Cleaning robot control method and device and terminal equipment
A cleaning robot and control method technology, applied in non-electric variable control, control/regulation system, two-dimensional position/channel control, etc., can solve the problem of inconsistent tilting state of photovoltaic modules, control system, sensor failure, falling, etc. problems, to avoid operational risks, ensure safe passage, and achieve the effect of collaborative control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
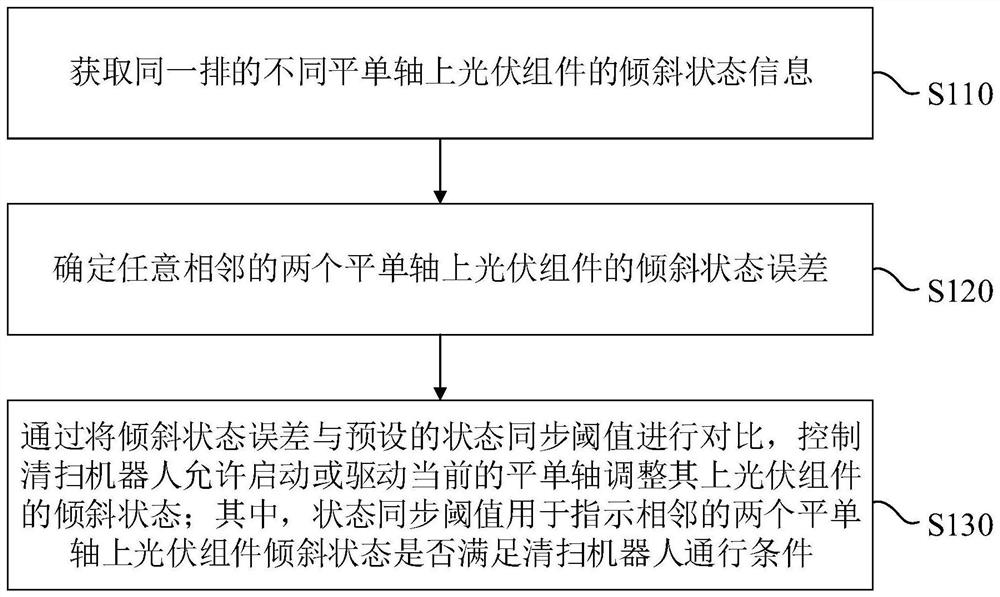
[0033] figure 1 It is a schematic flow chart of a cleaning robot control method provided in Embodiment 1 of the present invention. This method is applicable to the situation of the flat single-axis linkage control between the cleaning robot and the photovoltaic flat single-axis tracking system. This method can be controlled by the cleaning robot control device. Execution, wherein the device can be realized by software and / or hardware, and generally integrated on the terminal equipment. In this embodiment, the terminal equipment includes but not limited to computers, servers, management platforms, etc.
[0034] like figure 1 As shown, a cleaning robot control method provided in Embodiment 1 of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0035] S110. Obtain tilt state information of photovoltaic modules on different flat single axes in the same row.
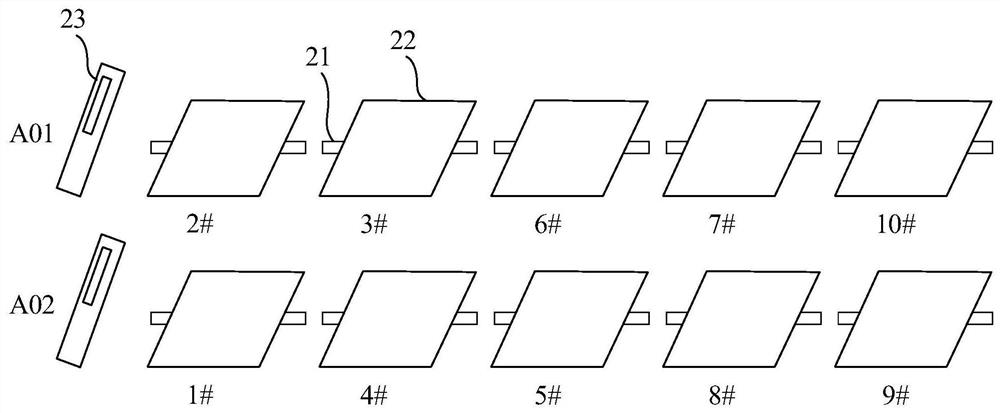
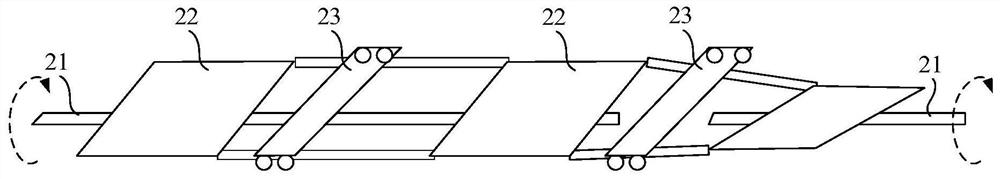
[0036] figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the arrangement of photovoltaic modules provided by the embodiment of ...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Figure 4 It is a schematic flow chart of a cleaning robot control method provided by Embodiment 2 of the present invention. This Embodiment 2 is optimized on the basis of the foregoing embodiments. In this embodiment, the acquisition of tilt state information of photovoltaic modules on different flat uniaxial axes in the same row is further embodied as: S210, acquiring rotation angle information of different flat uniaxial axes in the same row.
[0056] Further, this embodiment will also determine the tilt state error of any two adjacent flat single-axis photovoltaic modules, which is further embodied as: S220, calculate the rotation angle error of any two adjacent flat single-axis photovoltaic modules . In addition, by comparing the tilt state error with the preset state synchronization threshold, the cleaning robot is controlled to allow starting or driving the current flat single axis to adjust the tilt state of the photovoltaic module on it, which is further embodi...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Figure 6 It is a schematic flow chart of a cleaning robot control method provided by Embodiment 3 of the present invention. This Embodiment 3 is optimized on the basis of the foregoing embodiments. In this embodiment, the acquisition of tilt state information of photovoltaic modules on different flat single axes in the same row is further embodied as: 310. Obtain height information of preset end portions of photovoltaic modules on different flat single axes in the same row.
[0069]Furthermore, this embodiment will also determine the tilt state error of any two adjacent flat uniaxial photovoltaic modules, which is further embodied as: S320. Calculate the preset end of any two adjacent flat uniaxial photovoltaic modules height difference.
[0070] In addition, by comparing the tilt state error with the preset state synchronization threshold, the cleaning robot is controlled to allow starting or driving the current flat single-axis to adjust the tilt state of the photov...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com