Multi-mode traffic lane refined setting method based on branch and bound method
A branch-and-bound method, multi-method technology, applied in road vehicle traffic control systems, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of discontinuous bus lane setting, non-motor vehicle lane congestion, pedestrian and non-motor vehicle conflict To avoid waste and unreasonable road space resources, improve traffic efficiency and improve algorithm efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
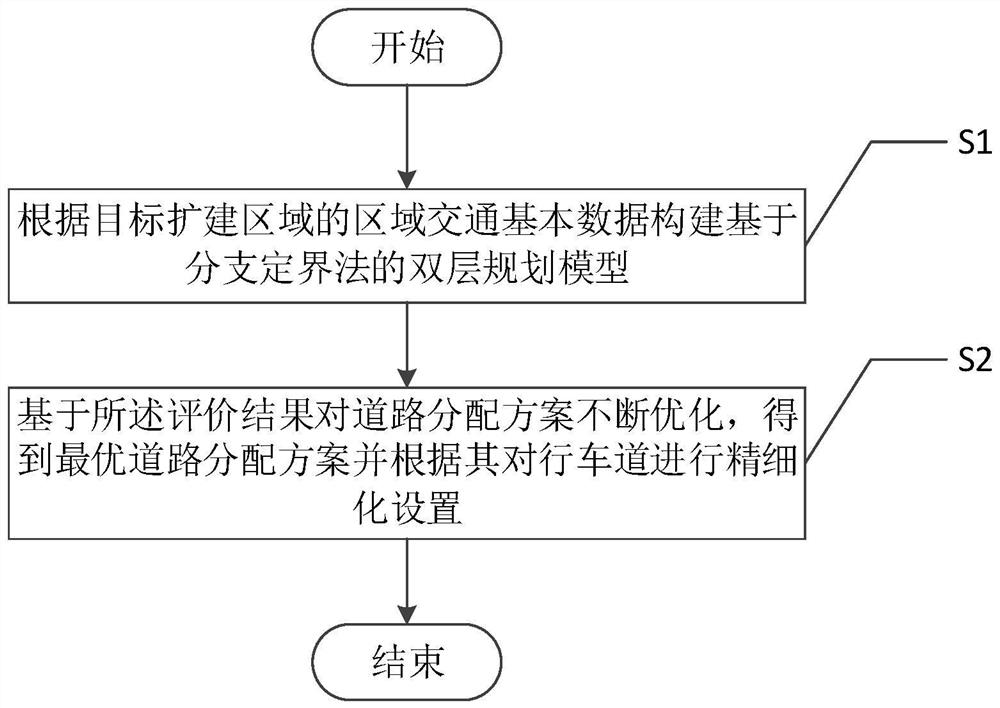
[0053] Such as figure 1 As shown, the multi-mode traffic lane refinement setting method based on the branch and bound method in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0054] S1. Construct a bi-level planning model based on the branch-and-bound method based on the basic regional traffic data of the target expansion area, including an upper-level planning model and a lower-level traffic distribution model. The upper-level planning model provides a multi-modal road space planning scheme, and the lower-level traffic distribution model The model simulation obtains the characteristic index after implementing the planning scheme of the upper-level planning model, and evaluates the road allocation scheme based on the upper-level model according to it;
[0055] S2. Continuously optimize the road allocation scheme based on the evaluation results, obtain the optimal road allocation scheme, and finely set the traffic lanes according to it.
[0056] The embodiment of the present ...
Embodiment 2
[0058] This embodiment is a further extension of step S1 in Embodiment 1;
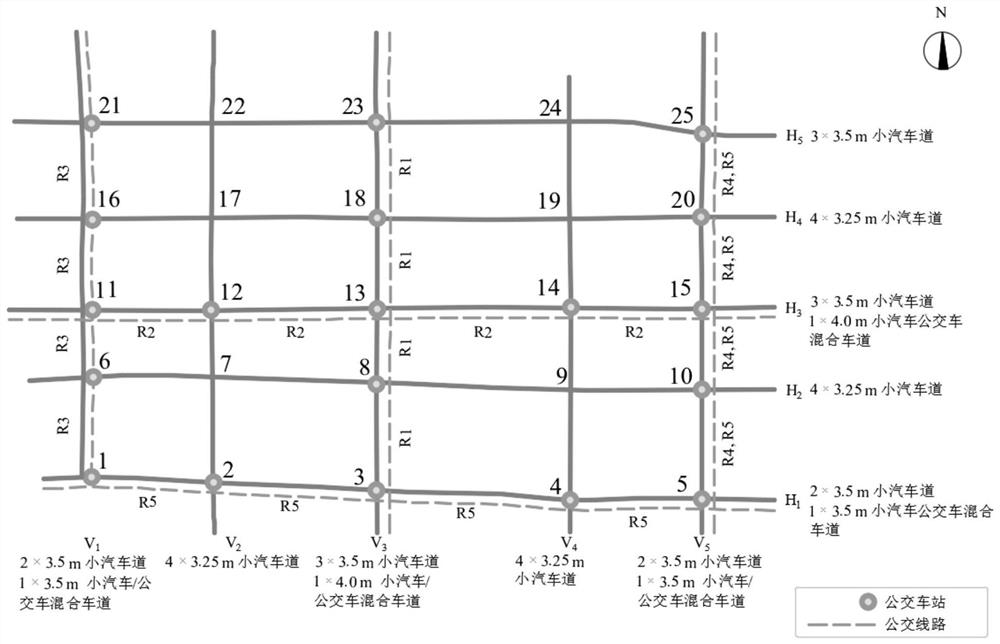
[0059] The basic regional traffic data in step S1 of this embodiment includes traffic facility physical data, traffic control data, and traffic demand data; wherein, the traffic facility physical data includes the two-way total width of road sections included in each street, the width of lanes, green belts, road shoulders, etc. , road section length, lane attributes such as HOV lanes, bus lanes, intermittent bus lanes, etc.; traffic management data include intersection signal cycle, phase, lane traffic control measures at each time period, parking charges, lane and vehicle speed limit, vehicle type limit Speed measures, the minimum width requirements of each functional lane, the planning accuracy of the general lane width, the hourly traffic capacity of the standard lane, etc.; the traffic demand data includes the departure point to the destination peak of the traffic travelers in the area (such as th...
Embodiment 3
[0109] This embodiment is a further extension of step S2 in Embodiment 1;
[0110] The method for obtaining the optimal road allocation scheme in step S2 of this embodiment is specifically as follows:
[0111] S21. Based on the new road allocation scheme, update the lower-level traffic distribution model and perform multi-modal dynamic traffic allocation to obtain allocation results and characteristic indicators;
[0112] S22. Based on the feature index, judge whether the new road allocation scheme generated by the current upper-level planning model is better than the previous road allocation scheme, if yes, proceed to step S23, if not, proceed to step S24;
[0113] S23. Based on the allocation results obtained by the current lower-level traffic distribution model, sort the congestion levels of streets in the area again, and then update the upper-level planning model, and obtain a new road allocation plan, and enter step S25;
[0114] S24. Screen the next priority street for ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com