Use of derivatives with C-O-P bonds in patients with renal failure
A kidney function and application technology, applied in the direction of medical preparations containing active ingredients, drug combinations, drug delivery, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
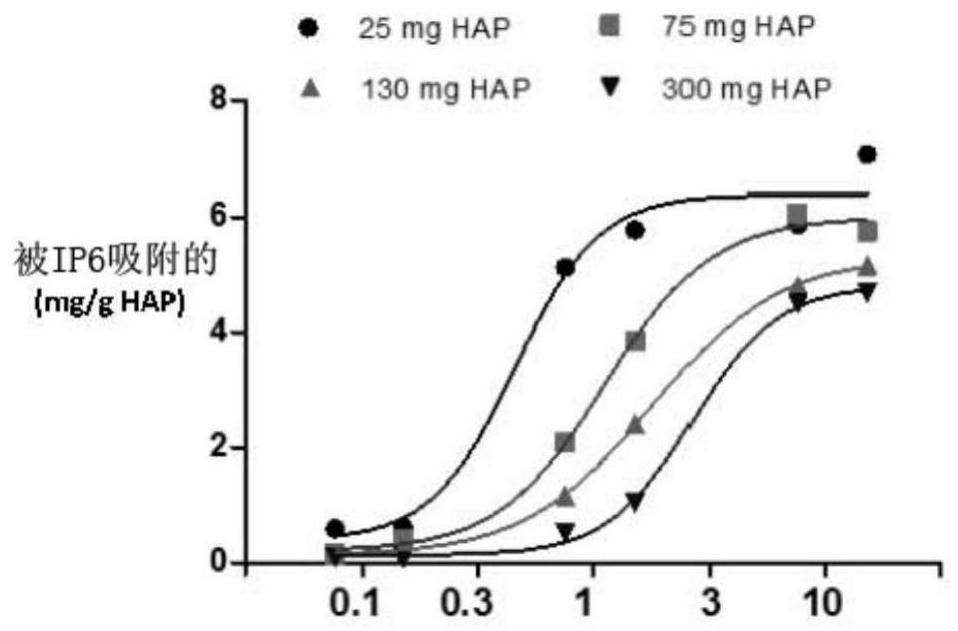
[0136] Example 2. In vitro determination of the affinity of IP6 for hydroxyapatite (HAP).
[0137] Purpose: The purpose of this study is to analyze the affinity of IP6 to its target, thereby obtaining the affinity curve of IP6 to HAP.
[0138] Assay: 4 different amounts of HAP were incubated with increasing concentrations of IP6 for 4 hours at 37°C, pH 7.4, with constant agitation. The total amount of IP6 bound to the surface of the target (HAP) was quantified.
[0139] Results: A dose-dependent adsorption curve was obtained and saturated at a concentration of 7.6 μM or higher. The maximum adsorption of IP6 on the HAP surface ranged from 4.8 mg when using 300 mg of target to 6.42 mg when using 25 mg of HAP, and was achieved in the presence of 7.6 μM IP6 over 8 hours. To characterize the binding behavior of IP6, the EC of its adsorption on HAP was calculated 50 and E max . Calculations were performed using a nonlinear regression model (Log[agonist] versus response-slope va...
