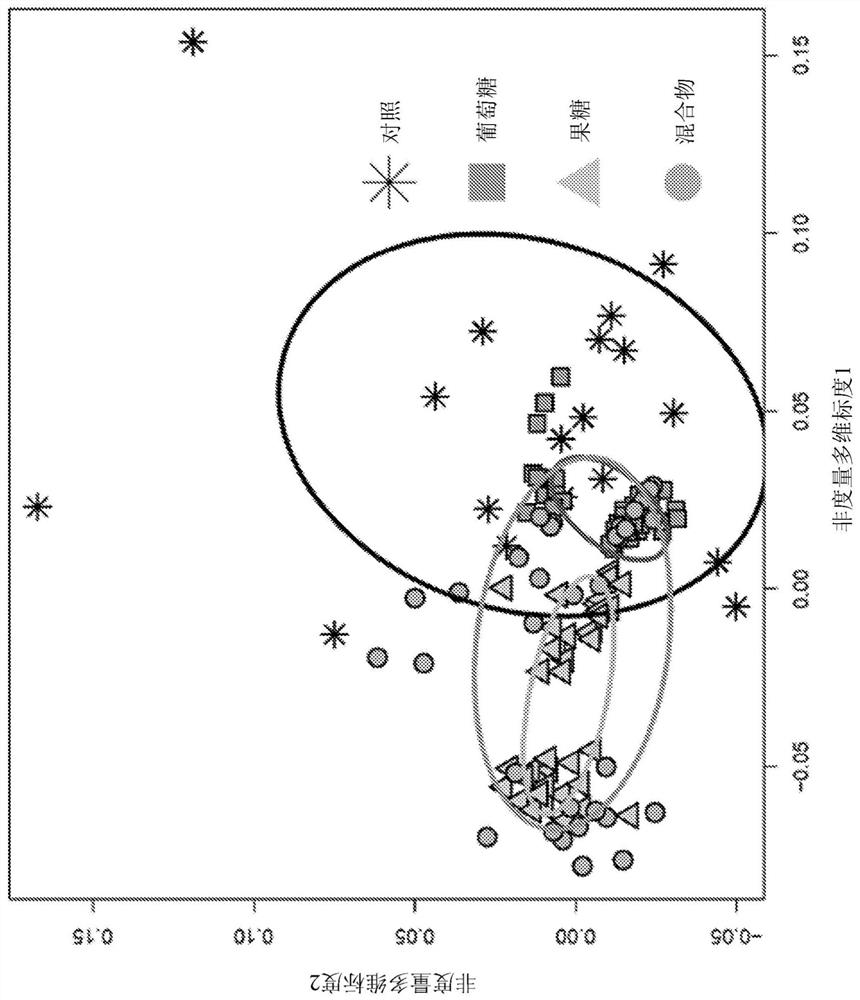
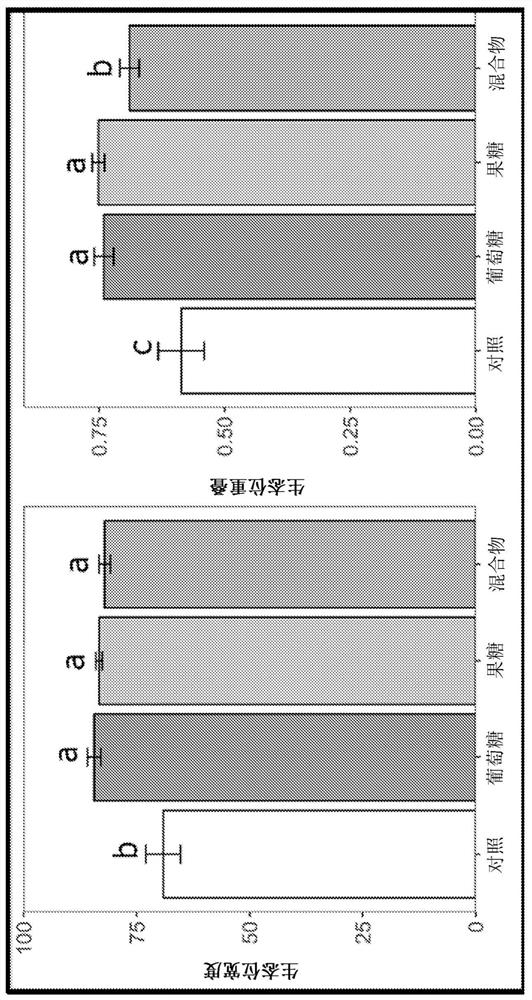
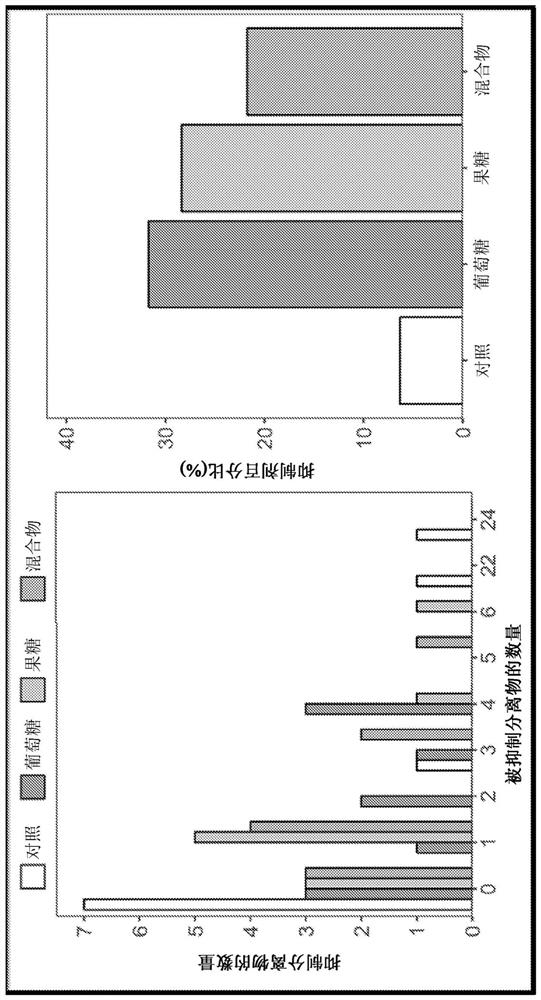
Platform for developing soil-borne plant pathogen inhibiting microbial consortia
A technology for plant pathogens and microbial flora, applied in microorganism-based methods, microbial determination/inspection, microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as low protection ability and single-strain inoculants cannot provide disease inhibition levels.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0387] Example 1: Soil-borne Plant Pathogen Inhibitory Microflora (SPPIMC) Development Platform
[0388] The SPPIMC platform enables the identification of soil microorganisms with phytopathogen inhibitory activity. In addition, the platform generates multi-strain compositions (interchangeably referred to herein as "flora") comprising two or more phytopathogen-inhibiting microorganisms that are comparable to individual microorganisms Possesses superior properties (eg, the ability to inhibit a wider range of plant pathogens and to utilize a wider range of nutrients). The microbial flora developed using this platform and its excellent properties are described in Example 9.
[0389] Figure 14 A flow chart of the Soil-borne Plant Pathogen Suppressed Microbiota (SPPIMC) development platform is shown. The first step of the platform involves the creation of enriched microbial libraries. Next, the pathogen inhibitory activity of each isolate was determined. Subsequently, a multid...
example 2
[0390] Example 2: Creation of a bacterial library exhibiting antimicrobial activity against plant pathogens
[0391] Over a thousand isolates of Streptomyces, Bacillus, Fusarium and Pseudomonas were collected from agricultural soils, forest soils, North American temperate grassland soils, wetland soils, savannah soils and peat soils across all continents except Asia.
