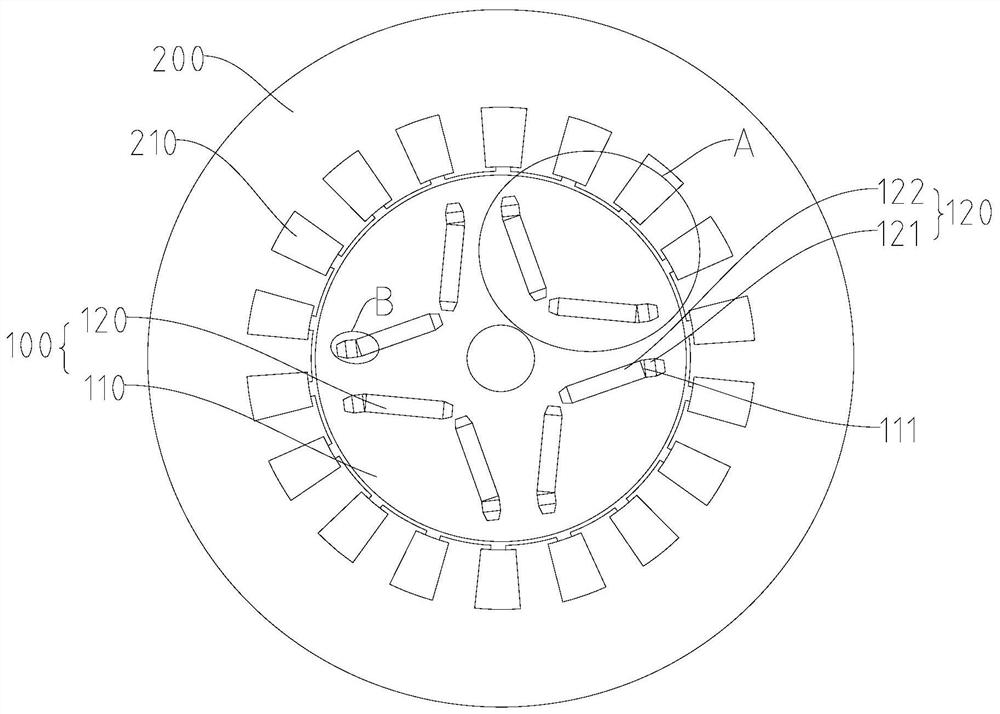
Motor rotor and IPM motor
A technology of motor rotor and motor stator, which is applied in the direction of electromechanical devices, electrical components, electric components, etc., and can solve the problems of complex process and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
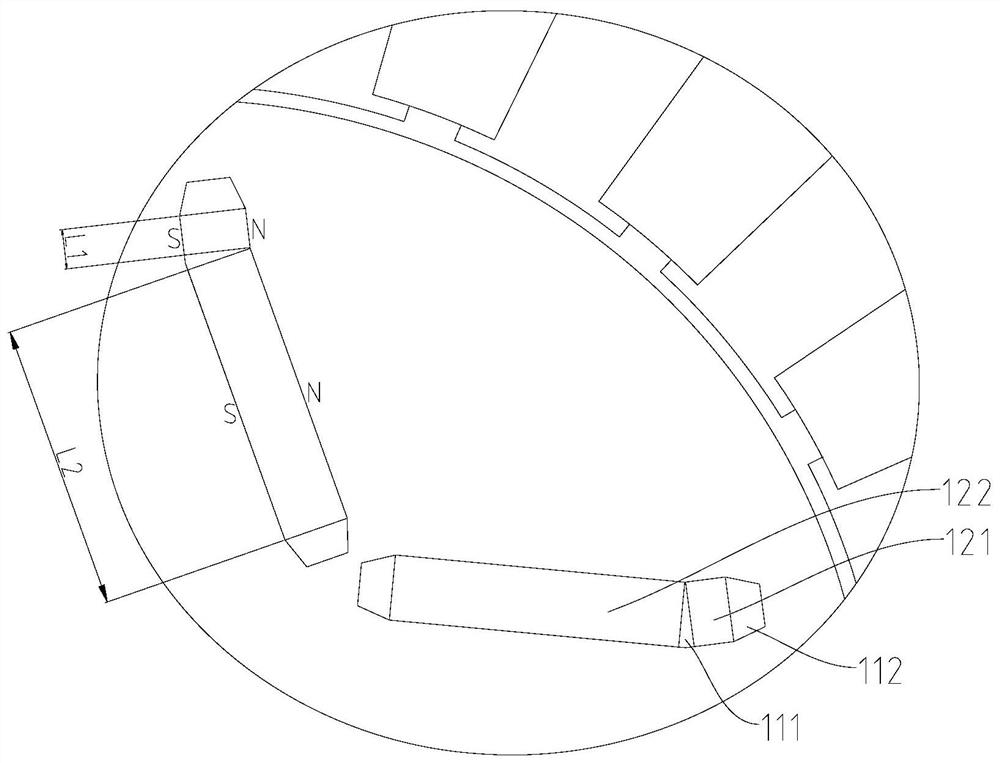
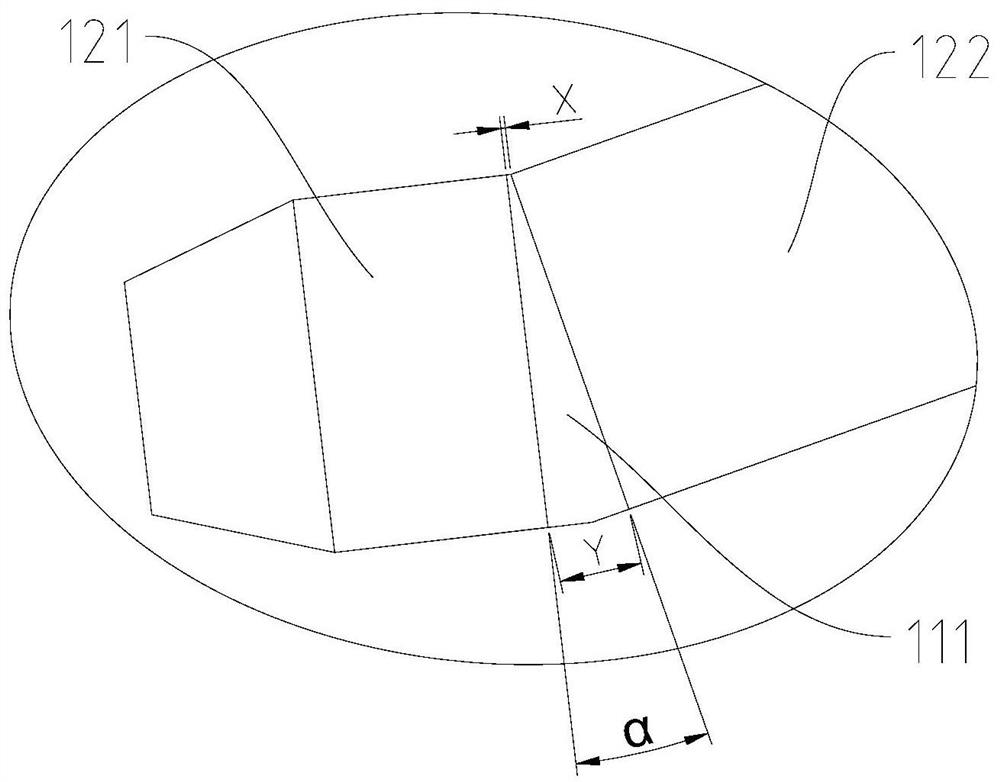
[0046] The length L2=22mm of the second magnet 122, the included angle α=0° between the adjacent surfaces of the first magnet 121 and the second magnet 122, the minimum between the adjacent surfaces of the first magnet 121 and the second magnet 122 Gap X=0.2 mm. Here, since the adjacent surfaces of the first magnet 121 and the second magnet 122 are parallel, the aforementioned minimum gap is also the maximum gap.
[0047] The length L1 of the first magnet 121 is 3 mm, 5 mm, 8 mm, and 11 mm, and the JMAG17.0 electromagnetic simulation calculation can be performed to obtain the total eddy current loss (ie, eddy loss) of the magnet 120, the output torque of the motor, and the first magnet 121 The temperature rise coefficient of the obtained table 1 below, temperature rise coefficient = (eddy loss 当前例 / volume 当前例 ) / (Eddy loss 对比例 / volume 对比例 ). Wherein, the percentage data in the table is with no gap between the first magnet 121 and the second magnet 122, and the situation (de...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Since the eddy current increases with the increase of the motor speed, the scheme of embodiment 1 is adopted. When the length L1 of the first magnet 121 is preferably 3mm, in order to further explore the possibility of reducing the eddy current loss, the second embodiment changes the first The included angle between the adjacent surfaces of