Multi-agent reinforcement learning method and system based on hierarchical consistency learning
A technology of reinforcement learning and consistency, applied in neural learning methods, neural architectures, biological neural network models, etc., can solve problems that hinder efficient exploration and collaboration of agents, difficult communication protocols, etc., to improve time efficiency and task completion Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] This embodiment relates to the specific implementation of the above-mentioned multi-agent reinforcement learning method based on hierarchical consistency learning in the large-scale automatic sorting scenario of sorting robot clusters in the field of warehouse automation, such as Figure 6 shown.
[0028] In the sorting task of this embodiment, 12 sorting robots are located in the central area of the square map, and 32 shelves are evenly distributed in the four corner areas of the square map. Sorting robots are rewarded for navigating to shelves. The local observation of each sorting robot includes all the information in a square area centered on itself and with a radius of 7 unit lengths, that is, the two-dimensional coordinates of the other sorting robots and the two-dimensional coordinates of the shelves. The decision-making actions of the sorting robot include Move up, move down, move to the left, move to the right, stay still and lift the shelf, and the moving d...
Embodiment 2
[0053]In this embodiment, on the basis of Embodiment 1, disturbance factors are introduced into the sorting environment, such as observation noise, decision-making delay, mistaken target, etc. These disturbance factors will affect the behavior of the sorting robot. In this embodiment, these real interference factors are generally and abstractly modeled