Method for predicting whether solid solution is formed or not based on atom combination data
A technology for data prediction and solid solution, applied in the direction of chemical property prediction, etc., can solve the problems that thermodynamic methods cannot predict the formation of unknown solid solutions, the problems are complex, and the liquidus cannot be predicted, so as to avoid blindness, low cost, and easy implementation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
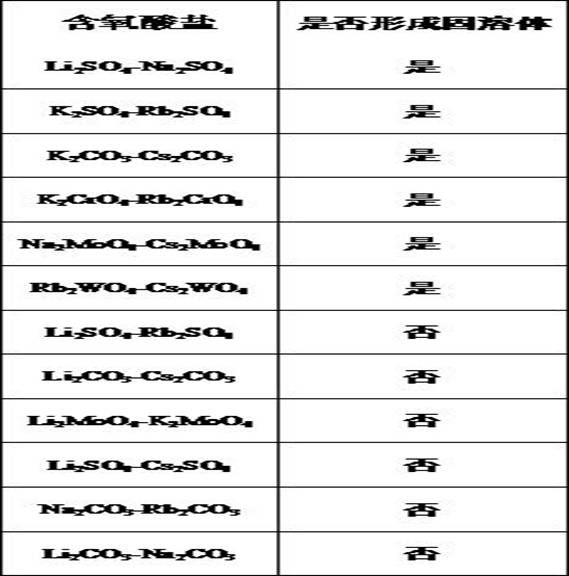
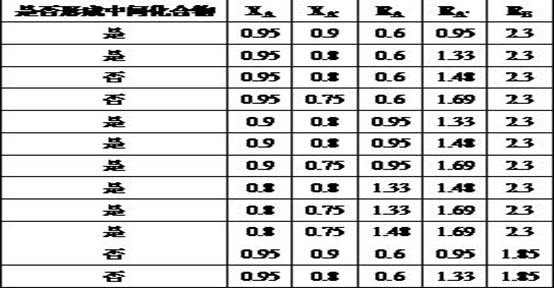
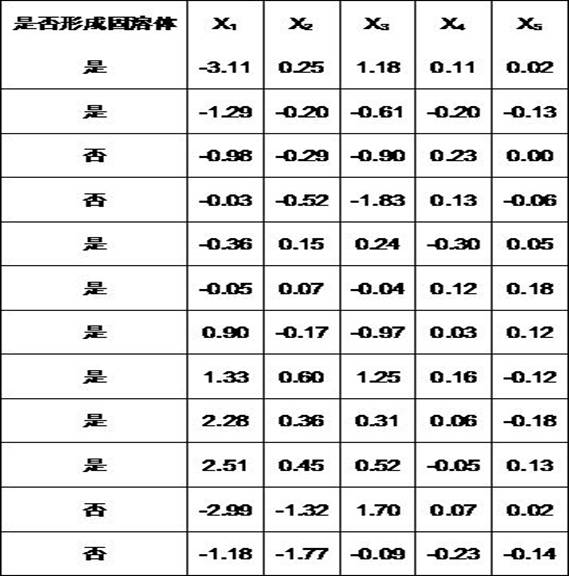
[0035] In this example, the modeling results of whether a solid solution model is established based on the atomic combination data of 39 oxo-acid salt binary phase diagram samples combined with the support vector machine classification algorithm, are shown in Table 4.
[0036] Table 4 Modeling accuracy
[0037]
[0038] It can be seen from Table 4 that in the modeling process, among the 26 samples that can form solid solutions, 23 are accurately discriminated, with an accuracy rate of 88.46%. Among the 13 samples that did not form a solid solution, 12 were discriminated correctly, with an accuracy rate of 92.31%. The overall accuracy is 89.76%. It shows that the accuracy of the solid solution model established based on the support vector machine classification algorithm is relatively high.
Embodiment 2
[0040] For the 39 data, the internal cross-validation results of the leave-one-out method established based on the support vector machine classification algorithm for the formation of solid solution models are shown in Table 5. The leave-one-out method of internal cross-validation means that only one sample is left as the test set at a time, and the other samples are used as the training set. There are a total of 39 samples, which requires 39 training and 39 testing times.
[0041] Table 5 Leave-one-out accuracy
[0042]
[0043] It can be seen from Table 5 that in the leave-one-out internal cross-validation process, among the 26 samples that can form solid solutions, 21 are accurately discriminated, with an accuracy rate of 80.77%. Among the 13 samples that did not form a solid solution, 11 were accurately discriminated, with an accuracy rate of 84.62%, and the overall accuracy rate was 82.51%. It shows that the accuracy of leave-one-out method based on the support vector...
Embodiment 3
[0045] In this example, the established solid solution model is used to predict the three newly collected samples, and the results are shown in Table 6.
[0046] Table 6 Forecast results
[0047]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com