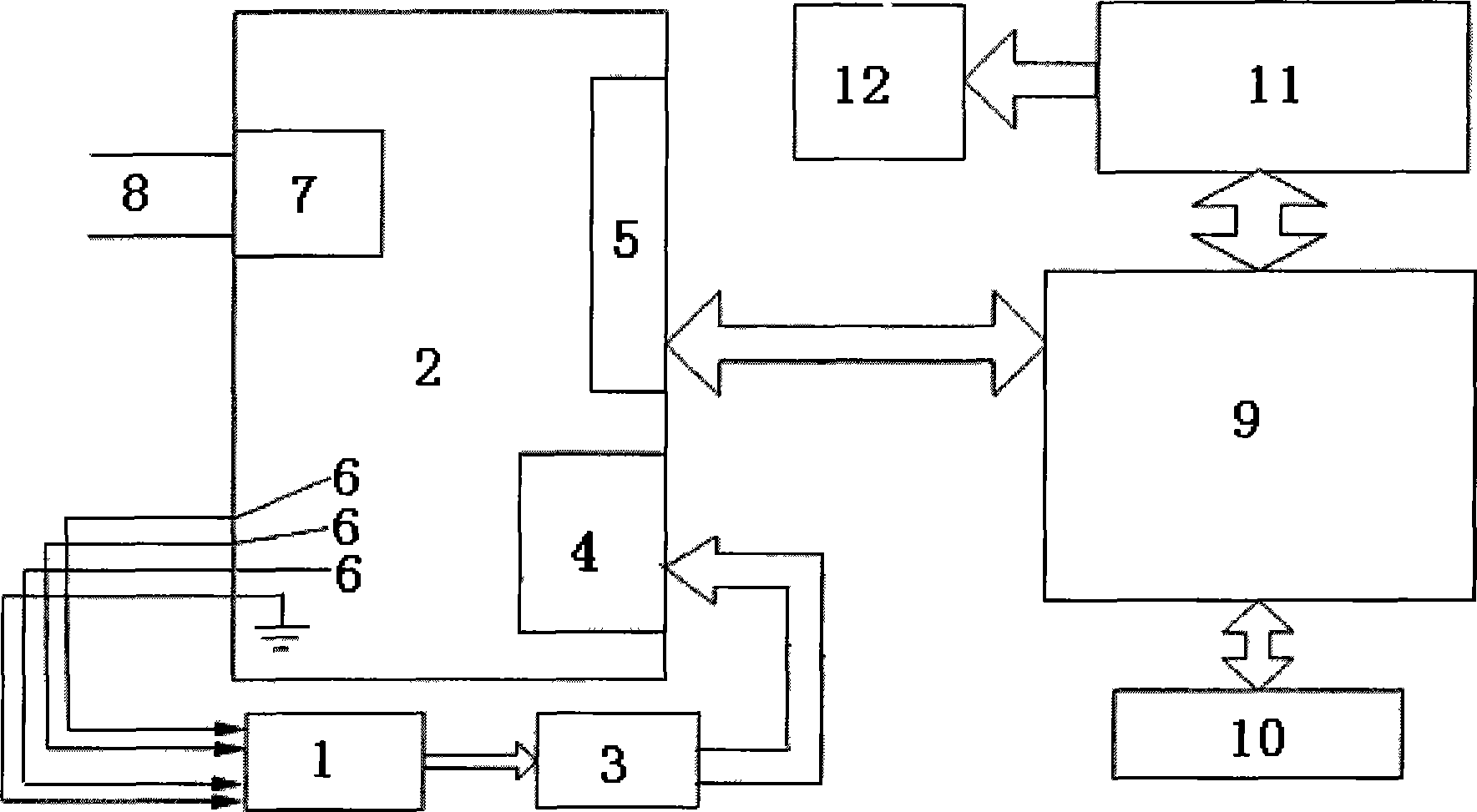
InactiveUS6924893B2Amount be controlImprove system performanceMicroscopesLight polarisation measurementOptical propertyControl signal
A microscope system for determining optical properties of a specimen includes a source of polarized light, a detector for detecting the intensity of light incident thereon, an optical path extending from the source to the detector, a condenser for providing light from the source to the specimen, an objective for receiving light from the specimen, a support for mounting the specimen, a sectored variable retarder mounted in the optical path, and a polarized light analyzer mounted in the path between the sectored variable retarder and the detector. The variable retarder has a multiple sectors. Each sector is individually addressable by a control signal that affects the light retardation characteristics of the sector.
Owner:MARINE BIOLOGICAL LAB
Automated polarized light microscope combined with a spectroscopy/spectral imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20060082762A1Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansFtir spectraMid infrared
There is disclosed a device or apparatus that is particularly suitable for use in the analytical fields of polarized light microscopy and spectroscopy / spectral imaging. The apparatus comprises an automated polarized light microscope combined with means for achieving spectroscopic analysis. The apparatus may optionally include means for spectral imaging associated with the means for achieving spectroscopic analysis. Any means for achieving spectroscopic analysis may be utilized for example Raman, mid-infrared, near-infrared, ultraviolet, visible, luminescence, and the like.
Owner:CARGILL INC
High precision microscopic fatigue tester
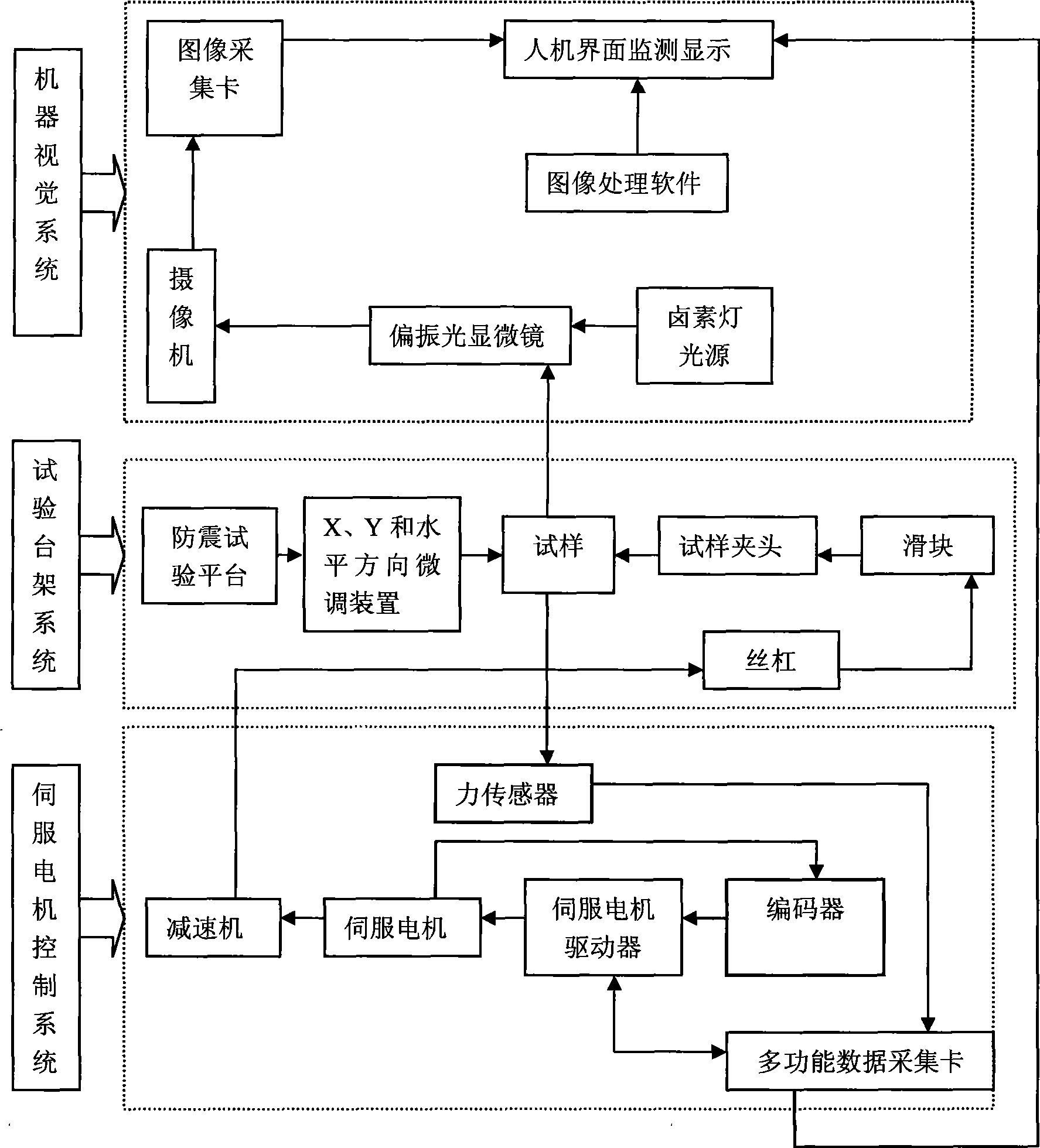
InactiveCN101441154ACompact and lightweightEasy to operateStrength propertiesHuman–machine interfaceData acquisition
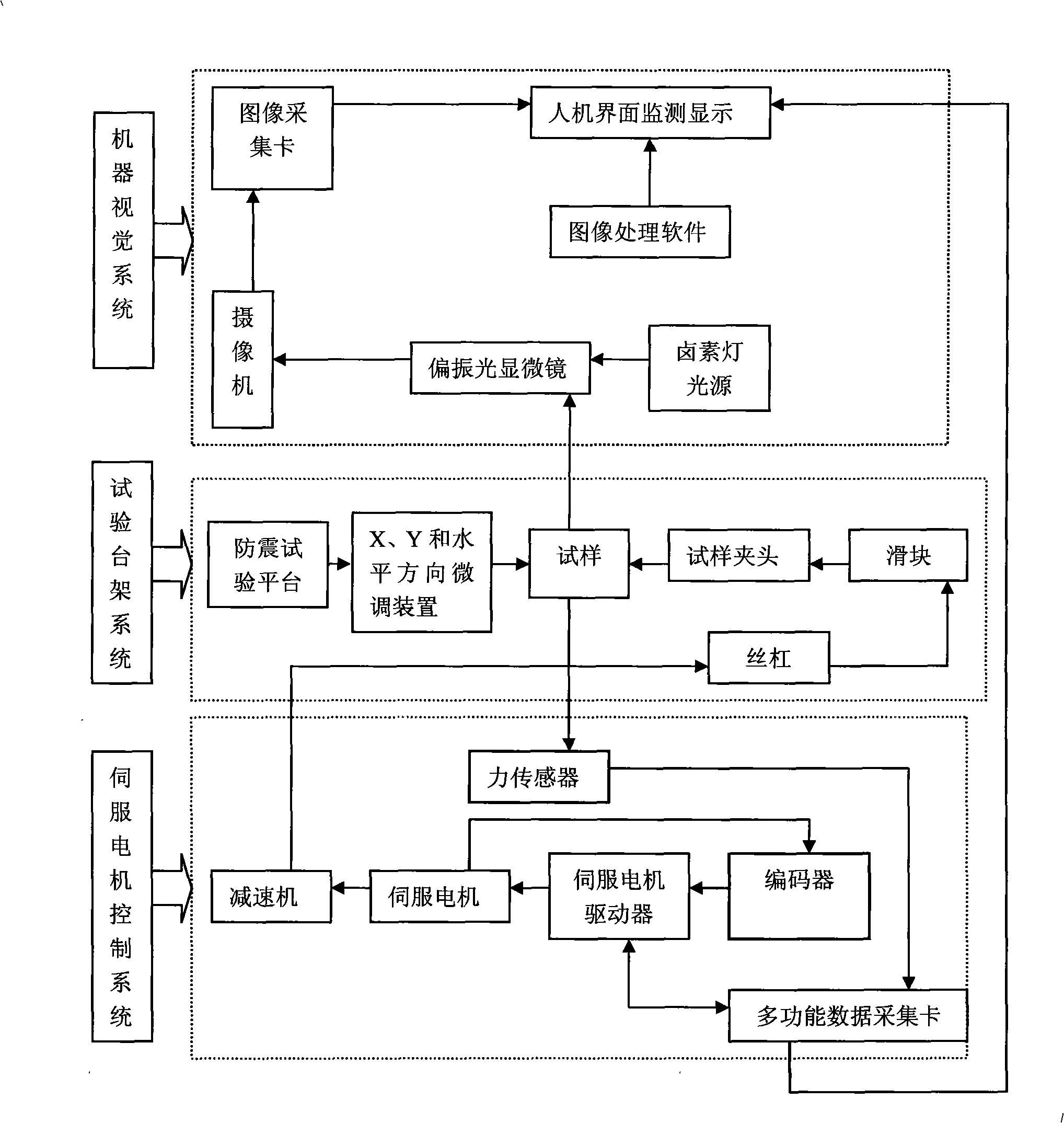
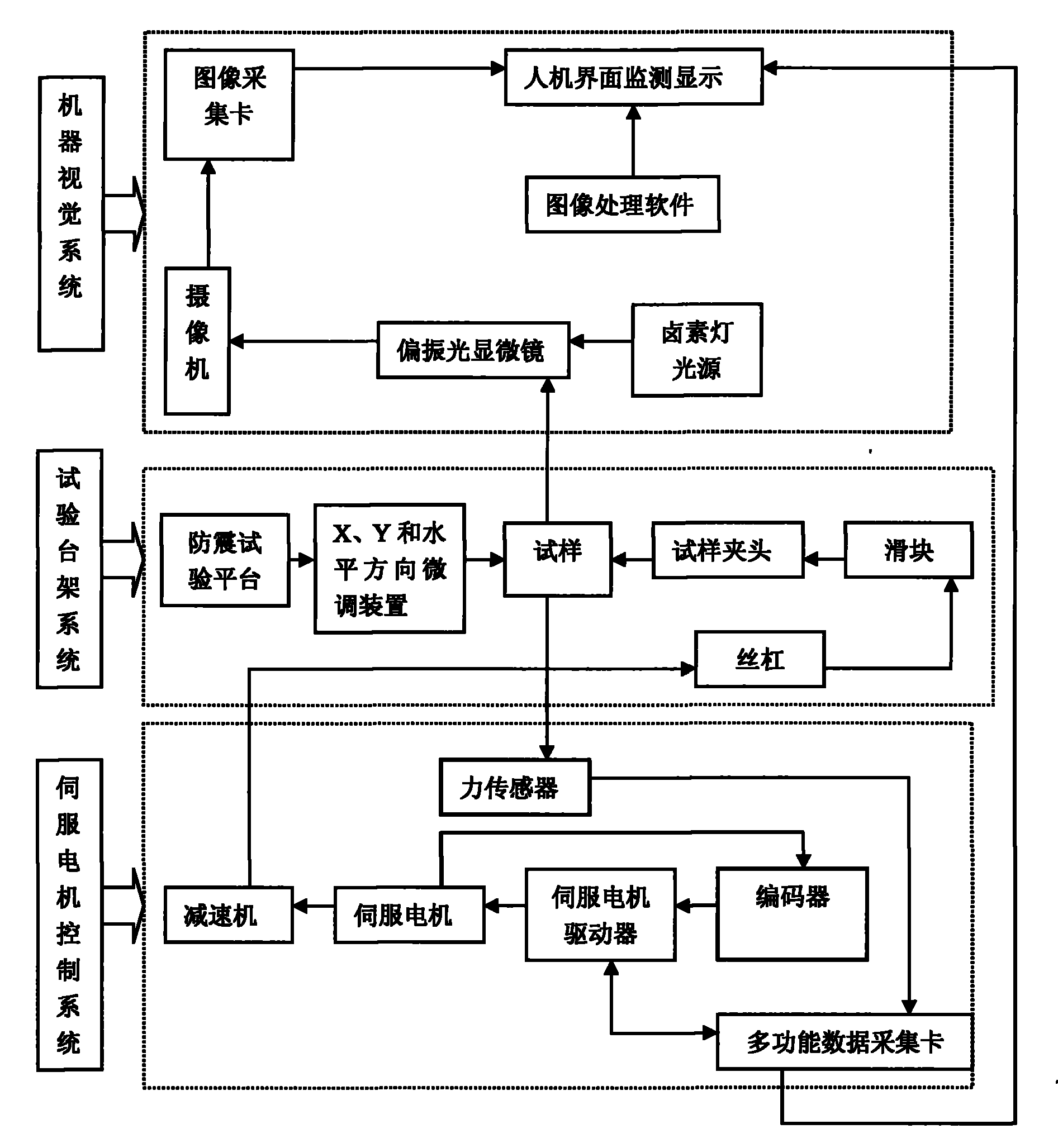
The invention discloses a high-precision micro fatigue testing machine which comprises a test bed system, a servo motor control system and a machine visual system, wherein the servo motor control system is connected with a servo motor driver through a multifunctional data acquisition card, while the servo motor driver is connected with a servo motor which is connected with a speed reducer, and the speed reducer is connected with a leading screw in the test bed system, the leading screw is connected with a clamp through a sliding block, the sample in the clamp is connected with a polarizing microscope connecting with a vidicon which is used for monitoring display on the man-machine interface through an image acquisition card, the size of the micro-crack is measured by image processing software. The invention has the advantages of compact structure, simple operation, easy maintenance, high efficiency and energy saving.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Visual observing system for growth process of microcrystalline silicon film and measurement method
ActiveCN104122209ARealize continuous dynamic detectionSimple structurePolarisation-affecting propertiesUsing optical meansImage resolutionBeam splitting
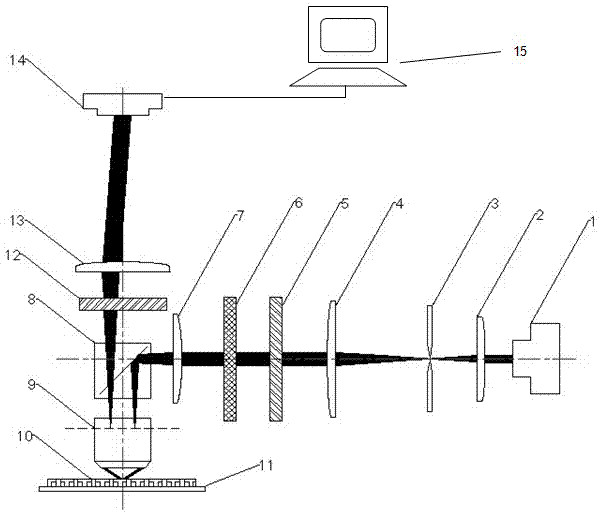