by introducing an additional interference agent. Specifically, compared with Embodiment 1, the schematic diagram of the automatic sorting task handled by this embodiment is as follows Figure 8 As shown, including: 16 interference robots, 16 sorting robots that move faster and 32 shelves. The sorting robot can only be rewarded by successfully reaching the shelf position and lifting the shelf, while the interference robot can be rewarded by arriving at the location of the sorting robot. The actions of all agents include moving up, moving down, moving to the left, moving to the right, and staying still; the sorting robot has an a...
Embodiment 3
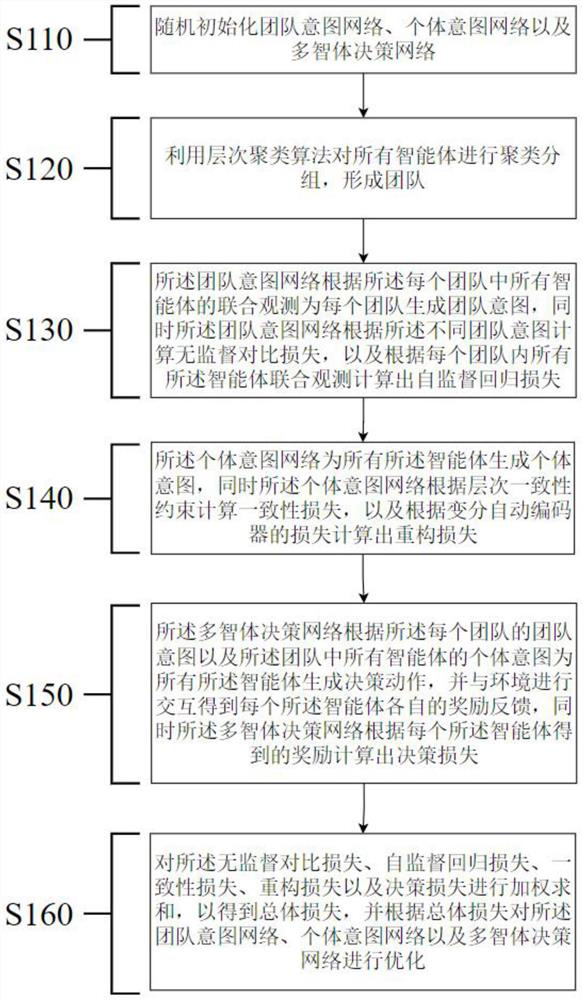
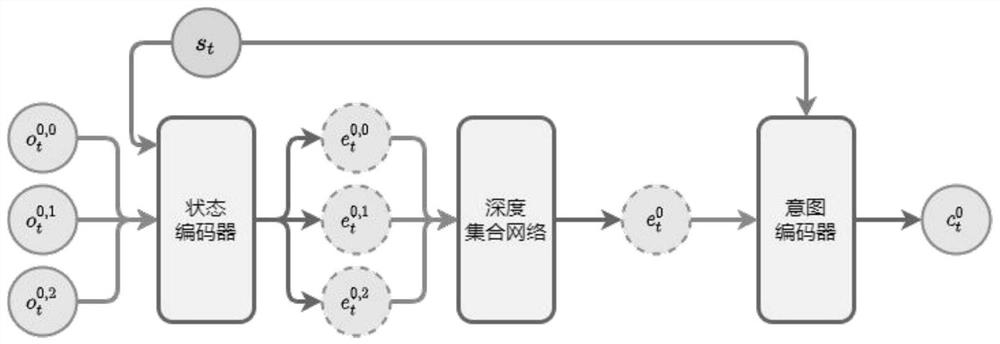
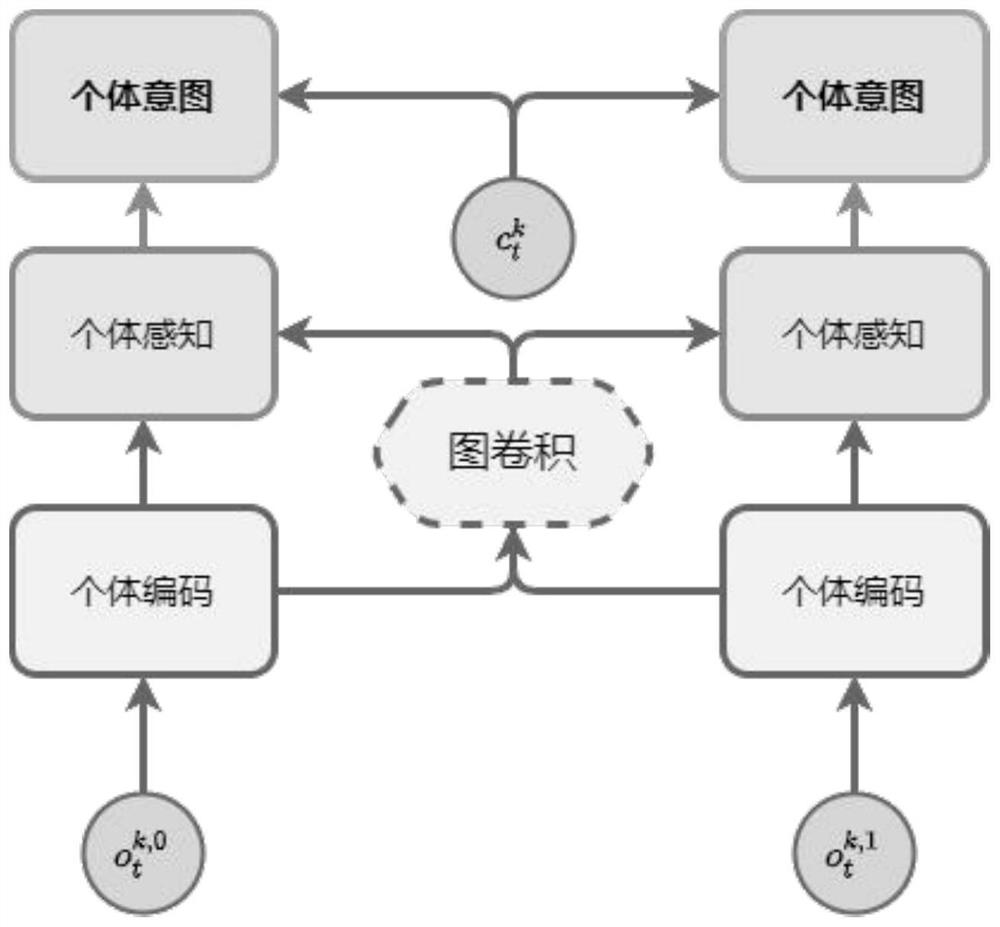
[0058] Such as Figure 8 As shown, it is a multi-agent reinforcement learning system based on hierarchical consistency that implements the above method, including: an initialization unit 510, a heuristic grouping unit 520, a team intention unit 530, an individual intention unit 540, and a multi-agent decision-making unit 550 And model optimization unit 560, wherein: initialization unit 510 constructs and randomly initializes team intention network, individual intention network and multi-agent decision-making network; heuristic grouping unit 520 utilizes hierarchical clustering algorithm to cluster and group all agents to form a team The team intention unit 530 uses the team intention network to generate team intentions for each team based on the joint observations of all agents in each team, and uses the team intention network to calculate unsupervised comparison losses according to different team intentions, and according to all The joint observation of agents calculates the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com