Multiplex fluorescent quantitative PCR method for detecting and identifying three food-borne pathogenic bacteria
A food-borne pathogenic bacteria, multiple fluorescence quantitative technology, applied in the field of microbial detection, can solve the problems of long time consumption, low detection sensitivity, uneven detection and identification of pathogenic bacteria and other problems, and achieve good repeatability.
Inactive Publication Date: 2021-11-09
河北省畜牧兽医研究所 +1
View PDF6 Cites 0 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
[0002] The most commonly used detection method for food-borne pathogens is bacterial isolation and culture combined with biochemical identification. Traditional bacterial identification requires three steps: proliferation culture, selective culture and biochemical identification, which is the "gold standard" for the detection of food-borne pathogens "The disadvantage is that it takes a long time, usually takes 5-6 days, and the detection sensitivity is low, and quantitative analysis cannot be performed
With the development and application of molecular biology, real-time fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) has become a powerful research and diagnostic tool. Simple, rapid, sensitive and specific are the four key aspects of qPCR to meet the needs of nucleic acid detection. , and has been applied to the detection of foodborne pathogens, but the effect on the detection and identification of pathogens is uneven
With the continuous emergence of new food-borne pathogens in recent years, there are currently no reports on simultaneous multiplex fluorescent quantitative PCR detection methods for Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella and Listeria monocytogenes. , there is an urgent need to establish a multiplex fluorescent PCR method that can simultaneously detect three food-borne pathogens of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella and Listeria monocytogenes, and use it for food testing
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment
[0031] 1. Materials
[0032] 1.1 Standard strain
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
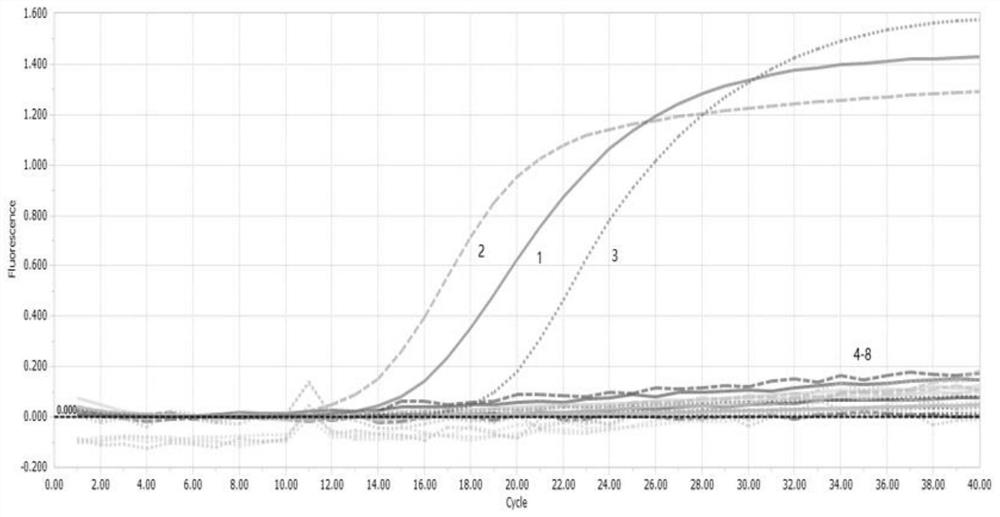
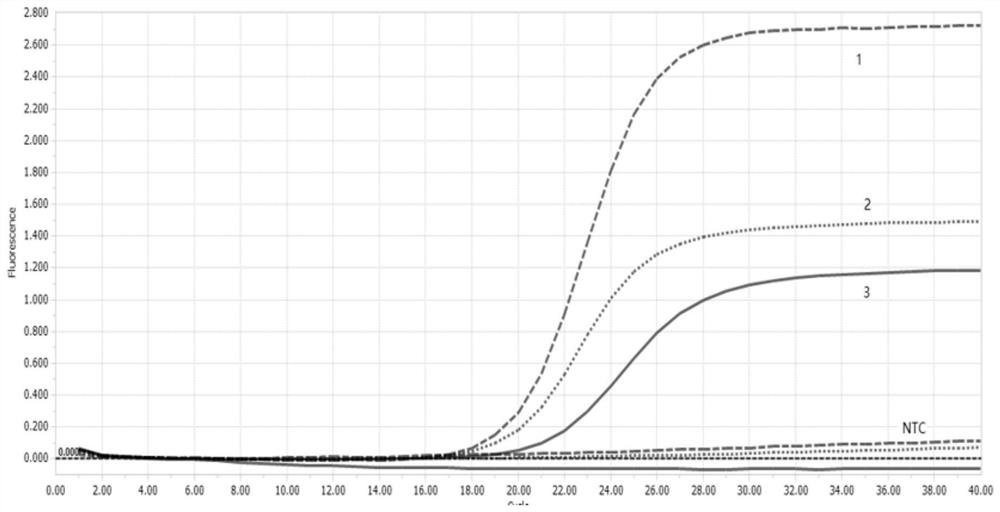
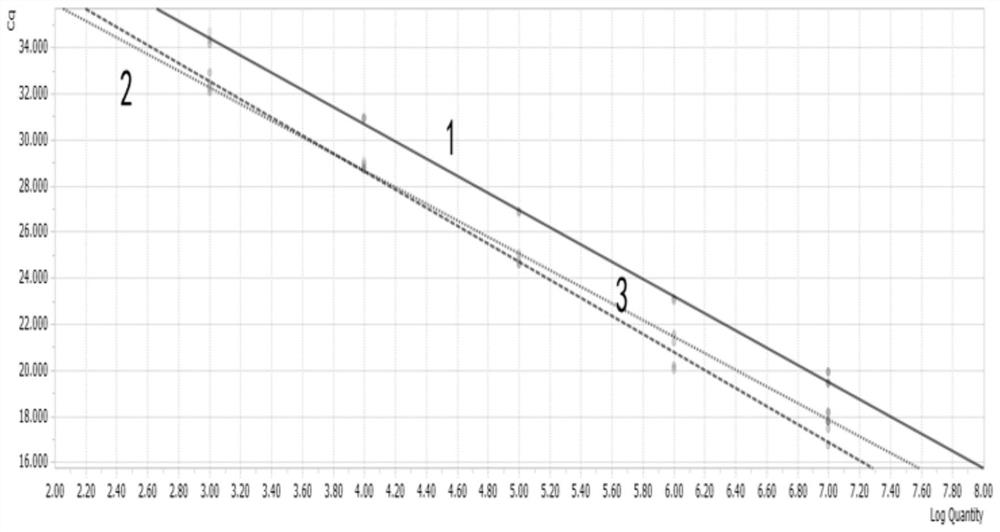
