Transient brain power supply positioning method and system based on non-negative block sparse Bayesian learning
A Bayesian learning and brain power location technology, applied in the field of EEG source tracing, can solve the problems of high false positives, non-negativity of unused signal power, influence of source location accuracy, etc., so as to improve the location effect and source location. effect of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
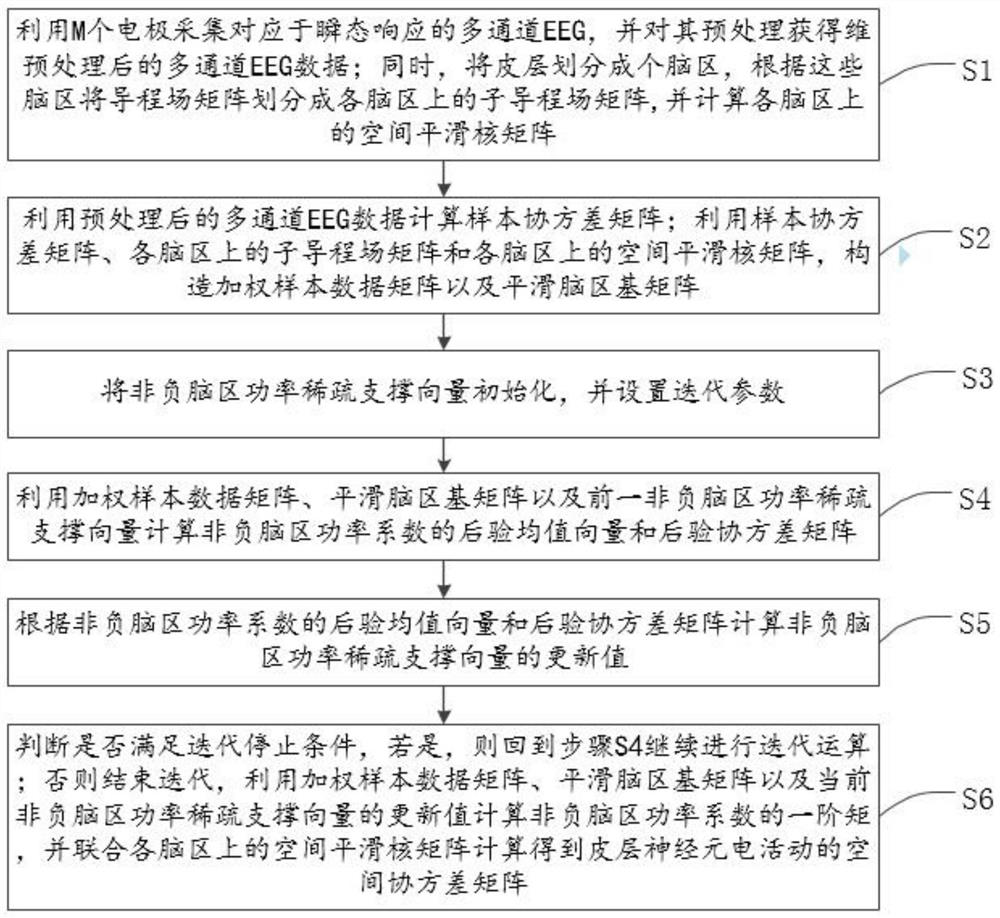
[0084] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments, so that those skilled in the art can better understand the present invention and implement it, but the examples given are not intended to limit the present invention.