The invention discloses a visual observing system for observing growth design of a microcrystalline silicon film in real time and a measurement method, which effectively improve the defect that a traditional polarization microscope is relatively low in resolution in an observing process. The visual observing system for the growth process of the microcrystalline silicon film comprises a light source, a pinhole, a polarizer, a 1 / 4 wave plate, a convergent lens, a beam splitting prism, a vertical objective lens, a sample, an objective table, a polarization analyzer, a CCD camera and a computer. The visual observing system has the beneficial effects that a scanning problem in a traditional film thickness detection method is effectively improved, the continuous dynamic detection of the film is realized, the detection efficiency and precision are improved, and the resolution is high; besides, the observing system disclosed by the invention is simple in structure, and the method is simple, convenient and feasible and is convenient to popularize.
Owner:上海裕诗实业有限公司
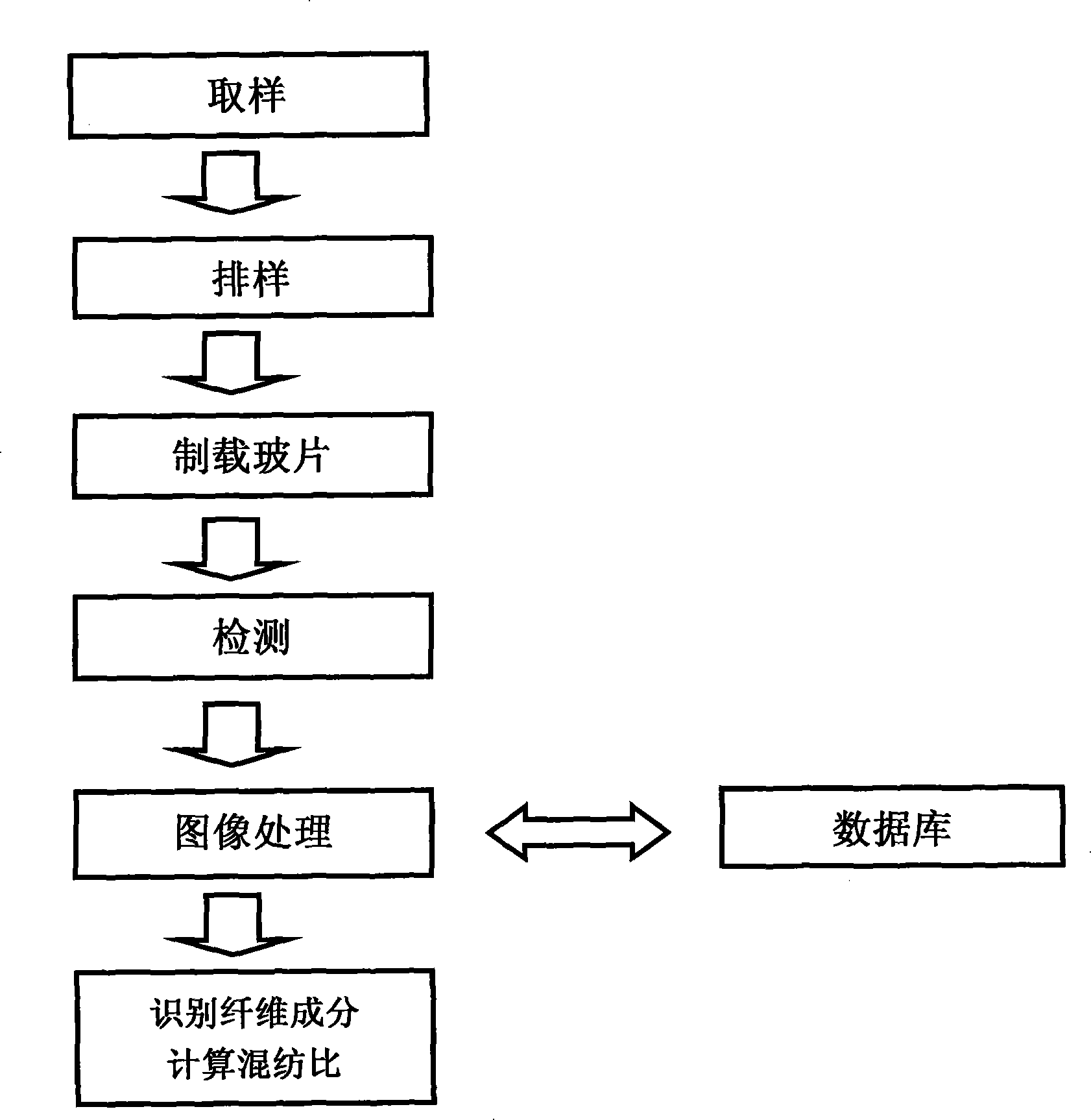
Yarn constituent detecting method based on polarizing microscope
InactiveCN101246121AAccurate identificationAccurate detection of content ratioMaterial analysis by optical meansTextile testingYarnEngineering
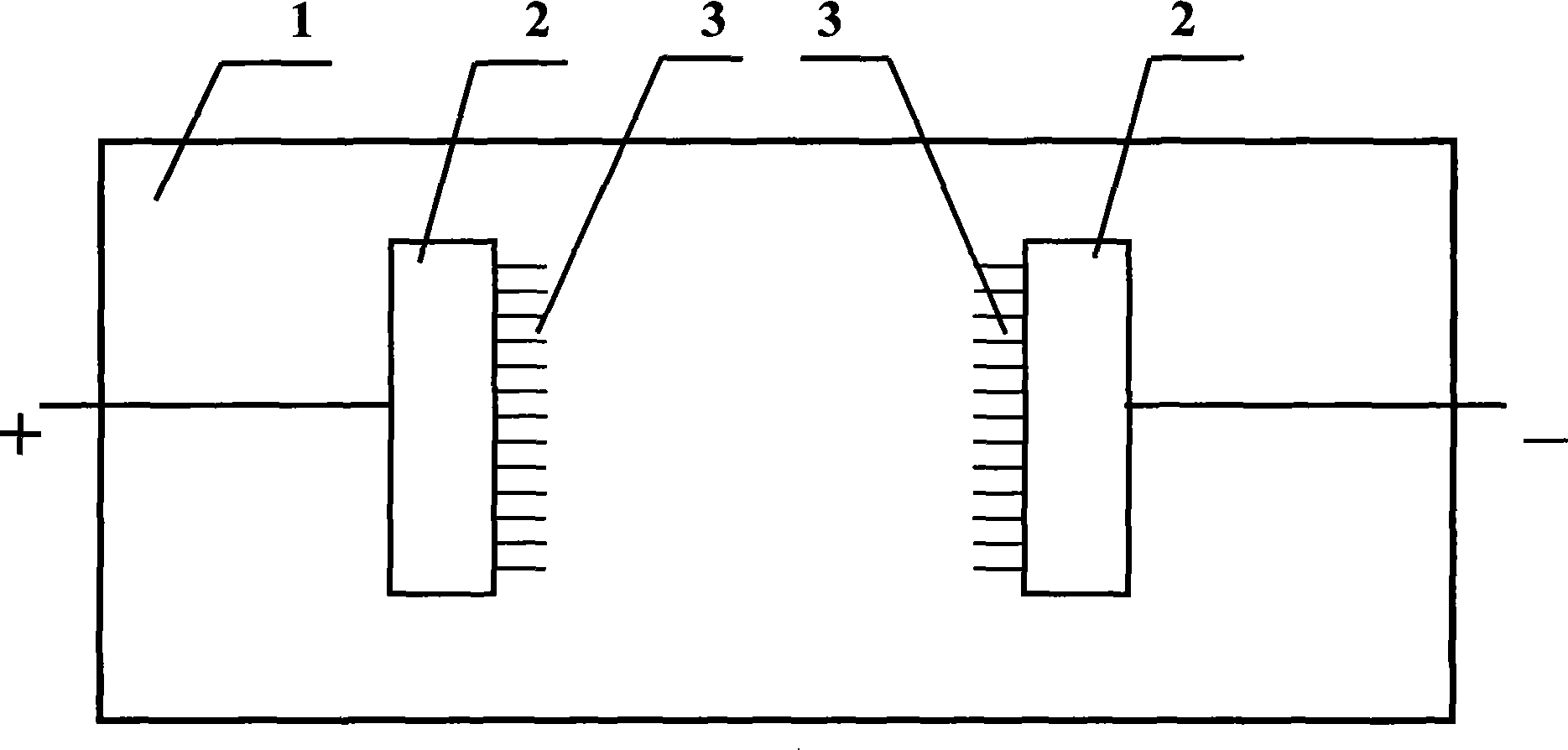
The present invention relates to a method for measuring the yarn component basing on the micropolariscope, and the method adopts the micropolariscope for detecting the fiber component of pure and blended yarn and each component ratio. The yarn sample with short segment is scattered to discrete fiber, the discrete fiber is leaded to be arranged trimly in a certain direction and is prepared to the sample piece which can be observed in the micropolariscope, the clear image of the sample piece under the micropolariscope is obtained, and the computer processes the image and outputs the fiber component style and blending ratio. The invention can accurate identify the style of the fiber comprising the yarn; can accurately detect the content proportion of each fiber component of the blending yarn; can totally realize the no-pollution testing and conforms to the basic national policy of energy saving and discharging reducing; the high-pressure electrostatic technique and computer image processing technique are adopted for realizing the automatic stock layout and automatic numbering to the fiber thereby realizing the yarn detecting with high precision and high efficiency, has low testing cost and facilitates the generalizing and applying.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Method for cell imaging by adopting polarized light microscope to observe nano particles
InactiveCN104711314AForce background abilityLow backgroundMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellOptical property
The invention discloses a method for cell imaging by adopting a polarized light microscope to observe nano particles; a single gold nanorod is observed by adopting the polarized light microscope; the polarized light microscope is found to be capable of selective imaging of an anisotropic nano material; under the polarized light microscope, scattering light spots of the gold nanorod has smaller size, the background value of imaging can be significantly reduced, and accordingly, the signal-to-noise ratio of an image is improved by at least 3 times or more. Due to the unique optical properties, the anisotropic nano material and the polarized light microscope have great application potentiality in imaging and detection of cancer cells.
