Multi-level cache security
A high-speed cache and high-speed cache line technology, applied in memory systems, multi-programming devices, climate sustainability, etc., can solve problems such as delay extension
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
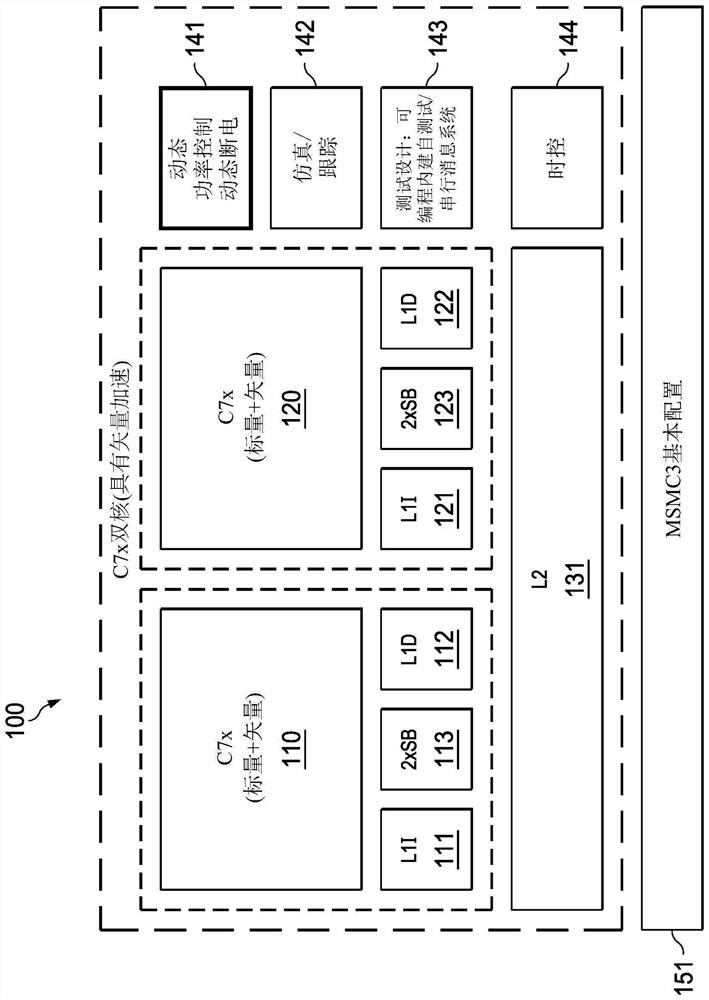
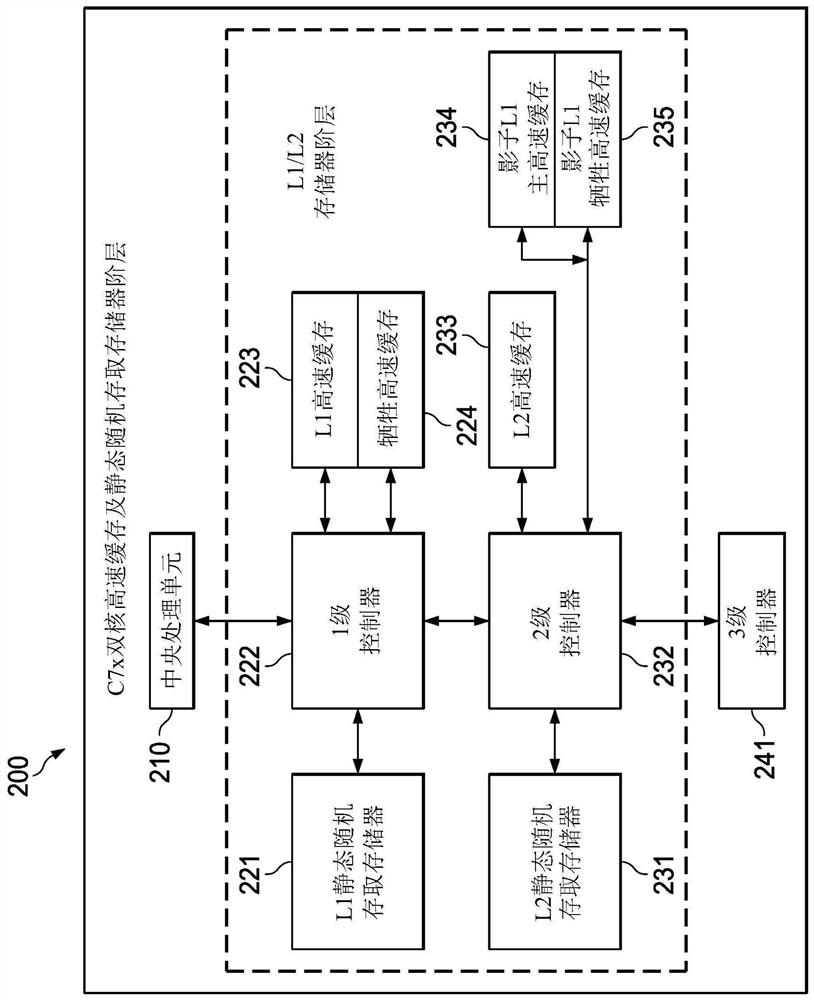
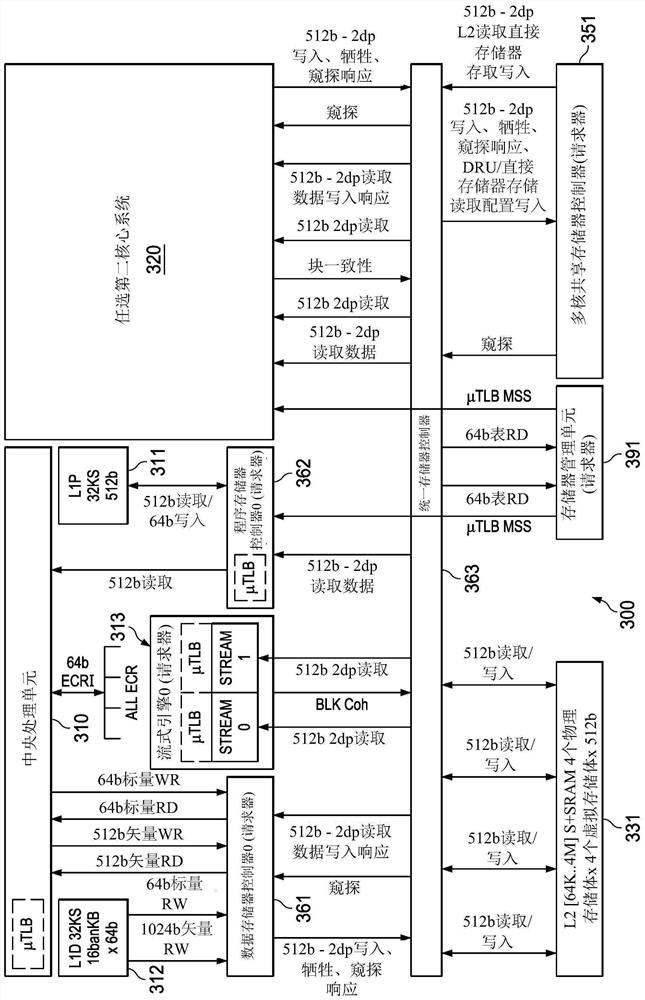
[0075] Example interfaces include CPU-DMC, CPU-PMC, DMC-UMC, PMC-UMC, SE-UMC, UMC-MSMC, MMU-UMC, and PMC-MMU interfaces. The CPU-DMC includes 512-bit vector reads and 512-bit vector writes and 64-bit scalar writes. The CPU-PMC contains 512-bit reads. The DMC-UMC includes 512-bit read and 512-bit write interfaces for performing cache transactions, snoop transactions, L1 DSRAM DMA, and external MMR accesses (eg, where each such interface can handle 2 data-phase transactions). The PMC-UMC interface contains 512-bit reads (which support 1 or 2 data phase reads). The SE-UMC interface contains 512-bit reads (which support 1 or 2 data phase reads). UMC-MSMC The UMC interface includes 512-bit reads and 512-bit writes (with overlapping snoop and DMA transactions). The MMU-UMC interface contains page table lookups from the L2. The PMC-MMU interface contains μTLB misses to the MMU.
[0076] L1P 311 contains a 32KB L1P cache as a 4-way set associative with a cache line size of 64 byt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com