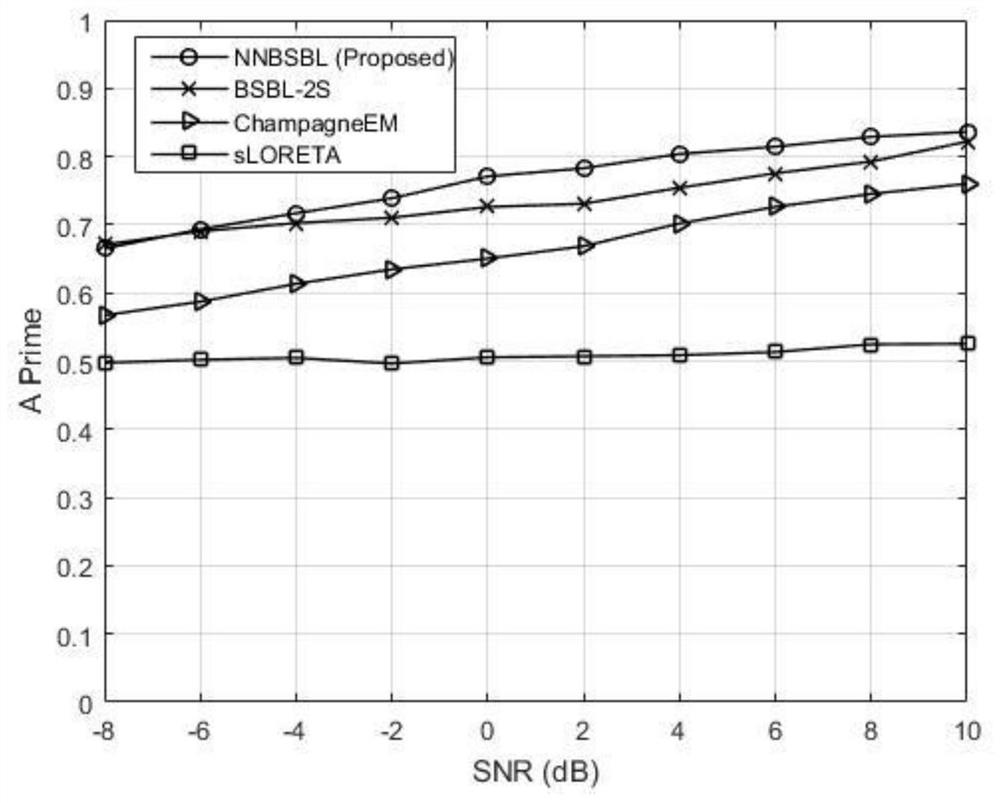
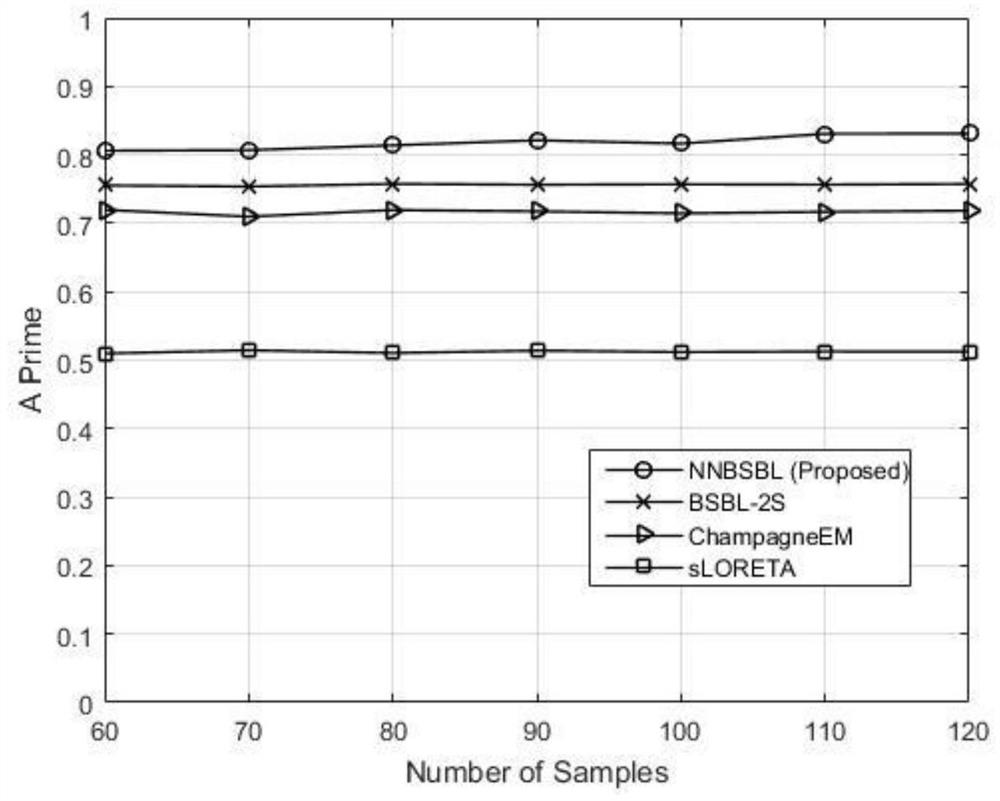
[0085] The present invention aims to propose a transient brain power location method based on non-negative block sparse Bayesian learning. The present invention first collects transient multi-channel EEG, calculates the sample covariance matrix, and weights each column of the matrix, which can be expressed as a sparse representation of non-negative blocks on each brain region after Laplace smoothing. Then set the iteration stop condition and the initial value of the sparse support vector of non-negative brain region power. Then iteratively update the posterior mean and covariance of the non-negative brain power vector based on the non-negative Gaussian distribution, and then updat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com