Owner:李乐 +2
Polychromatic polarization state generator and its application for real-time birefringence imaging
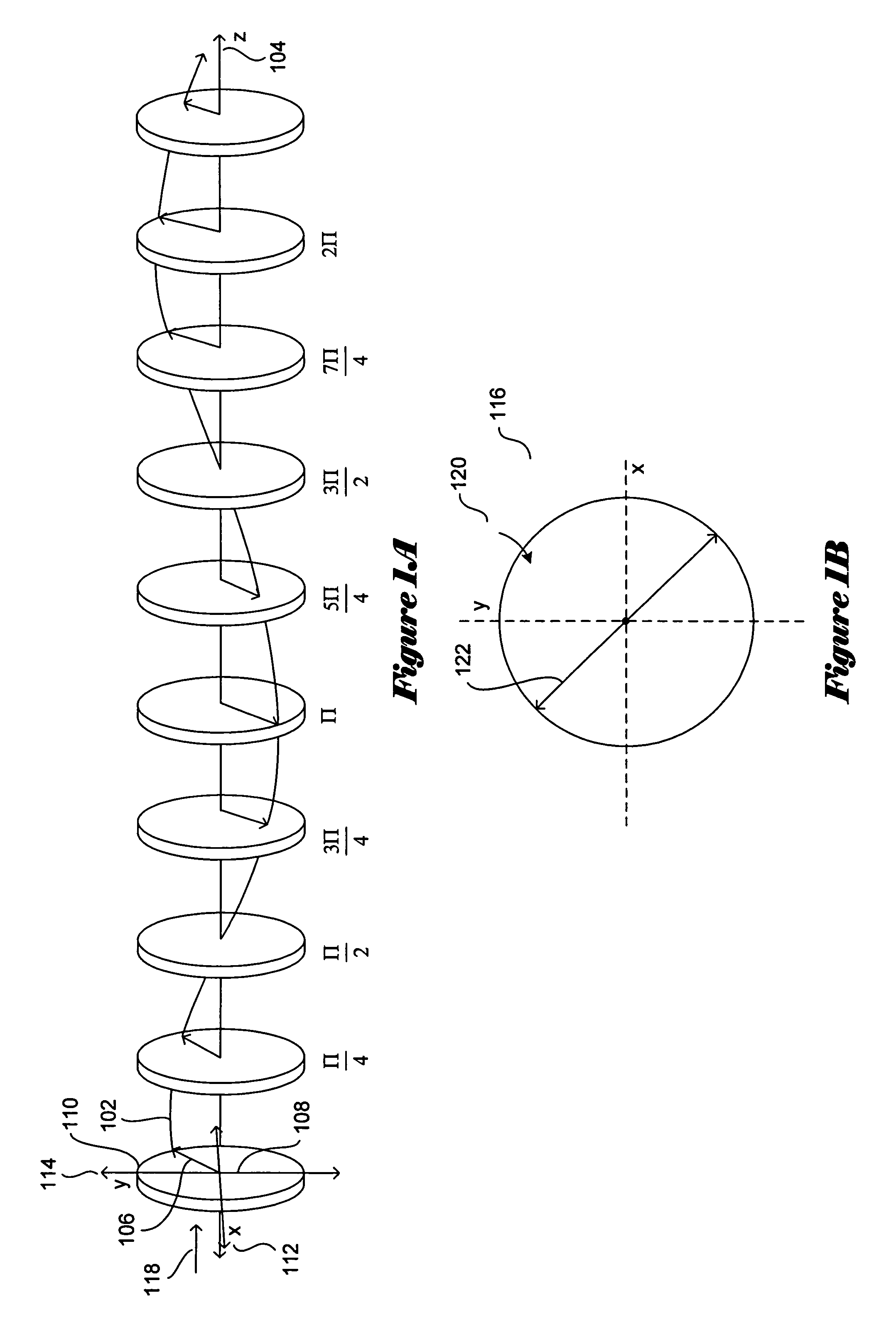
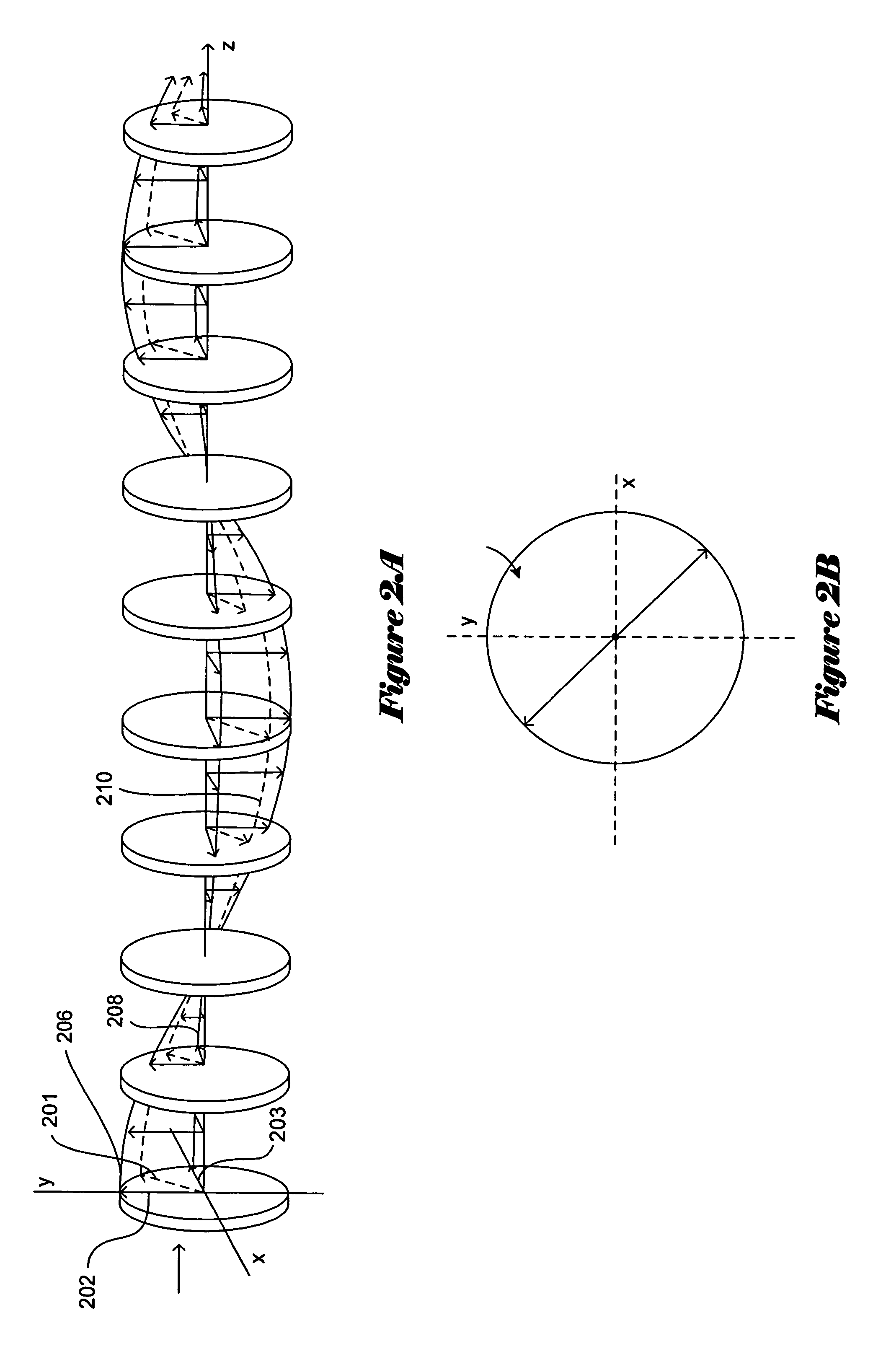
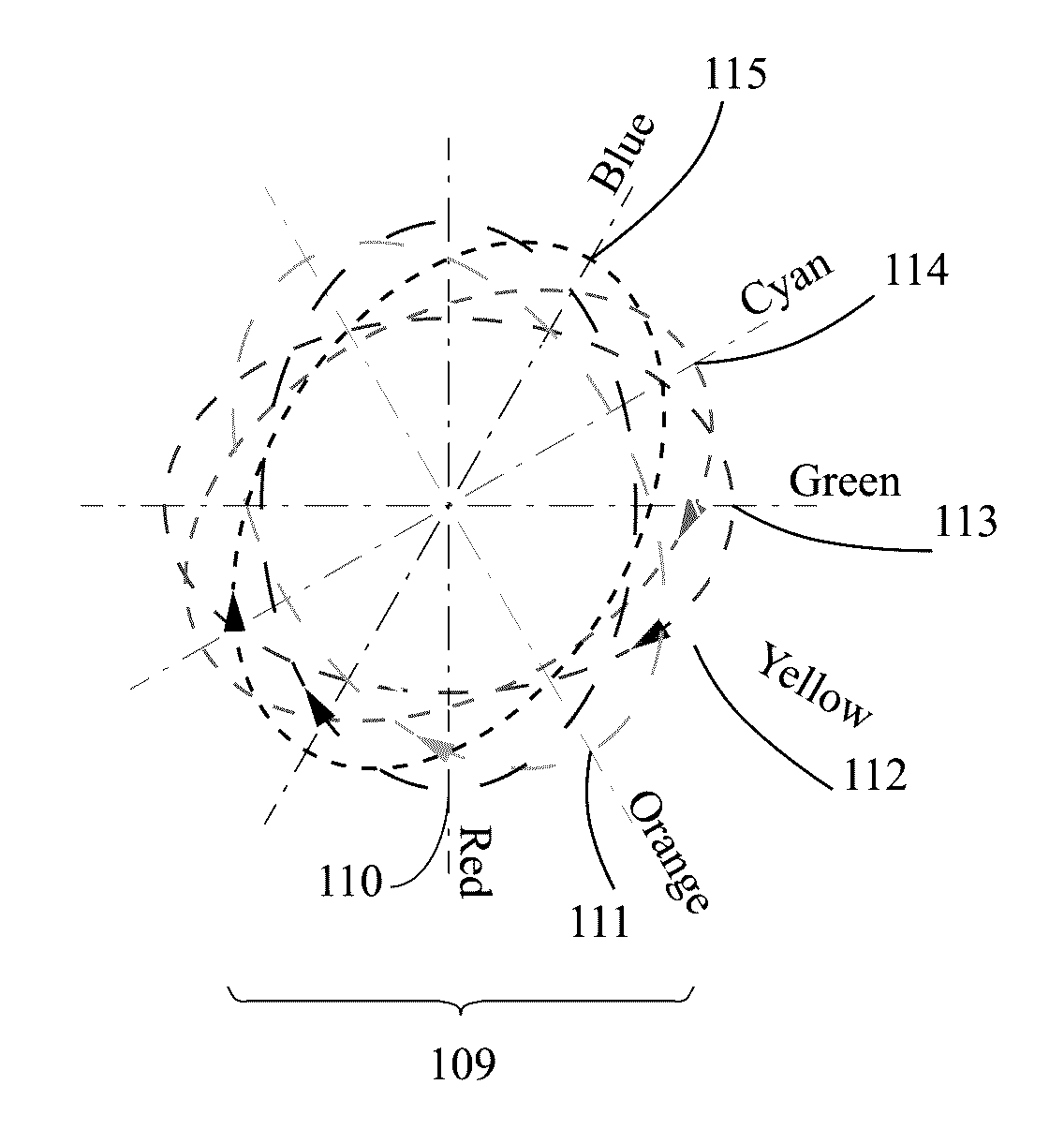
Apparatus for generating polychromatic polarized light with the polarization ellipse orientation determined by the wavelength. The proposed polychromatic polarization state generator can be used in various configurations of polarized light microscope (called “polychromatic polscope”) for imaging birefringent samples. The polychromatic polscope produces a spectral-modulated visual scene, in which birefringent structures are evident because their appearance is different from the background. New polarized light microscope can subtract the background and produce video-enhanced color image of birefringent structures. The obtained picture can be also mathematically processed in order to obtain a map of quantitative distribution of specimen retardation and orientation of the principal axes.