Embodiment 3
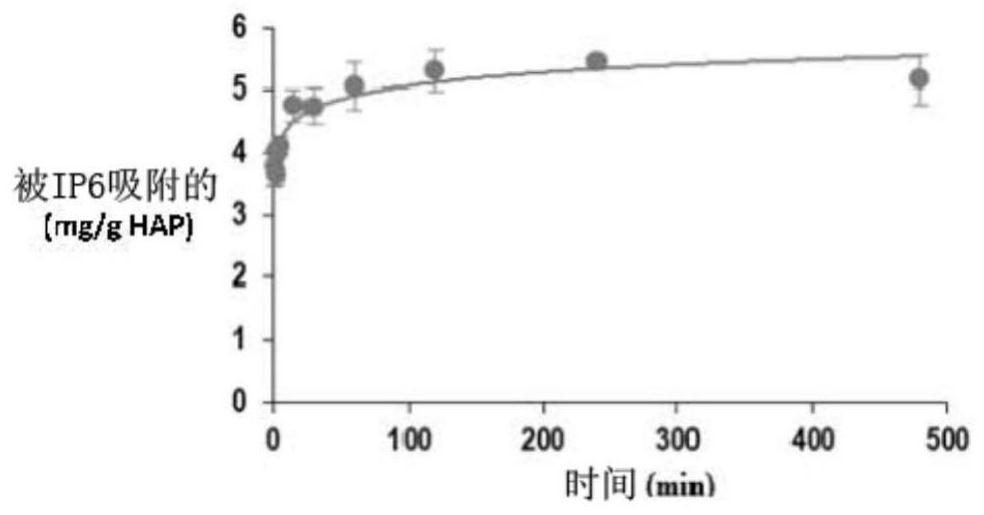
[0141] Example 3. In vitro determination of the binding kinetics of IP6 to HAP.
[0142] Objective: To analyze the binding rate of IP6 and HAP.
[0143] Test: 130 mg HAP was incubated with 7.6 μM IP6 (3 replicates) for different time intervals at 37° C., pH 7.4, with constant agitation.
[0144] Results and Discussion: Rapid binding of IP6 to HAP was observed ( figure 2 ), and reached the adsorption maximum at 60 min. Approximately 80% of maximum binding was achieved after 5 minutes.
Embodiment 4
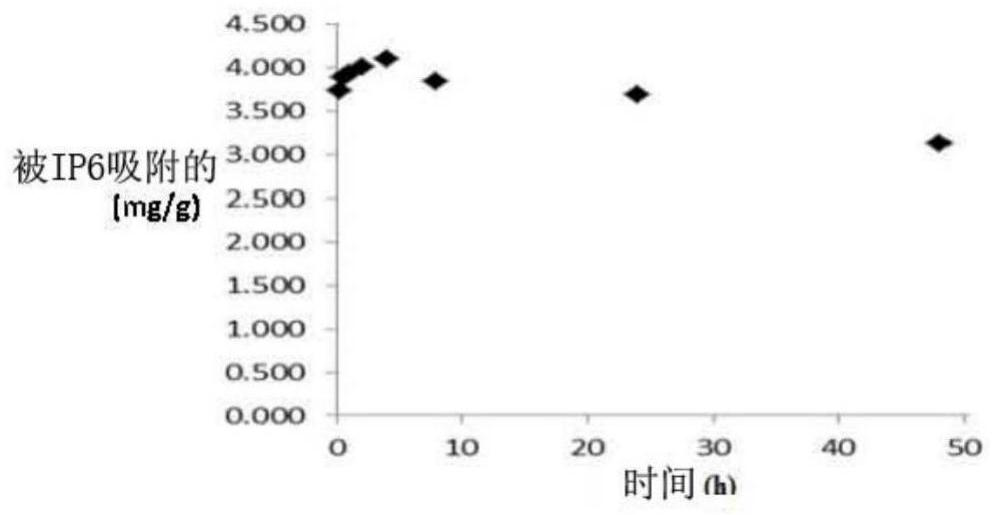
[0145] Example 4. In vitro affinity of IP6 for HAP. Release research.
[0146] Objective: To analyze the release rate of IP6 from HAP.
[0147] Test: 130 mg HAP was incubated with 7.6 μM IP6 for different time intervals at 37° C., pH 7.4, with constant agitation. Subsequently, the HAP with adsorbed IP6 was placed in a solution without IP6, and the amount of IP6 released from the surface of the HAP was evaluated at different time points.
[0148] Results and Discussion: A relatively slow release of IP6 from the surface of HAP was observed ( image 3 ). After 2 days of incubation, 80% of IP6 remained bound to the surface of HAP.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com