[0392] Bacteria are isolated using standard nutrient media (including water agar, oat agar, sodium caseinate agar, etc.). Habitat selection should both capture a broad range of ecological conditions and target the following environments: i) suppressor phenotypes may be enriched (Kinkel, L.L.), Schlatter, D.S. (Schlatter, D.S. ), Baker, M.B. (Bakker, M.B.) and Arenz, B. (Arenz, B.) (2012), Streptomyces competition and coevolution in relation to disease suppression, Research in Microbiology: dx.doi.org / 10.1016 / j.resmic.2012.07.005); or ii) long-term agricultural management was implemented.
[0393] Microbial iso...
example 3
[0394] Example 3: Characterization of isolates of a bacterial library of plant pathogen antimicrobial activity ("Determination of Pathogen Inhibitory Activity").
[0395] like Figure 14 Each microorganism in the library was subjected to a node involving "Multidimensional Ecological Function Balance (MEFB) node analysis", ie "Determining Pathogen Inhibitory Activity" as described below, as shown in .
[0396] method:
[0397] Fungal pathogen working stock isolates were grown on a benchtop (22°C-25°C) on 0.5x potato dextrose agar (15ml) for two days (Rhizoctonia and Sclerotinia) or five days (Grain Fusarium and Fusarium oxysporum). Fusarium solani cultures were grown on SMDA (Soy Milk Dextrose Agar) in the dark at (22°C-25°C) for approximately 20 days. Pythium was grown on a benchtop (22°C-25°C) on V8 agar for two days. Phytophthora were grown on V8 agar for two days on a benchtop (22°C-25°C). Pathogens tested included those of scab and Verticillium wilt (V. dahliae or Ver...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com