Owner:SHRIBAK MICHAEL
Real-time linear-birefringence-detecting polarization microscope
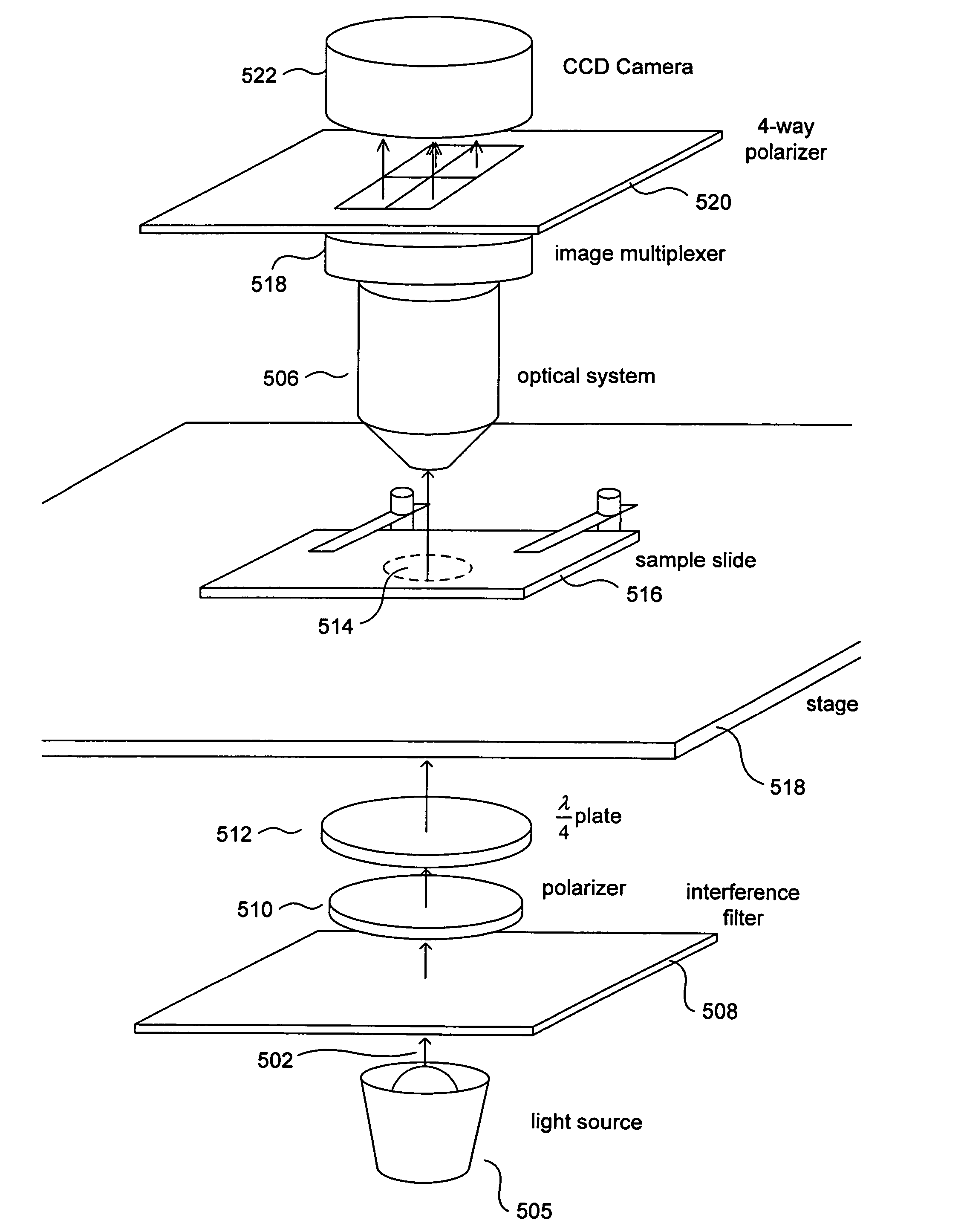
Various embodiments of the present invention are directed to real-time capture, analysis, and output of polarizing microscopy images that quantify detected LB signals at discrete locations within the image. In one embodiment of the present invention, circularly polarized light is passed through a sample and optically imaged by traditional polarizing-light-microscope components. The resulting image is then split four ways and analyzed by a four-way polarizer / analyzer, and the four resulting analyzed subimages are computationally processed to produce three false-color, real-time images that represent per-pixel linear birefringence, extinction angle, and transmission at each position within a quarter-sized representation of the original image produced by conventional light-microscope imaging components. The false-color images can be produced at a rate of 30 frames per second or at greater rates by employing highly efficient image capture and computational processing of captured images through efficient programming techniques.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Polychromatic polarization state generator and its application for real-time birefringence imaging
Owner:SHRIBAK MICHAEL
Real-time linear-birefringence-detecting polarization microscope
Various embodiments of the present invention are directed to real-time capture, analysis, and output of polarizing microscopy images that quantify detected LB signals at discrete locations within the image. In one embodiment of the present invention, circularly polarized light is passed through a sample and optically imaged by traditional polarizing-light-microscope components. The resulting image is then split four ways and analyzed by a four-way polarizer / analyzer, and the four resulting analyzed subimages are computationally processed to produce three false-color, real-time images that represent per-pixel linear birefringence, extinction angle, and transmission at each position within a quarter-sized representation of the original image produced by conventional light-microscope imaging components. The false-color images can be produced at a rate of 30 frames per second or at greater rates by employing highly efficient image capture and computational processing of captured images through efficient programming techniques.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Composite fiber component and structure detection method based on micropolariscope analysis
InactiveCN101504358AAccurate detection of ingredient typesObservable Structural RelationshipsMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberStructural analysis
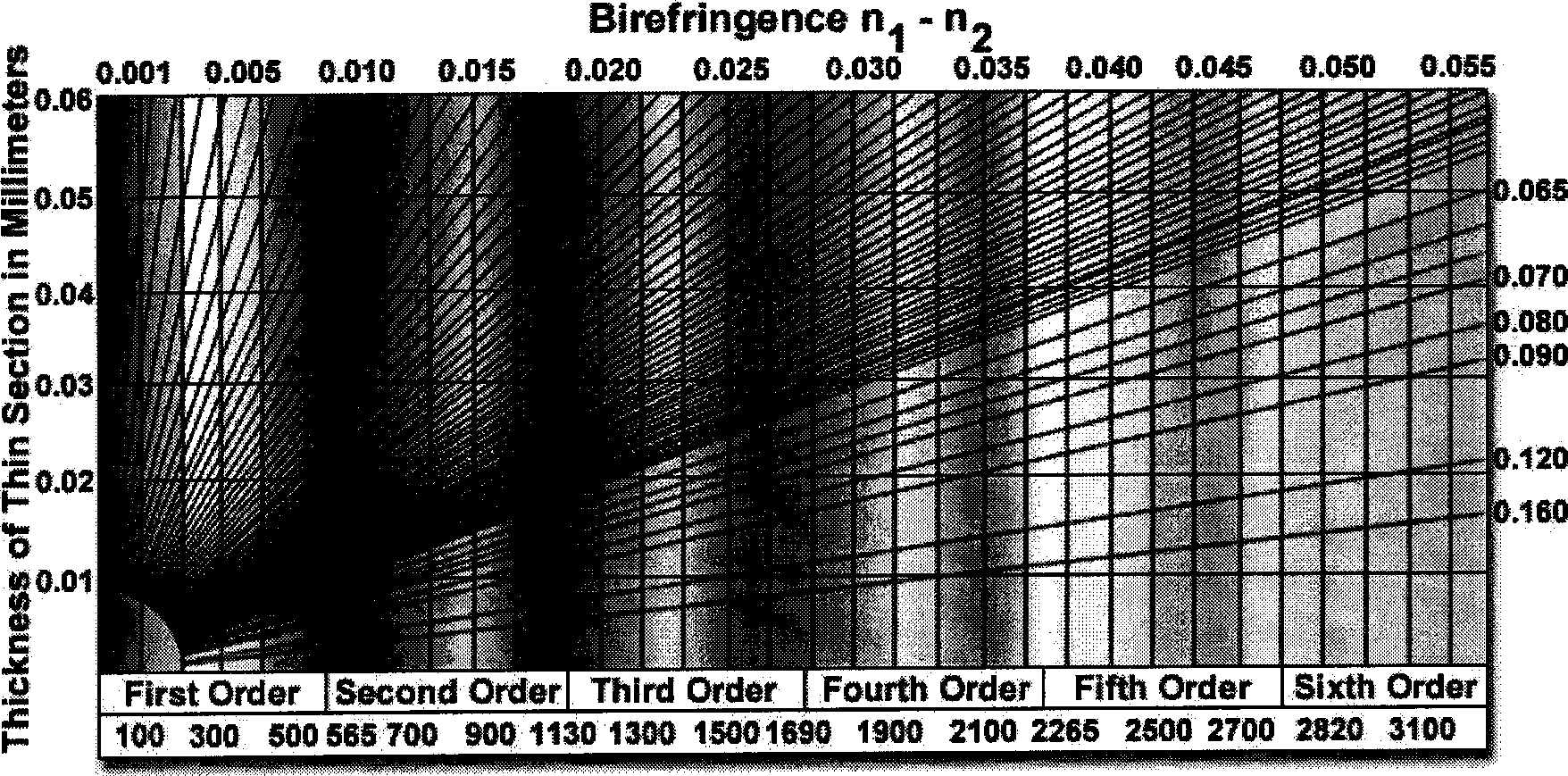
The invention relates to a method for detecting compositions and a structure of composite fiber based on polarizing microscope analysis, which adopts a method based on polarizing microscope analysis to perform composition detection and structural analysis on composite fiber containing two or more compositions. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing a fiber specimen to be tested into a sample wafer which can be observed under a polarizing microscope; placing the sample wafer under the polarizing microscope for detection; and analyzing an acquired fiber specimen image, and determining internal compositions and a structure of fiber to be tested by combining an Michel levy chart. The method is a physical detection method, adopts completely pollution-free detection, and meets the development trend of energy conservation and environmental protection. The method has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, high efficiency, high precision, low detection cost, and convenient popularization and application.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Method for displaying temperature elevation of ferromagnetic substance with simulated blood vessel bed
ActiveCN1670498ASimple methodEasy to observeThermometers using physical/chemical changesThermometer applicationsPolyethylene glycolBlood vessel
This invention relates to analogue blood bed display iron magnetic substance heating method, which comprises the following steps: quickly cooling it down and cracking it into parts; re-piecing the cracked blood cover slices on the glass slides with gaps between; dripping melted poly glycol between blood cover slice and glass slice; deleting the poly glycol in gaps after the poly glycol solidified; filling the dried iron magnetic power to the above gaps to get the analogue blood bed; putting the above analogue blood bed in the alternating magnetic field and then putting the analogue blood bed under bias microscopes for observation.