The invention discloses a multiplex fluorescent quantitative PCR method for detecting and identifying three food-borne pathogenic bacteria, and belongs to the technical field of microbial detection. The invention discloses multiplex fluorescent quantitative PCR amplification primers and probes for detecting and identifying three food-borne pathogenic bacteria, wherein the primers and probes comprise the following sequences: a primer pair and a probe for amplifying an escherichia coli O157:H7rfbE gene as shown in SEQ ID NO:1-3; a primer pair and a probe for amplifying a salmonella invA gene as shown in SEQ ID NO:4-6; and a primer pair and a probe for amplifying a listeria monocytogenes hlyA gene as shown in SEQ ID NO: 7-9; and the sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO:1-9 are used together in one detection. The multiplex fluorescent quantitative PCR method disclosed by the invention can provide methods and data support for accurate and rapid detection of three food-borne pathogenic bacteria including escherichia coli O157: H7, salmonella and listeria monocytogenes in food.
Description
technical field [0001] The invention relates to the technical field of microbial detection, in particular to a multiplex fluorescence quantitative PCR method for detecting and identifying three kinds of food-borne pathogenic bacteria. Background technique [0002] The most commonly used detection method for food-borne pathogens is bacterial isolation and culture combined with biochemical identification. Traditional bacterial identification requires three steps: proliferation culture, selective culture and biochemical identification, which is the "gold standard" for the detection of food-borne pathogens "The disadvantage is that it takes a long time, usually 5-6 days, and the detection sensitivity is low, and quantitative analysis cannot be performed. With the development and application of molecular biology, real-time fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) has become a powerful research and diagnostic tool. Simple, rapid, sensitive and specific are the fou...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More Patent Type & Authority Applications(China)
IPC IPC(8): C12Q1/689C12Q1/6851C12Q1/06C12N15/11C12R1/19C12R1/42C12R1/01
CPCC12Q1/689C12Q1/6851C12Q2600/16C12Q2531/113C12Q2563/107C12Q2537/143C12Q2545/113
Inventor 李杰峰张宁杨威赵志强李茜王珏王华健陆安田勇
Owner 河北省畜牧兽医研究所
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com