Method for reducing surface fusion and surface adhesion of high internal phase emulsion in polymerization process
A technology of surface adhesion and polymer materials, which is applied in the field of reducing surface fusion and surface adhesion of high internal phase emulsions during the polymerization process, and can solve problems such as uneven pore size of porous polymers and unqualified polymerization degree
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] Example 1: Preparation of HIPE and preparation of foam from HIPE
[0062] For the preparation of HIPE, the water phase, oil phase and initiator phase contained the components shown in Table 1 below.
[0063] Table I:
[0064]
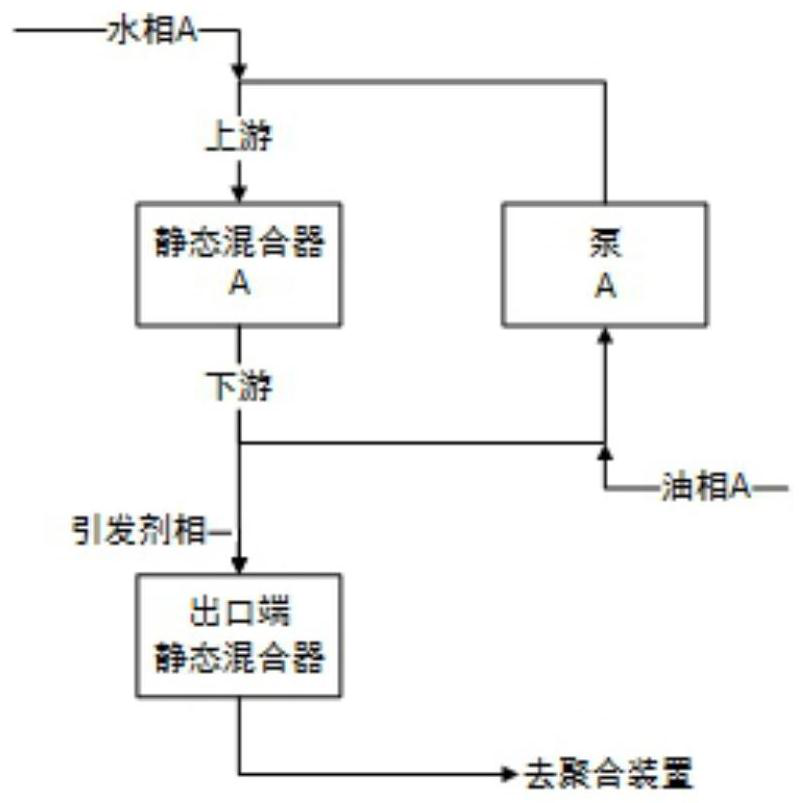
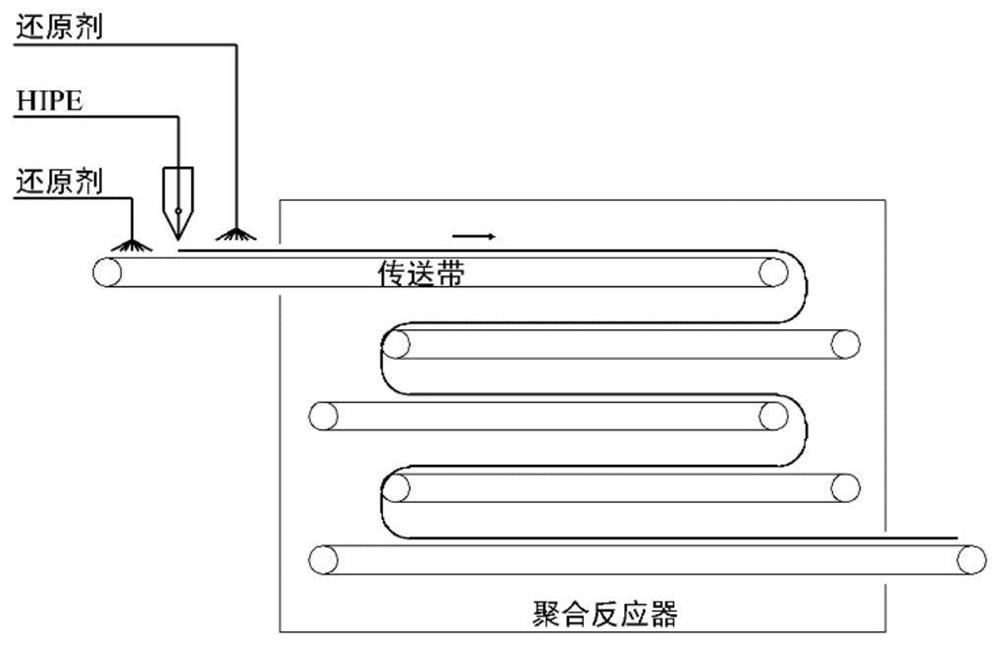
[0065] HIPE preparation. Follow the attached figure 1 As shown in the process flow, start the HIPE emulsification equipment. Composed of static mixer A (static mixer type Model GX, element combination 35.5*24+26.4*36, that is, 24 elements with a diameter of 35.5mm and 36 elements with a diameter of 26.4mm in series) and pump A (Herold WK- Pumps, three-bladed helical rotor) and their supporting pipelines (the pipeline includes temperature measuring points, pressure measuring points, and flow measuring points) constitute the first circulation pipeline. The water phase was continuously pumped through the shell and tube heat exchanger at a flow rate of 8100 g / min, the temperature of the water phase was controlled at about 80 °C, and delivered t...
Embodiment 2~5
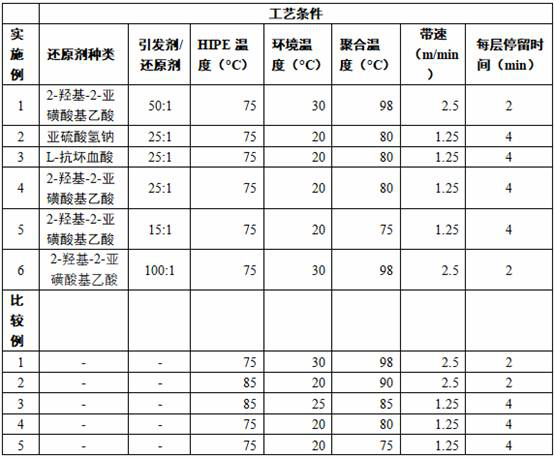
[0067] Embodiment 2~5 and comparative example 1~5:
[0068] The variables of each embodiment and comparative example are adjusted as described in Table 2, and the raw materials are the same as in Example 1; the implementation effects of Examples 1-5 and Comparative Examples 1-5 are shown in Table 3.
[0069] Table 2 Variable adjustment and implementation effect of Examples 1-5 and Comparative Examples 1-5
[0070]
[0071] Table 3 Implementation Effects of Embodiments 1 to 5 and Comparative Examples 1 to 5
[0072]
[0073] By comparing the examples with the comparative examples, it can be seen that the application of an aqueous reducing agent solution can effectively inhibit surface fusion and surface adhesion. In addition, the tensile strength of the polymer is routinely tested. In Examples 2 to 4, the polymer tensile strength obtained in Example 4 The tensile strength is the highest, being respectively 1.2 times of that of Example 2 and 1.35 times of that of Example ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com