the first magnet 121 and the second magnet 122 is used for simulation experiments. Here, the length L2 of the second magnet 122 = 22 mm, the length L1 of the first magnet 121 = 3 mm, and the minimum gap X between adjacent surfaces of the first magnet 121 and the second magnet 122 = 0.2 mm.
[0053] The angle α between the adjacent surfaces of the first magnet 121 and the second magnet 122 is 0°, 2°, 8°, 10°, 15°, and 20° through computer simulation calculation, and the magnet 120 can be obtained. The total eddy current loss, the output torque of the motor and the temperature rise coefficient of the first magnet 121 are obtained in th...
Embodiment 3
[0058] The length L2 of the second magnet 122 is 22 mm, the length L1 of the first magnet 121 is 3 mm, and the angle α between adjacent surfaces of the first magnet 121 and the second magnet 122 is 15°.
[0059] Perform computer simulation calculations for different situations in which the minimum gap X between the first magnet 121 and the second magnet 122 is different values, and the eddy current loss, the output torque of the motor and the temperature rise coefficient of the first magnet 121 can be obtained to obtain the following table 3, wherein , the percentage data in the table is based on the situation that there is no gap between the first magnet 121 and the second magnet 122, and the sum of the lengths of the two is 25mm (the first magnet 121 and the second magnet 122 can be in close contact or as a whole) as a reference .
[0060] Table 3 (embodiment three)
[0061] X(mm) Eddy current loss (%) Output torque (%) Temperature rise coefficient of the fi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Coercivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Coercivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com