Method of obtaining lipids from microbial cell composition by enzyme and ph shock
A microbial cell and composition technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, microorganism dissolution, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve a large number of cost and time problems, reduce monetary costs, reduce processing time, and reduce variability Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0169] Embodiment 1. Pilot test (AEX-O-1150-tank B)
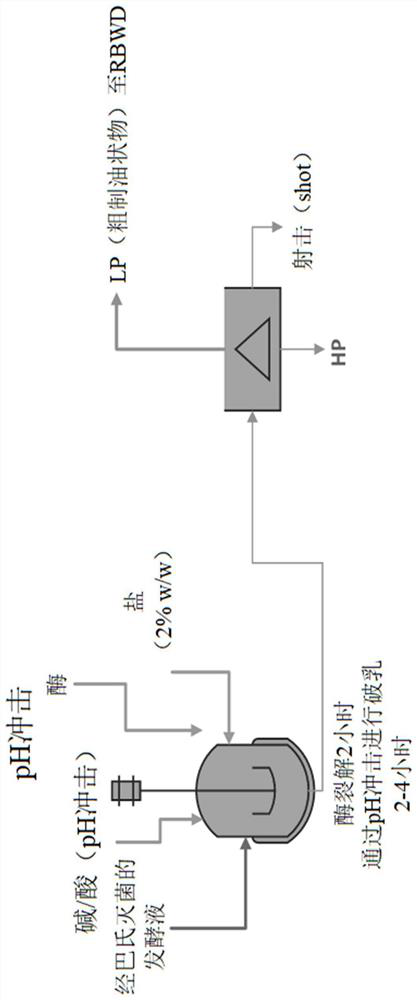
[0170] 524.6 kg of fermentation broth containing about 10% w / w of Schizochytrium microbial cells was heated to 60°C and the pH was adjusted by adding 50% NaOH (available from Colonial Chemicals Solutions, 916 W Lathrop Ave, Savannah, GA 31415). Adjust to 8.3. The amount of 0.3% based on the weight of the culture medium 2.4 FG (available from Novozymes, Franklinton, N.C.) was added to the broth for enzymatic cleavage, and after 30 minutes the pH drifted to 6.9 and readjusted to 8.1. After 2 hours of enzymatic cleavage, the demulsification process was started by raising the pH to 10.5 and the temperature to 90°C. When the temperature reached 90°C, the pH drifted to 8.0 and readjusted to 10.2. After breaking the emulsion for 2 hours, 10.49 kg of NaCl salt were added. Thirty minutes after salt addition, the pH was lowered to 5.4 by adding 50% citric acid (prepared in house from solid citric acid (available from Tate & Lyle...
Embodiment 2
[0171] Embodiment 2. Pilot test (AEX-O-1150-tank C)
[0172] 525.2 kg of the fermented liquid containing about 10% w / w of the Schizochytrium microbial cells (the fermented liquid of the same batch as tank B in Example 1) was heated to 60° C., and added 50% NaOH (can be Obtained from Colonial Chemicals Solutions, 916W Lathrop Ave, Savannah, GA 31415) the pH was adjusted to 7.9. The amount of 0.3% based on the weight of the culture medium 2.4 FG (available from Novozymes, Franklinton, N.C.) was added to the culture medium for enzymatic cleavage. After 30 minutes, the pH drifted to 6.7 and readjusted to 8.1. After 2 hours of enzymatic cleavage, the demulsification process was started by raising the pH to 10.5 and the temperature to 90°C. When the temperature reached 90°C, the pH was readjusted to 10.3. After 1.5 hours of demulsification, 10.5 kg of NaCl salt were added. After 30 minutes of salt addition, the temperature was lowered to 85°C and the pH was lowered to 5.5 by a...
Embodiment 3
[0178] Embodiment 3. pilot test
[0179] 1797.6 kg of fermentation broth containing about 10% w / w of Schizochytrium microbial cells was heated to 60°C and the pH was adjusted by adding 50% NaOH (available from Colonial Chemicals Solutions, 916W Lathrop Ave, Savannah, GA 31415). Adjust to 8.0. The amount of 0.3% based on the weight of the culture medium 2.4 FG (available from Novozymes, Franklinton, N.C.) was added to the medium for enzymatic cleavage for two hours. The pH of the lysed composition was adjusted to 10.5 and heated to 90°C. When the temperature reached 90°C, the pH drifted to 8.8, and the pH was adjusted to 10.1. After 1 hour at 90°C, the temperature was lowered to 82°C and the pH was lowered by adding 50% citric acid (prepared in house from solid citric acid (available from Tate & Lyle, 2200E Eldorado St, Decatur Illinois USA, 62521)). to 5.2 for 30 minutes. The pH was then raised to 10.1 for 40 minutes and the pH was again lowered to 5.4. After 30 minutes ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Reynolds number | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com