Frequency domain equalization method based on generalized approximated message passing
An approximate message and frequency domain equalization technology, applied in baseband systems, transmission systems, digital transmission systems, etc., can solve problems such as BER performance loss, difficult convergence of receiving demodulation algorithms, and large condition numbers of two-dimensional interference matrices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0070] The present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and examples.
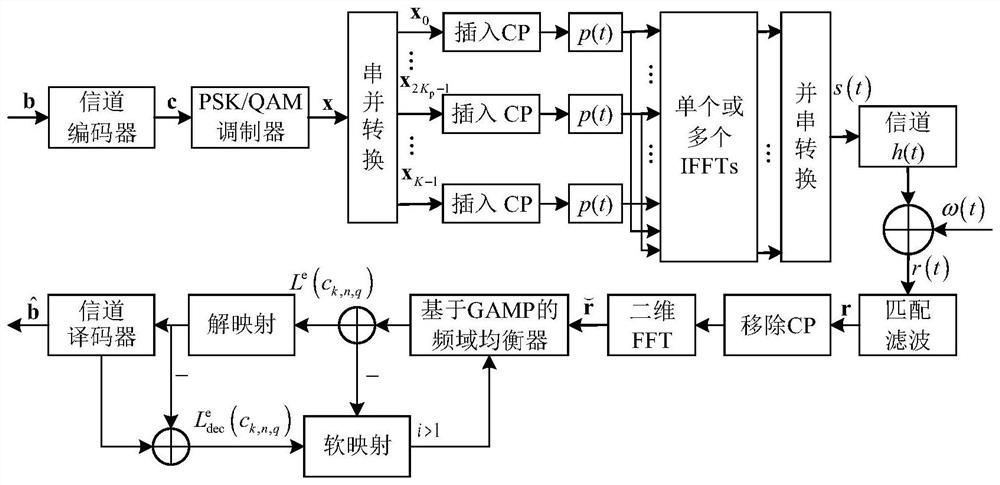
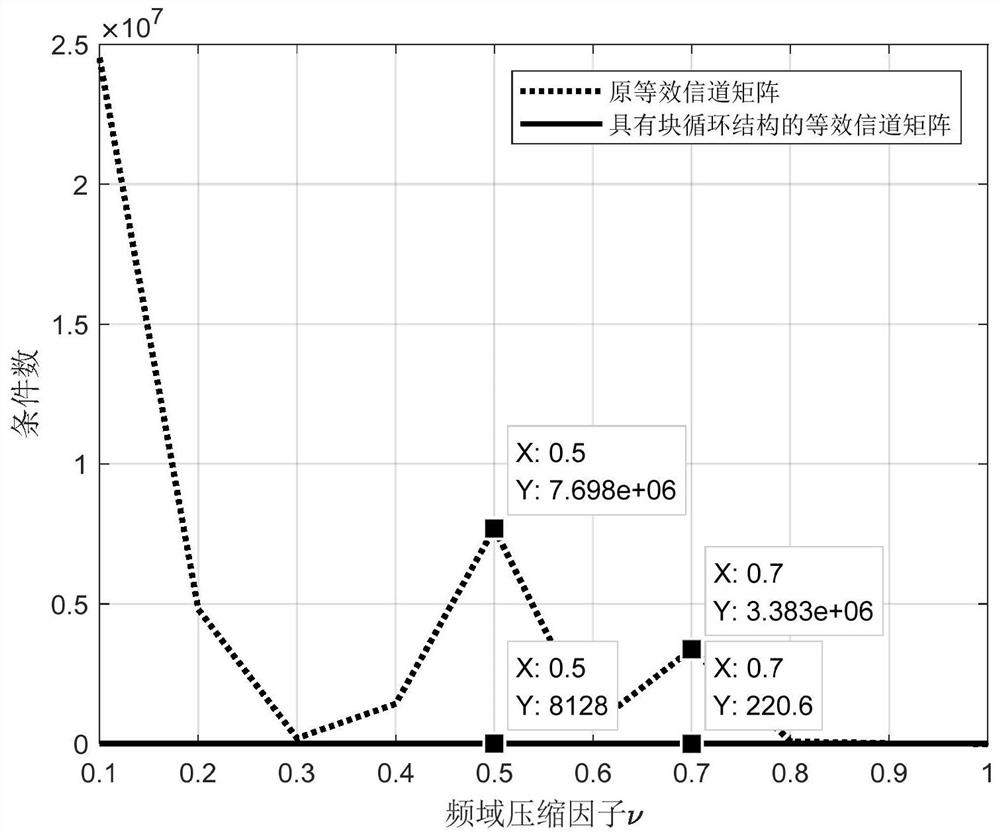
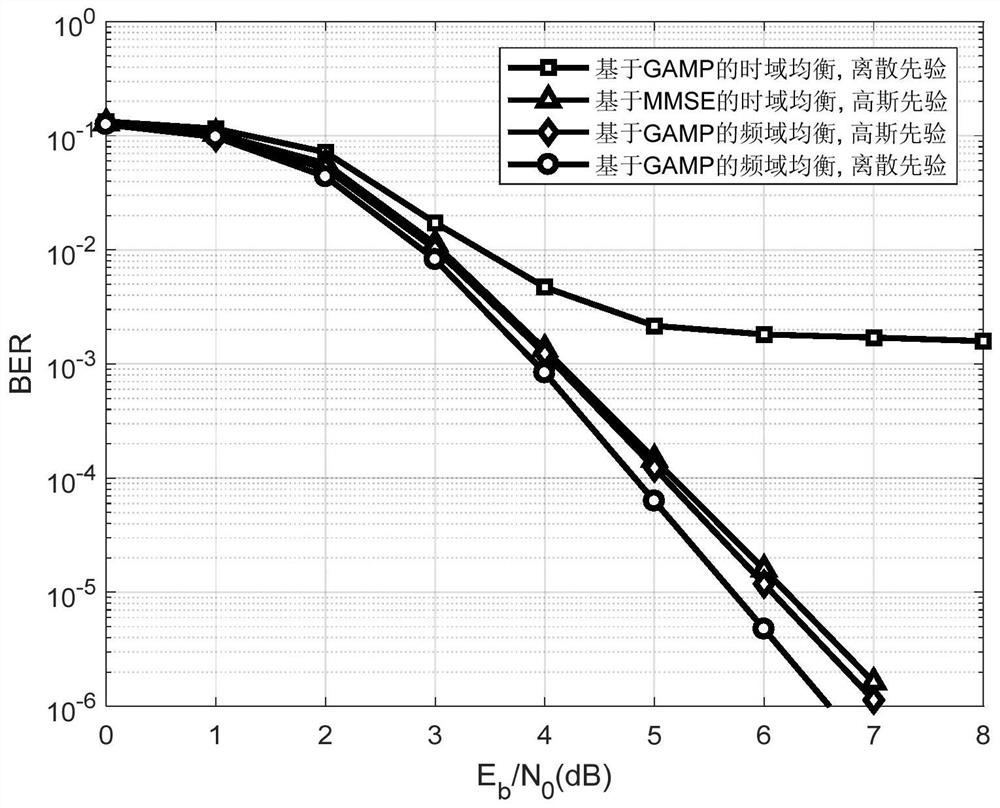
[0071]The present invention proposes a frequency domain equalization method based on generalized approximate message passing. First, under the frequency-selective fading channel, by constructing a block cycle equivalent channel matrix (including two-dimensional interference matrix and channel matrix) with cyclic blocks, it can effectively reduce The condition number of the equivalent channel matrix in the MFTN system, so as to alleviate the ill-conditioned problem on the performance of the receiving demodulation algorithm. Then, according to the singular value decomposition characteristics of the block circulant matrix, the received signal model in frequency domain is constructed by two-dimensional inverse Fourier transform (IFFT), and the time domain color noise with off-diagonal covariance matrix is transformed into The frequency-domain white noise of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com