Owner:CHINA JAPAN FRIENDSHIP HOSPITAL
Dyeing method for observing collagenous fibers by adopting polarization microscope
ActiveCN107063811AStrong adsorptionClear colorPreparing sample for investigationTissue fibrosisPermeation
The invention provides a dyeing method for observing collagenous fibers by adopting a polarization microscope. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, using saturated picric acid-sirius red dye liquor for dyeing, then using a weak acid solution in concentration of 1-10%w / v for immersing tissue slices, and finally conventionally leaching, drying and fixing the tissue slices. The permeation of the tissue is enhanced by the heated picric acid, so that the lining dyeing background is brighter; the heated sirius red dye liquor has firmer adsorption for the collagenous fibers and the coloring is clear; the weak acid solution can wash off the picric acid crystal separated out of the tissue slices and is difficult to wash off the yellow lining dyeing background, so that the excellent coloring of the collagenous fibers can be guaranteed, the yellow lining dyeing background is obvious, and the collagenous fibers are clear; the dyeing method provided by the invention has high repeatability, the collagenous fibers are obviously colored, and the fiber structure is clear; and the method is beneficial to the positioning and quantitative analysis for different collagenous fibers and is convenient for the judgment for the degree of tissue fibrosis.
Owner:GUANGZHOU WOMEN AND CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENTER
Visual detection method for observing lipid adsorption of montmorillonite based on polarization microscope
ActiveCN105203463AQualitative and semi-quantitative characterization of adsorptionPolarisation-affecting propertiesLipid formationMontmorillonite
The invention relates to a visual detection method for observing lipid adsorption of montmorillonite based on a polarization microscope. Firstly the montmorillonite and high fat food or feed are mixed uniformly; then a sample is prepared into a smear piece; the smear piece is dyed through a neutral lipid dye oil red 0; the prepared smear piece is placed under the polarization microscope for detection. The adsorption property of the montmorillonite to lipid in the high fat food is observed. The method is a physical detection method, can be used for directly observing lipid adsorption of the montmorillonite, and is simple in operation and intuitive and convenient in observing.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for identifying mineral drugs based on polarized light microscopy technology
PendingCN111829960APrecise positioningFull display of pleochroismPolarisation-affecting propertiesColor imageGlycerol
The invention relates to the field of polarized light detectionand particularly relates to a method for identifying mineral drugs based on a polarized light microscopy technology. The method comprisesthe following steps of (1) putting mineral medicine with the thickness of 1-2mm on a coarse grinding stone, adding a proper amount of water, and grinding the mineral medicine back and forth on the coarse grinding stone until the two sides are ground to be smooth and the thickness is 0.2-0.9 mm; (2) transferring the mineral medicine ground in the step (1) to a fine grinding stone, adding the water, grinding the mineral medicine back and forth till the mineral medicine is transparent, washing the ground mineral medicine with water, treating the ground mineral medicine with ethanol, and fillingthe ground mineral medicine with a glyceryl ethanol test solution; and (3) putting the abrasive disc prepared in the step (2) under a polarized light microscope with a compensator, setting the angle of semi-polarized light, and shooting under a 10-time objective lens by adopting a large-image splicing technology in combination with a real-time depth-of-field extended imaging technology to obtain color image data. According to the method, the birefringent mineral structure can be accurately positioned, and the multi-color property of anisotropy of structures of different parts of the mineral under polarized light is fully displayed.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
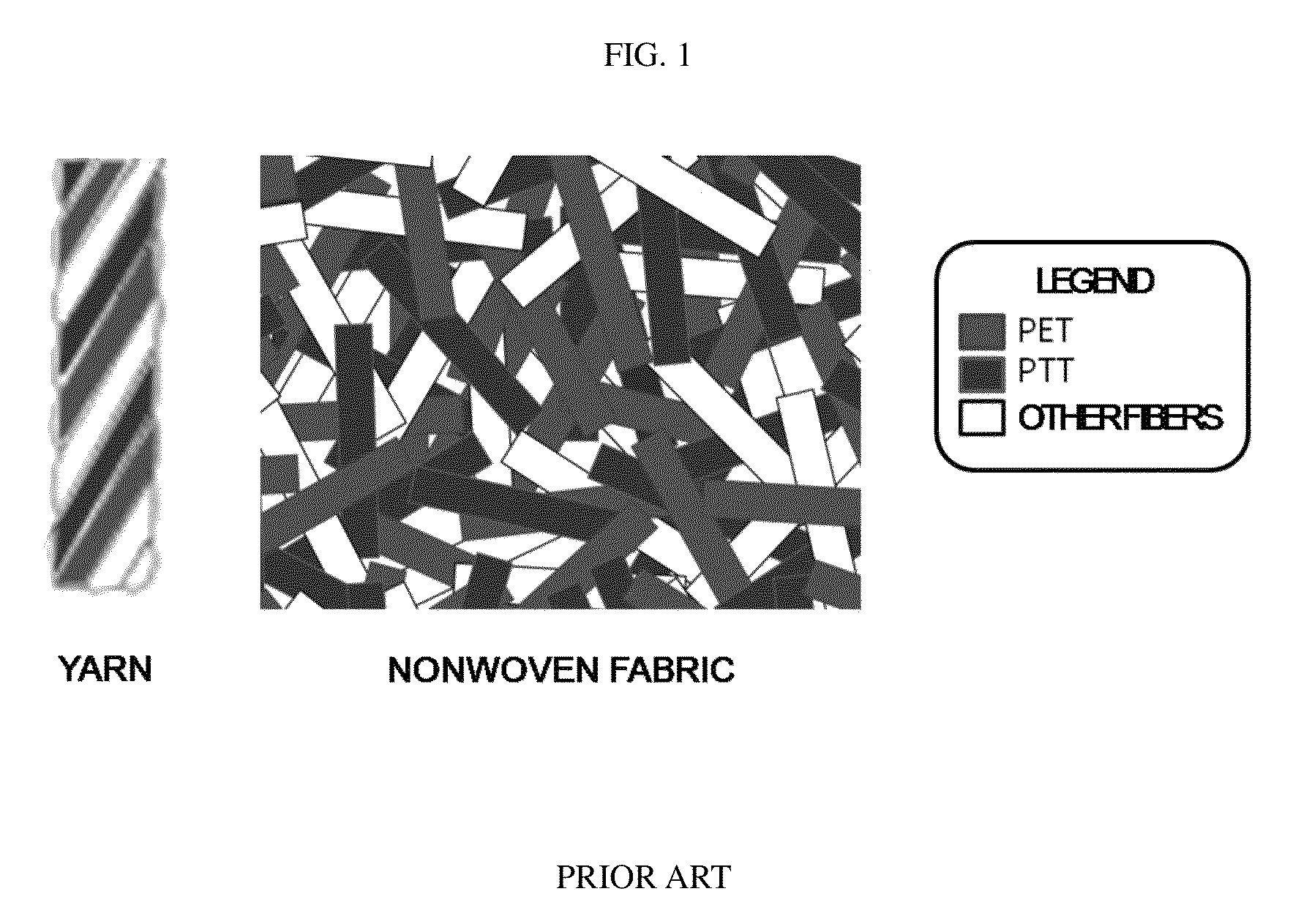
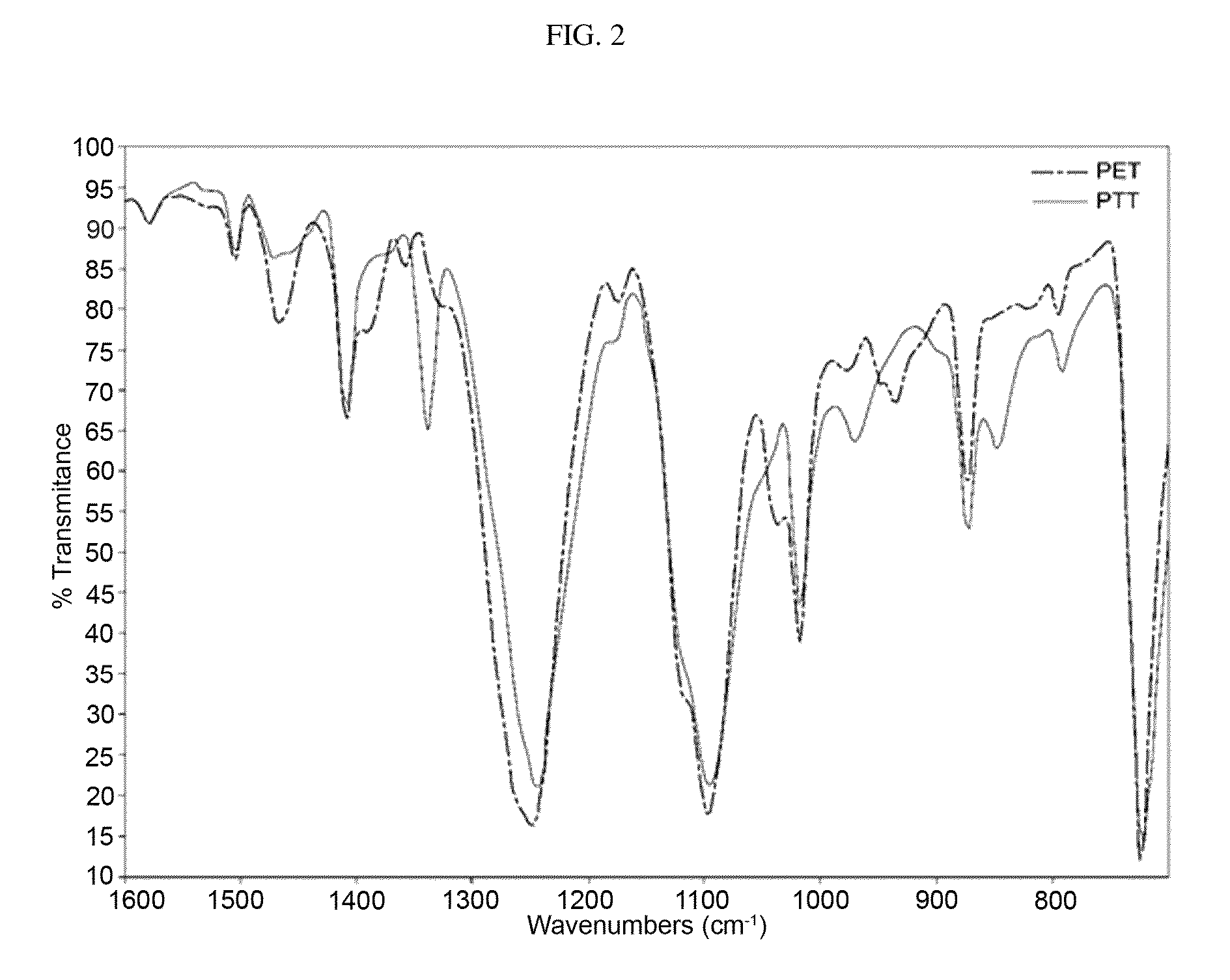
Method for measuring fiber content of polyethyleneterephthalate and polytrimethyleneterephthalate fibers
InactiveUS9121815B2Improve accuracyPractical and convenientRadiation pyrometryTextile testingFiberQualitative analysis
Disclosed is a method for measuring a fiber content of polyethyleneterephthalate (PET) and polytrimethyleneterephthalate (PTT) fibers, particularly wherein the method includes: a qualitative analysis step of identifying a presence of polyethyleneterephthalate (PET) and polytrimethyleneterephthalate (PTT) fibers in a mixed-spun fiber product; and a quantitative analysis step of measuring the fiber content by a microscopic count through difference in color between PET and PTT fibers by birefringence in a cross polarization state of a polarized light microscope (PLM). Through the present invention, it is possible to simply and accurately calculate the fiber content of PET and PTT fibers in a mixed-spun fiber material in which various kinds of fibers are mixed.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Device for shooting large-area sample on microscope and use method thereof
