Solenoid straight-through type relay
A straight-through, relay technology, applied in the direction of relays, electromagnetic relays, detailed information of electromagnetic relays, etc., can solve the problems of complex processing of iron core parts 1, large matching reluctance, and easy shaking, etc., to achieve simple and fast assembly process, avoid The effect of turning and strengthening the stability of the connection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
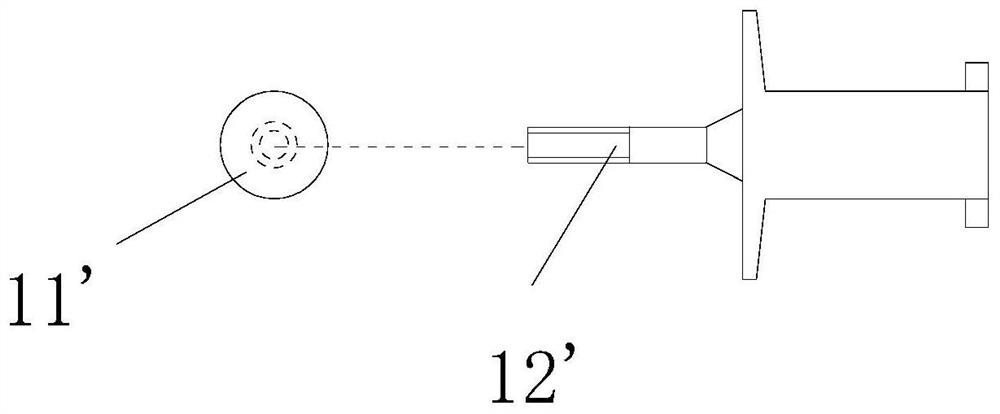
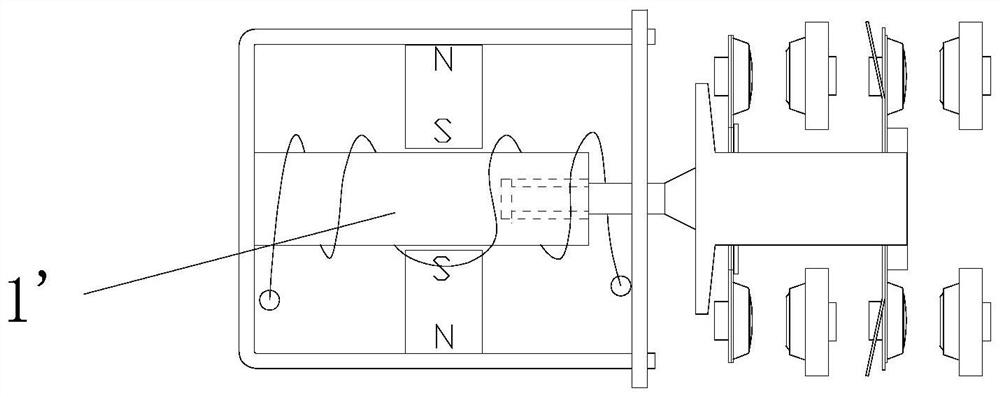
[0079] see Figure 6-17 As shown, a solenoid feed-through relay is provided, comprising: a base 2, a magnetic circuit part 3, a contact part 4 and a push card 12 arranged on the base 2, and the magnetic circuit part 3 controls the contact by pushing the card 12 The contacts of part 4 contact or separate;
[0080] The magnetic circuit component 3 includes a wire frame 31, a yoke and an iron core 11. The wire frame 31 is provided with a through hole in the contact separation direction for pushing one end of the card 12 into. The wire frame 31 is wound with a coil to form a magnetic control circuit. The iron core 11 is connected with the push card 12 to form the iron core part 1 and can move linearly in the wire frame 31, and the iron core part 1 cooperates with the through hole of the wire frame 31 to form a circumferential anti-rotation structure;
[0081] The iron core 11 is in the shape of a sheet, and at least one connection position is provided on one side of the thickness...
Embodiment 2
[0096] Embodiment 2, for the sake of brevity, this embodiment only describes the difference from Embodiment 1:
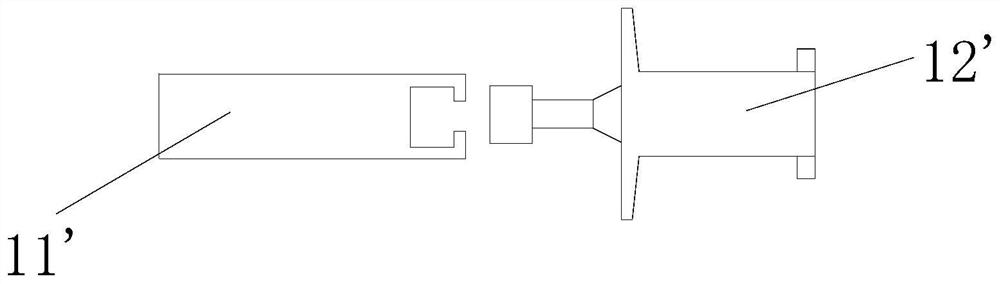
[0097] see Figure 18-19 As shown, the iron core 11 is a sheet-like U-shaped iron core 11 with two convex buds 7 on the inside and two sliding convex buds 10 on the outside, two grooves 8 on one side of the push card 12, There are two protruding buds 7 on the side, the protruding buds 7 on the inner side of the sheet-shaped U-shaped iron core 11 and the groove 8 on the side of the push card 12 form two connection positions to be connected, and then assemble to form the iron core part 1, and the inner part of the wire frame 31 There are sliding grooves 9 on both sides, the sliding convex buds 10 on the outside of the sheet-shaped U-shaped iron core 11 in the iron core part 1 and the convex buds 7 on the other side of the push card 12 cooperate with the sliding grooves 9 of the wire rack 31 to form a gap limit respectively. .
[0098] Of course, in other embodiments, ...
Embodiment 3
[0099] Embodiment 3, for the sake of brevity, this embodiment only describes the difference from Embodiment 2:
[0100] see Figure 20-22 As shown, the difference from Embodiment 2 is that the iron core 11 is a plane iron core 11, and the plane iron core 11 and the push card 12 have two sets of convex and groove structures (corresponding to form two connection positions) for connection.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com