Indoor sand tank experimental device and experimental method for simulating groundwater exploitation near a river
The technology of a simulation device and an experimental device, which is applied in related research fields, can solve the problems of consuming a lot of manpower and material resources, unclear changes in biogeochemical processes, and threatening the safety of groundwater water quality, and achieve labor cost savings, high reliability, and reliable experimental processes. repeat effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
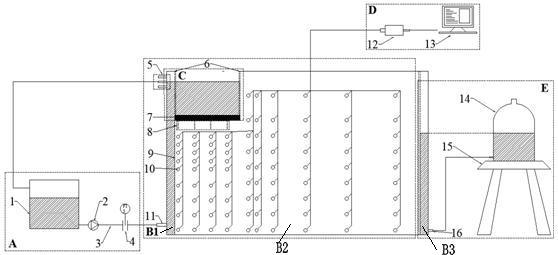
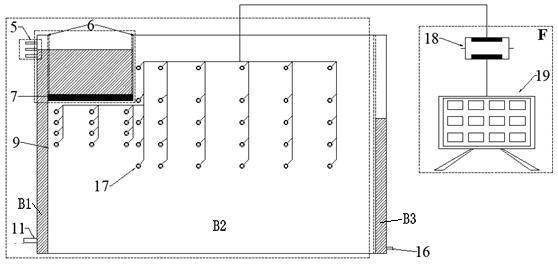
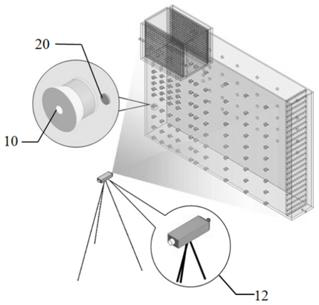
[0036] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 3 As shown, an indoor sand tank experimental device for simulating groundwater exploitation near a river, including water supply system A, sand tank B, river simulation device C, dissolved oxygen monitoring module D, drainage system E and pressure monitoring module F:
[0037] The water supply system A is composed of a liquid supply tank 1, a water pump 2, several conduits 3 and a flowmeter 4, wherein the liquid supply tank 1 is used to store the solution required for the experiment, and the conduit 3 is connected to the water pump 2 and the flowmeter 4 in sequence, and then connected to the side of the sand tank The water inlet holes 11 of the wall are connected, the water pump 2 is used to control the infiltration rate, and the flow meter 4 is used to monitor the infiltration flow through the river simulation device during the experiment;
[0038] The sand tank B is placed vertically, and the interior is divided into left sub-chamber B1, mi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com