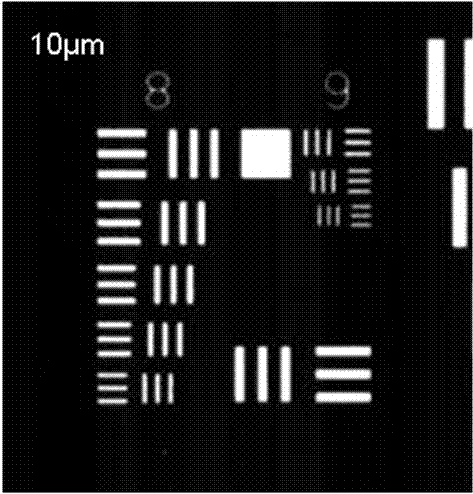
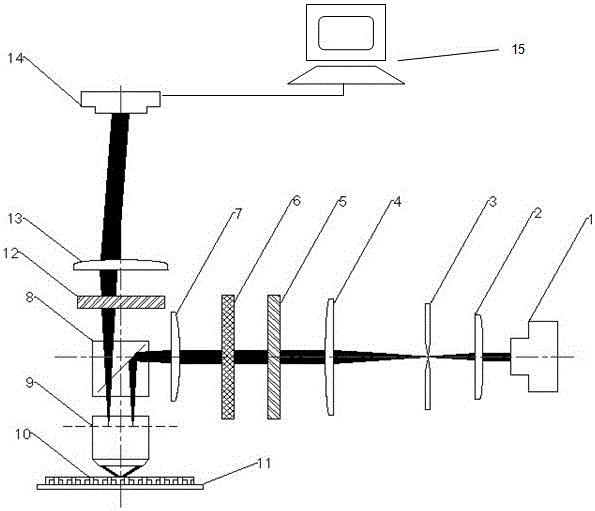
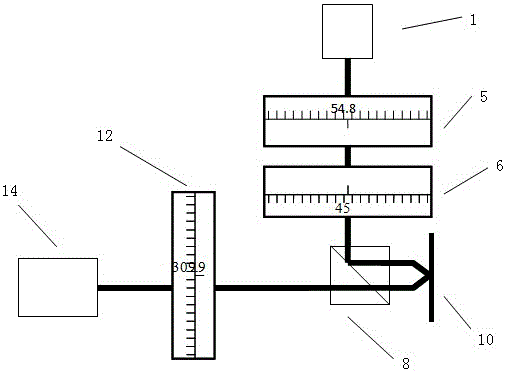
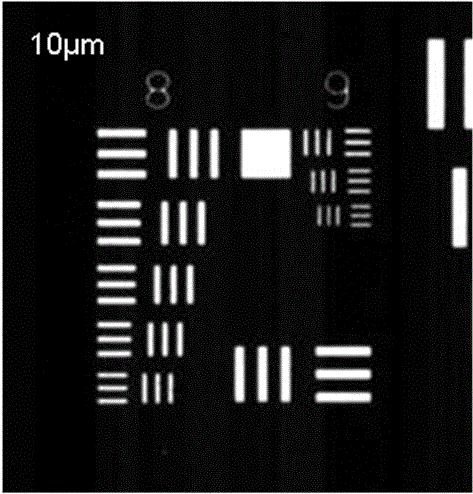
The invention discloses a device for shooting a large-area sample on a microscope and a use method thereof. Two electric translation platforms which are orthogonally stacked and mounted together are arranged on a base of the microscope, and a sliding block of the electric translation platform located at the upper part is used as a sample placement platform; an image acquisition sensor is arrangedat the top of the microscope and used for shooting the sample and acquiring an image of the sample; the image acquisition sensor of the microscope is connected with an upper computer, the upper computer controls the image acquisition sensor to shoot, and the image acquired by the image acquisition sensor through shooting is transmitted back to the upper computer for splicing processing of subsequent images; the electric translation platforms are connected with the upper computer, and the upper computer controls the two electric translation platforms to move so as to control the shooting position of the sample. The imaging advantage of the optical polarized light microscope can be fully utilized, compared with a digital camera picture, the shooting resolution is increased by hundreds of times, and a breakthrough is brought to the imaging range of an existing microscope.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
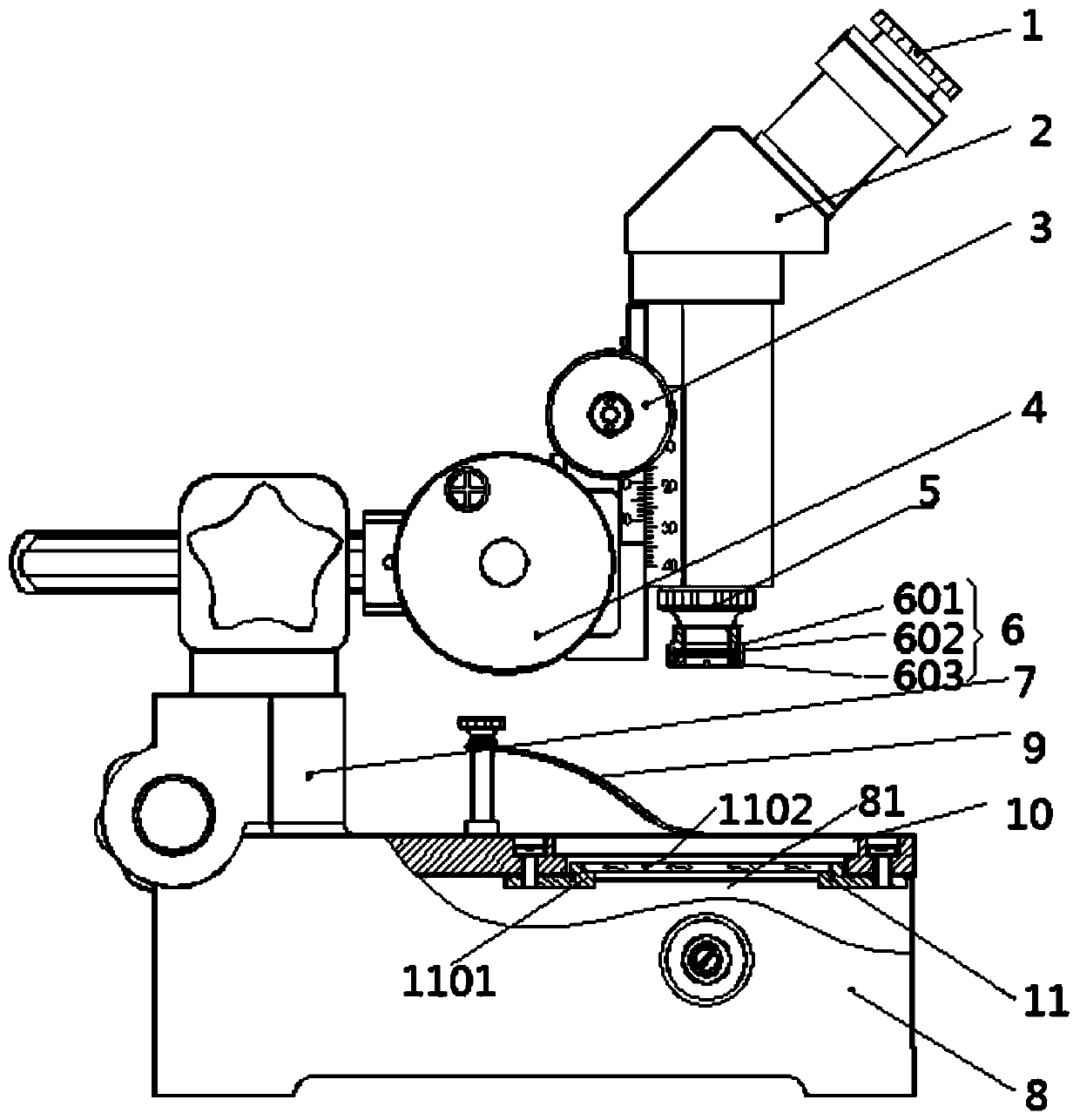
Polarized light reading microscope
The invention discloses a polarized light reading microscope. The microscope comprises an eyepiece, a lens cone, a lens cone movement adjusting mechanism, an objective lens, a base, a tabletting clamp, a working table plate and a supporting column group for connecting the base and the lens cone movement adjusting mechanism, wherein a light source facing the lens cone is arranged in the base, a polarizer detachably connected with the base is arranged above the light source, and an analyzer matched with the polarizer is sleeved on the periphery of the objective lens. The polarized light readingmicroscope can be used as a common optical microscope and can also be used as a polarized light microscope, multiple purposes are achieved through the one microscope, and the equipment cost and the equipment occupied space are reduced.
Owner:CHANGCHUN YUHENG TIMES OPTOELECTRONICS TECHCO
Polariscope of polarizing microscope for mineral identification
InactiveCN106990050AIncrease the accuracy of microscopyPolarisation-affecting propertiesMicroscopesPolarizerEngineering
The invention discloses a polarizer for a polarizing microscope used for mineral identification, which comprises a base bottom plate, a base support lower polarizer assembly and an upper polarizer assembly, and the base support is vertically arranged on one side of the base base plate , the polarizing microscope is installed on the base plate through a fixing device, the lower polarizing assembly is installed at the middle and lower part of the base support, and the upper polarizing assembly is installed at the upper part of the base support. The automatic polarizer of the polarizing microscope of the present invention realizes the automatic operation of the orthogonal polarized light microscope inspection and the single polarized light microscope inspection through the cooperation of the upper polarizer component and the lower polarizer component, and can perform precise measurement at the same time to increase the accuracy of the microscope inspection.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Visual observation system and measurement method of microcrystalline silicon thin film growth process
ActiveCN104122209BRealize continuous dynamic detectionSimple structurePolarisation-affecting propertiesUsing optical meansBeam splittingImage resolution
The invention discloses a visual observing system for observing growth design of a microcrystalline silicon film in real time and a measurement method, which effectively improve the defect that a traditional polarization microscope is relatively low in resolution in an observing process. The visual observing system for the growth process of the microcrystalline silicon film comprises a light source, a pinhole, a polarizer, a 1 / 4 wave plate, a convergent lens, a beam splitting prism, a vertical objective lens, a sample, an objective table, a polarization analyzer, a CCD camera and a computer. The visual observing system has the beneficial effects that a scanning problem in a traditional film thickness detection method is effectively improved, the continuous dynamic detection of the film is realized, the detection efficiency and precision are improved, and the resolution is high; besides, the observing system disclosed by the invention is simple in structure, and the method is simple, convenient and feasible and is convenient to popularize.
Owner:上海裕诗实业有限公司
An Intuitive Detection Method Based on Polarized Light Microscopy for Adsorbed Lipids on Montmorillonite
ActiveCN105203463BQualitative and semi-quantitative characterization of adsorptionPolarisation-affecting propertiesSmear sampleLipid formation
The invention relates to an intuitive detection method based on polarized light microscope observation of montmorillonite adsorbed lipids. First, montmorillonite is mixed with high-fat food or feed, and then the sample is made into a smear, and the neutral lipid dye oil Red 0 was used to stain the smear, and the prepared smear was detected under a polarized light microscope. Observe the adsorption properties of montmorillonite to lipids in high-fat food. The invention is a physical detection method, which can directly observe the adsorption of montmorillonite to lipid, and is simple in operation, intuitive and convenient.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
High precision microscopic fatigue tester
InactiveCN101441154BCompact and lightweightEasy to operateStrength propertiesHuman–machine interfaceData acquisition
The invention discloses a high-precision micro fatigue testing machine which comprises a test bed system, a servo motor control system and a machine visual system, wherein the servo motor control system is connected with a servo motor driver through a multifunctional data acquisition card, while the servo motor driver is connected with a servo motor which is connected with a speed reducer, and the speed reducer is connected with a leading screw in the test bed system, the leading screw is connected with a clamp through a sliding block, the sample in the clamp is connected with a polarizing microscope connecting with a vidicon which is used for monitoring display on the man-machine interface through an image acquisition card, the size of the micro-crack is measured by image processing software. The invention has the advantages of compact structure, simple operation, easy maintenance, high efficiency and energy saving.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Polarized light microscopy-X-ray diffraction method for qualitative detection of asbestos in electronic products
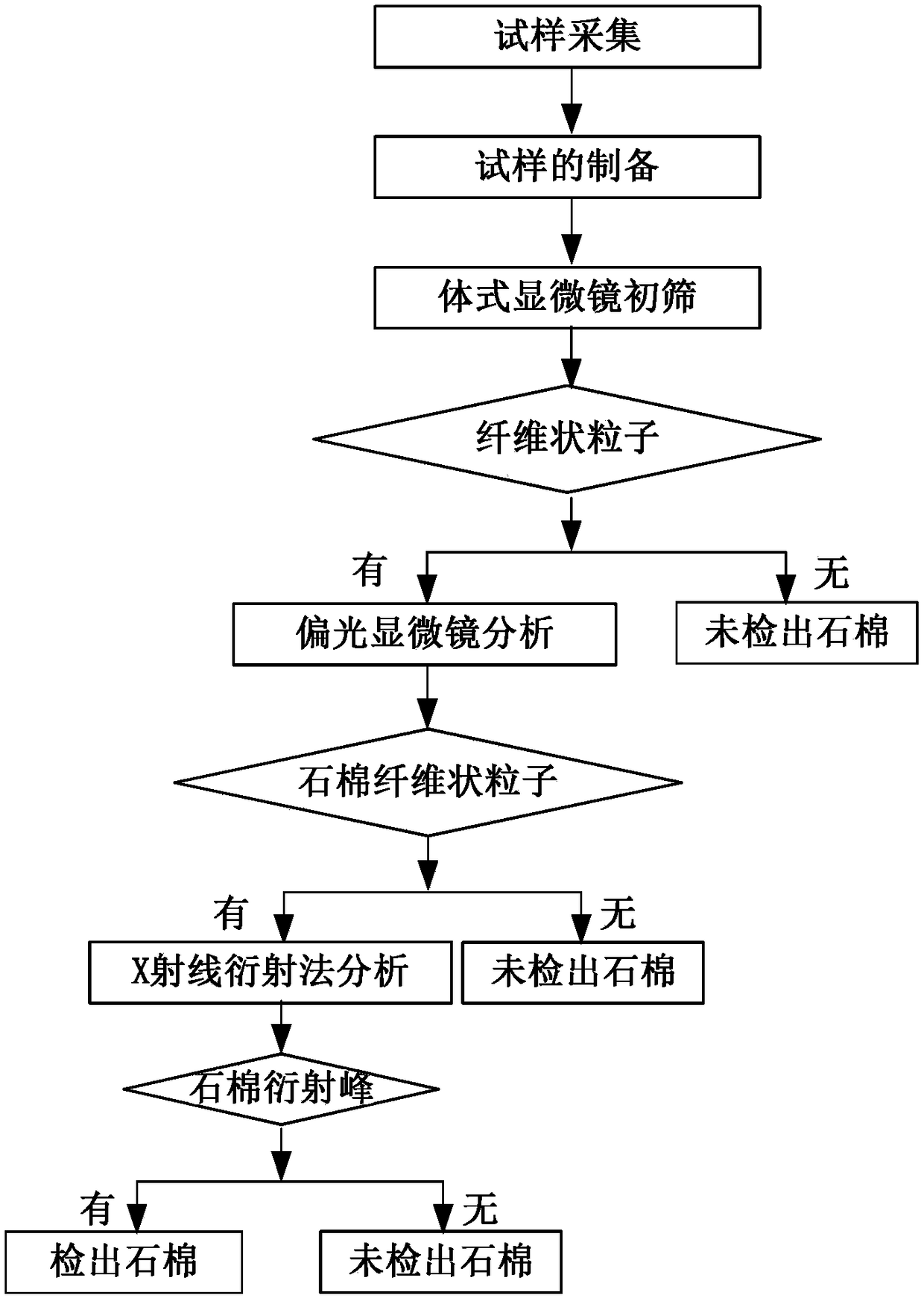
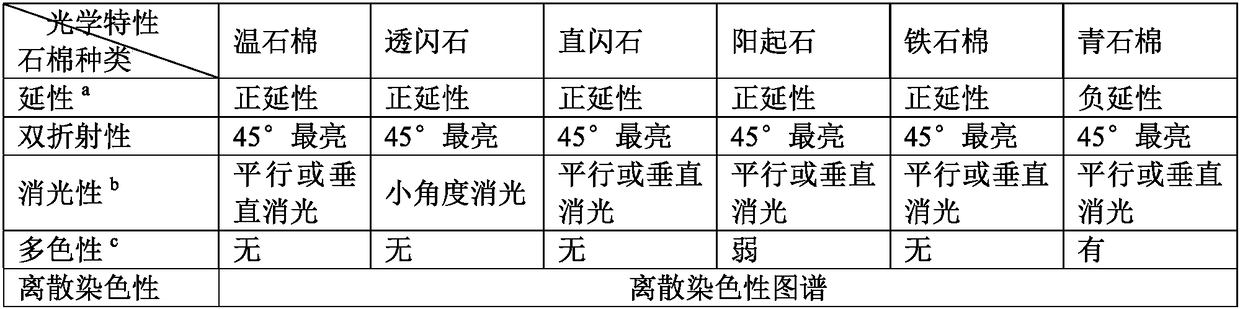
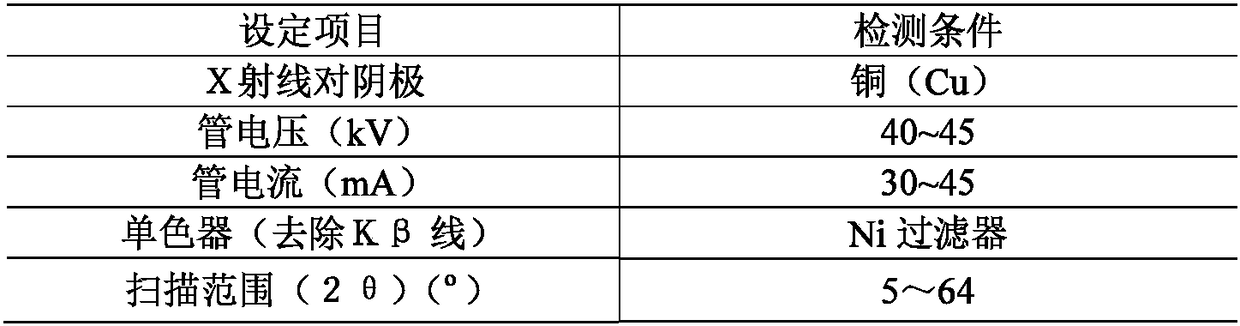
InactiveCN108445028AAvoid harmReduce riskMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by optical meansSoft x rayOptical property
The invention relates to a polarized light microscopy-X-ray diffraction method for qualitative detection of asbestos in electronic products. The method combines X-ray diffraction and polarized light microscopy observation. By means of observation of a polarized light microscopy, the optical properties of a sample in oil with different refractive indexes are considered, and the asbestos type is preliminarily identified; compared with the separately used X-ray diffraction method, the polarized light microscopy-X-ray diffraction method enables diffraction observation to be targeted, and is accurate in results and good in reproducibility. The method can be used for accurately identifying the trace amount of asbestos contained in a to-be-tested sample of an electronic product, is suitable for the inspection of the asbestos in the various electronic products, and can effectively avoid asbestos hazard and trade risks of the electronic products.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
A staining method for observing collagen fibers by polarized light microscope
ActiveCN107063811BImprove adsorption capacityClear colorPreparing sample for investigationOphthalmologyTissue fibrosis
Owner:GUANGZHOU WOMEN AND CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENTER
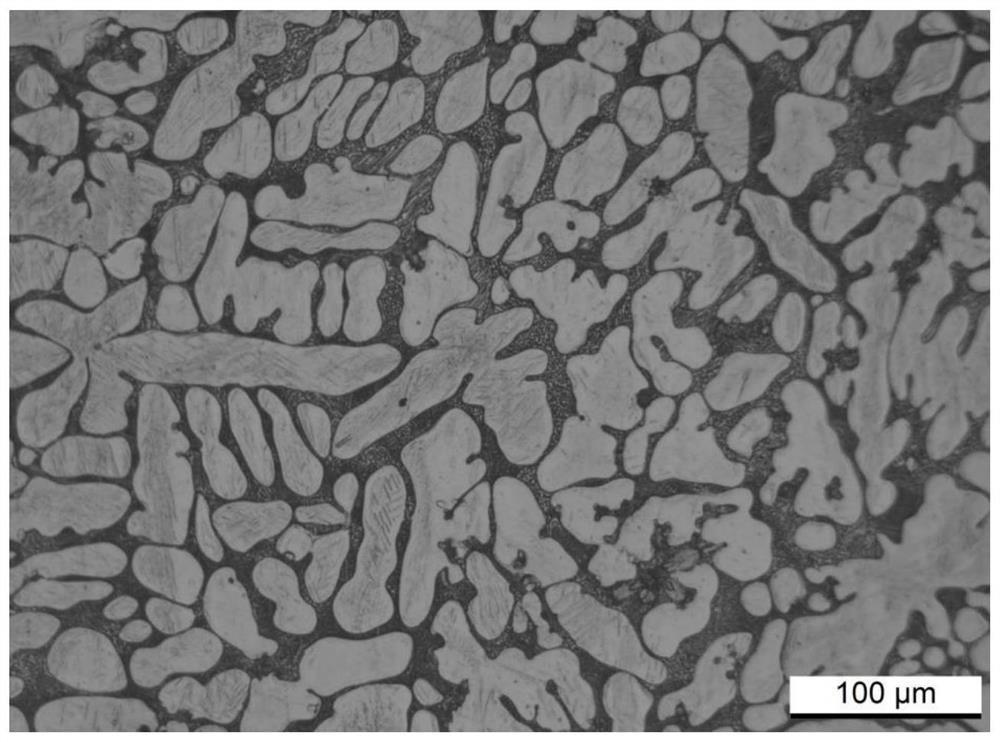
Al-free medical zinc-based alloy dendrite corrosion reagent and preparation method and use method thereof
ActiveCN113933136AReduce over erosionAvoid churnInvestigating crystalsPreparing sample for investigationZinc alloysZinc based alloy
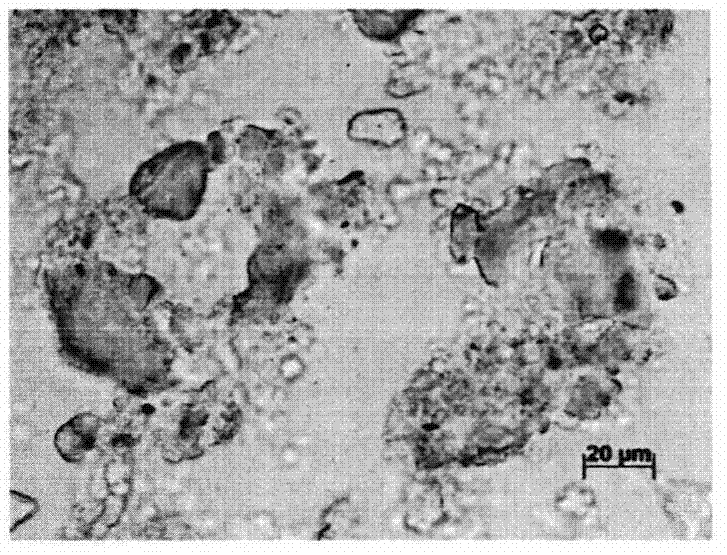
The invention provides an Al-free medical zinc-based alloy dendrite corrosion reagent, and a preparation method and a use method thereof, and relates to the technical field of metallographic analysis of as-cast zinc alloys. The Al-free medical zinc alloy dendrite corrosion reagent is prepared from 3.5-4.5 g of citric acid, 2-3 ml of glacial acetic acid, 4.4-5 g of picric acid, 40-45 ml of ethanol and 50-60 ml of deionized water. Before corrosion, a sample is ground by 1000 #, 2000 #, 3000 # and 5000 # abrasive paper in sequence, and then chemical polishing is carried out by using a nitric acid methanol solution with a specific proportion. The corrosion reagent is dropped on the surface of a zinc alloy in an inclined mode, and when the corrosion agent on the surface of the alloy is turned into reddish brown from light yellow, the zinc alloy is immediately immersed in an ethanol / hydrochloric acid mixed solution for ultrasonic cleaning and air-dried by cold air for later use. A polarized light microscope is adopted to inspect the refined dendritic structure of the alloy. The Al-free medical zinc alloy dendrite corrosion reagent has the advantages of good stability and simple formula, can obtain high-quality contrast in the specific use process, and can finish effective distinguishing of refined dendritic structures and microstructures.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Fiber comparison sheet for court science polarized light microscope inspection and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113533329AMeet the needs of inspection and identificationPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringFiber type
The invention discloses a fiber comparison sheet for court science polarized light microscope inspection and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, bonding a plurality of fibers of known materials on a glass slide to form a net shape; S2, covering a cover glass on the glass slide, drying, and marking a fiber type at one end of the glass slide; wherein the length of the fiber is 1-2cm; separating the fibers from a textile or fiber sample of known material using scissors, tweezers, and separation needles. The polarized light inspection of the fibers is mainly used for identifying and distinguishing the types by observing the interference characteristics of different fibers, and the requirement on practical experience is very high. The conditions that characteristics are difficult to confirm and the like often exist only through inspection of a single inspection material or sample, and different types of fibers and fibers of the same type, different manufacturers and different processes can be quickly, effectively and accurately identified and distinguished by comparing the fiber comparison sheet with a known result with the inspection material or sample.
Owner:INST OF FORENSIC SCI OF MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY
Microscopic shooting method for joint development of single-refraction plant tissue and double-refraction plant tissue
PendingCN112596222AImprove the efficiency of microscopic identificationResolve clarityMicroscopesMicroscopic imageDigital imaging
The invention relates to the field of polarized light detection, in particular to a microscopic shooting method for the joint development of a single-refraction plant tissue and a double-refraction plant tissue. The method comprises the following steps: (1) taking a to-be-observed part of a plant tissue, and preparing a plant tissue slide according to a microscopic slide preparation method under four microscopic identification methods (general rule 2001) of Chinese Pharmacopoeia in edition 2020; (2) taking the slide in the step (1), placing the slide under a polarized light microscope, and adjusting a basic imaging mechanism to be in single-refraction and double-refraction tissue structure common imaging mode; and (3) shooting an image by adopting a large-image splicing technology and a real-time depth-of-field extension imaging technology of a digital imaging system. According to the method, the defects that partial tissue structure characteristic information of a single-refraction microscopic image is lost under the traditional orthogonal polarized light condition, the microscopic image cannot quickly and accurately position a double-refraction microscopic characteristic marker under the normal light condition, and the definition and the integrity of the image are difficult to consider at the same time during microscopic shooting imaging are overcome.
Owner:崔亚君
Method for hair analysis by polarized light
ActiveUS20200393366A1Improve analytical precisionImprove accuracyPolarisation-affecting propertiesPreparing sample for investigationAnalyteTurpentine
A method of hair analysis based on microscope pictures of the hair in polarized light includes a hair conditioning phase performed in a container made of polyethylene or a polymer being in a position lower than polyethylene in the triboelectric series; this is followed by a hair testing phase in which polarized light microscope images of the hair, contacted with a turpentine oil, are taken and further processed using unmixing to obtain information on the amount of analytes present in the hair. Advantageously the present method shows high accuracy even in presence of accidental movements applied to the microscope / sample to be analyzed, such as possibly occurring during daily laboratory practice. Also advantageously, the high accuracy is maintained when different operators are involved in the procedure, being thus substantially unaffected by different ways of manipulating / preparing / photographing the hair sample.
Owner:I LOVE MY BODY RES SRL
Method for displaying temperature elevation of ferromagnetic substance with simulated blood vessel bed
ActiveCN100337100CSimple methodEasy to observeThermometers using physical/chemical changesThermometer applicationsPolyethylene glycolBlood vessel
This invention relates to analogue blood bed display iron magnetic substance heating method, which comprises the following steps: quickly cooling it down and cracking it into parts; re-piecing the cracked blood cover slices on the glass slides with gaps between; dripping melted poly glycol between blood cover slice and glass slice; deleting the poly glycol in gaps after the poly glycol solidified; filling the dried iron magnetic power to the above gaps to get the analogue blood bed; putting the above analogue blood bed in the alternating magnetic field and then putting the analogue blood bed under bias microscopes for observation.
Owner:CHINA JAPAN FRIENDSHIP HOSPITAL
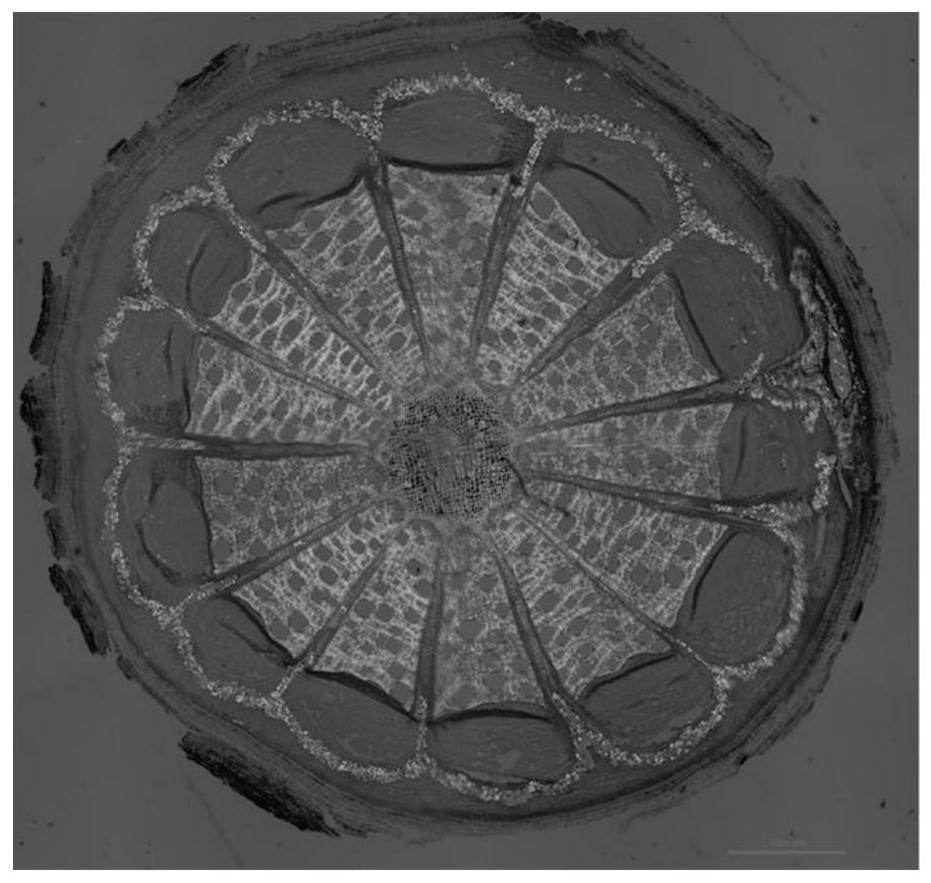
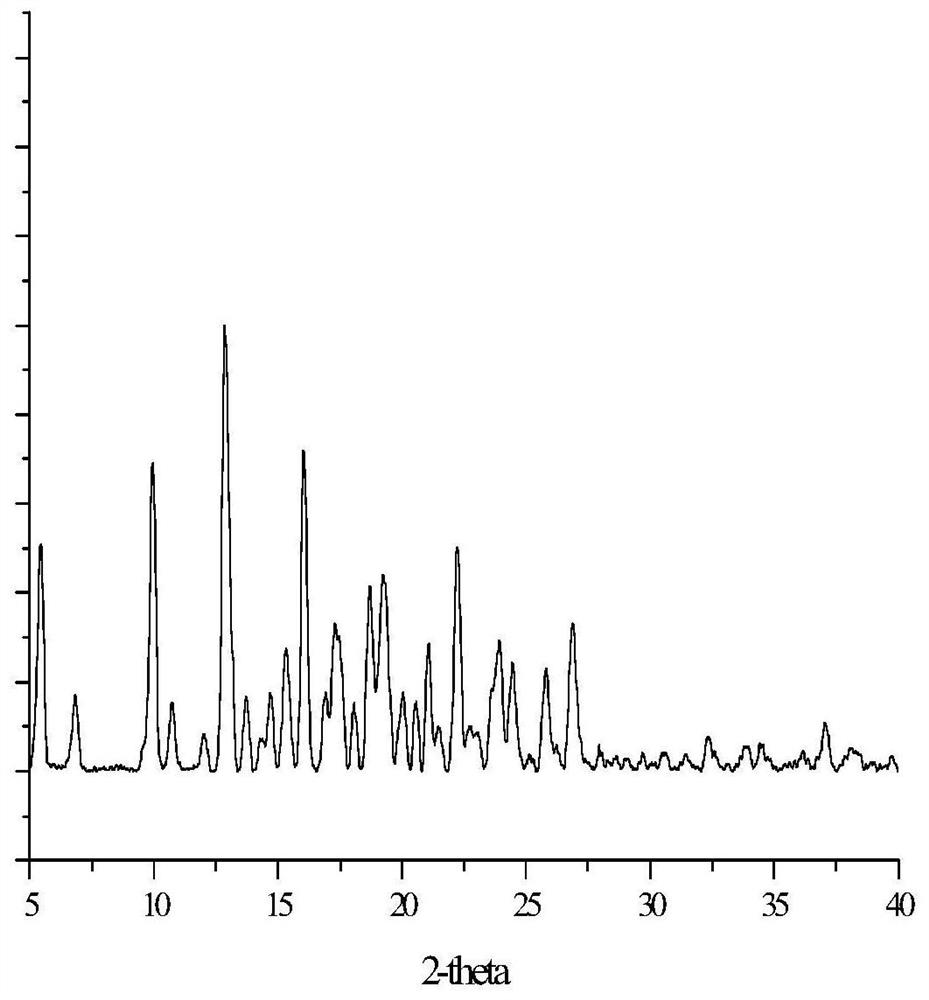
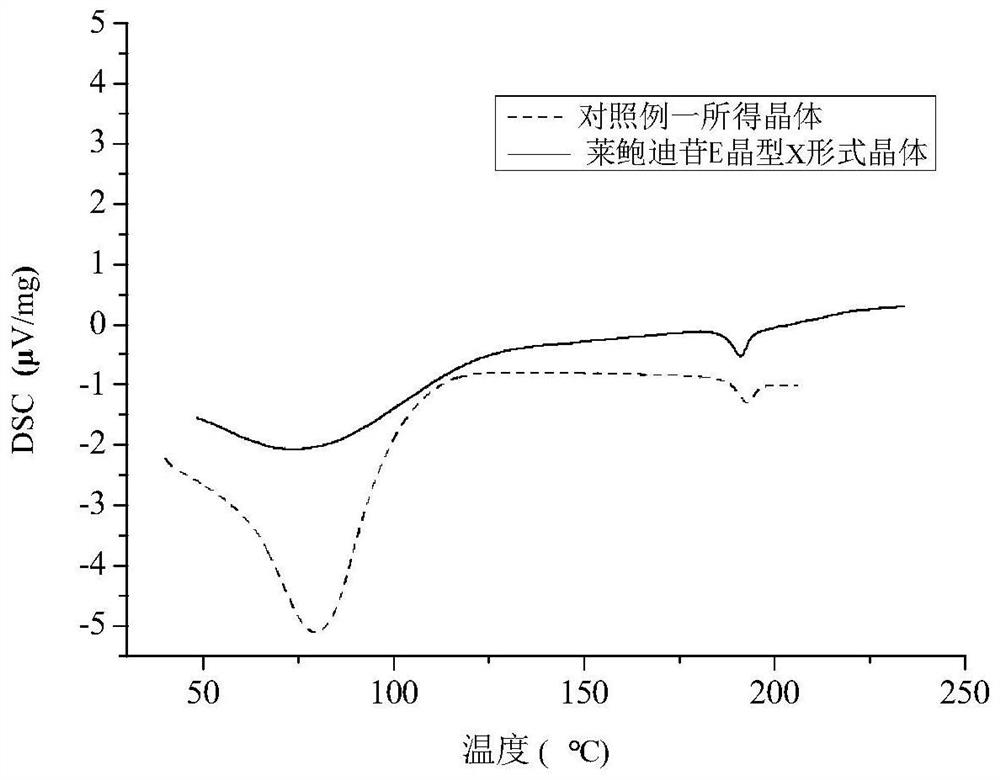
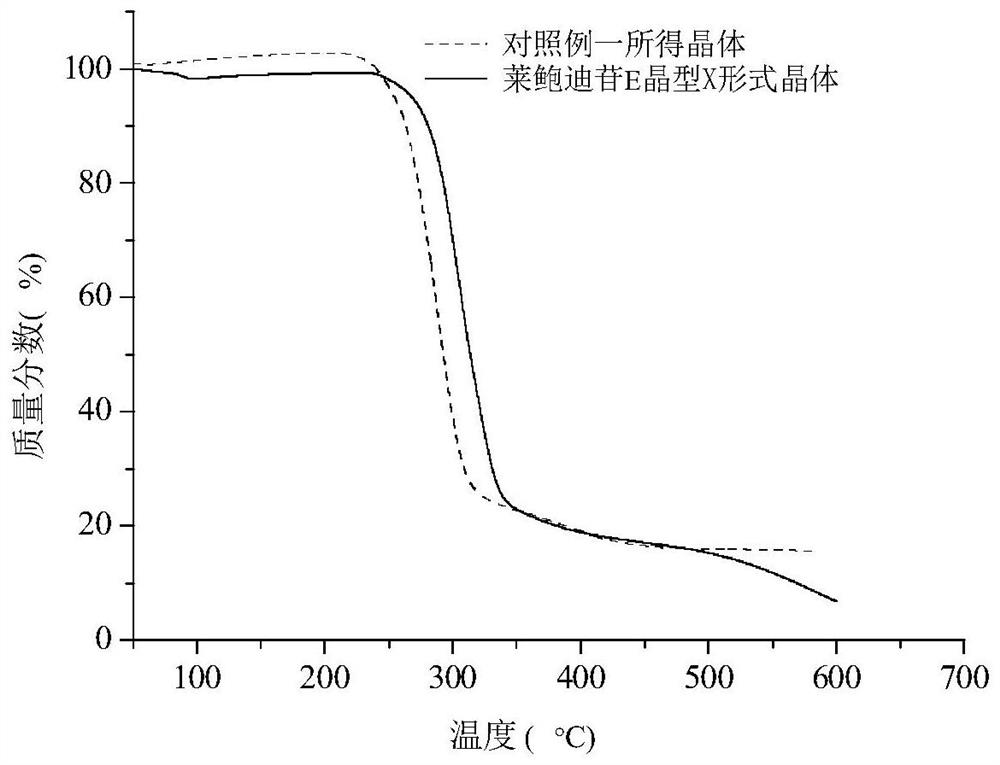
A crystal form x of rebaudioside e, its preparation method and use
ActiveCN111423480BImprove solubilityEasy to separateSugar derivativesOrganic chemistry methodsSolubilityAlcohol
The invention discloses a crystal form X of rebaudioside E, a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of chemical pharmacy. The technology provided by the present invention can. The present invention utilizes low-carbon alcohol water as a solvent, utilizes rubus glycoside to solubilize, and crystallizes to obtain rebaudioside E crystals whose crystal form is X, and overcomes the low solubility of rebaudioside E in alcohol-water solvents, so that Difficulty in obtaining crystals in large quantities with high efficiency. Using technical means such as XRD, DSC, TGA and polarized light microscopy to characterize the rebaudioside E crystal with crystal form X, it was found that the rebaudioside E crystal with crystal form X had high crystallinity, stable Good sex and other advantages. The preparation method involved in the invention is simple, easy to operate, good in reproducibility, and can stably obtain target crystals in batches.
Owner:DONGTAI HIRYE BIOTECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com