Method for dynamically adjusting video time sequence
A technology of dynamic adjustment and timing, applied in the field of video transmission, can solve the problems of large memory space and increased system cost, and achieve the effect of reducing system cost and system complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
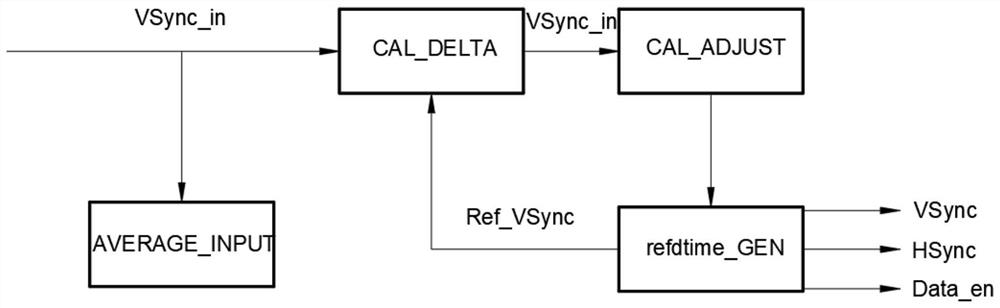
[0030] see figure 1 , a system structure diagram of a method for dynamically adjusting video timing.
[0031] A method for dynamically adjusting video timing, comprising: AVERAGE_INPUT module, CAL_DELTA module, CAL_ADJUST module and refdtime_GEN module;
[0032] AVERAGE_INPUT module, the AVERAGE_INPUT module is used to calculate the number of clocks between two adjacent VSync_ins by outputting clocks or displaying clocks;
[0033] CAL_DELTA module, the CAL_DELTA module is connected to the CAL_ADJUST module and the refdtime_GEN module, for receiving Vsync and calculating the phase and frequency difference between the real VSync_in and the expected VSync_in, that is, the phase_error value;
[0034] CAL_ADJUST module, described CAL_ADJUST module is connected to CAL_DELTA module and refdtime_GEN module, is used for calculating the value of Adjust_O when phase_error is greater than threshold value and needs to adjust output timing;
[0035] The refdtime_GEN module is used to rece...
Embodiment 2
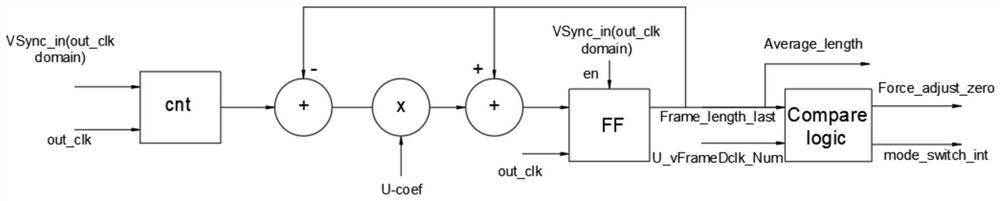
[0039] see figure 2 , figure 2 It is a block diagram of the AVERAGE_INPUT module that dynamically adjusts the video timing.
[0040] The working principle of the AVERAGE_INPUT module in this solution is as follows:
[0041]VSync_in (frame synchronization signal) is the frame synchronization signal of the video input module, and this frame synchronization signal works in the input clock domain. The main function of the AVERAGE_INPUT module is to use the output clock or display clock out_clk to calculate the number of clocks (in out_clk) between adjacent two VSync_in (frame synchronization signals), and to control the action of the subsequent algorithm module according to the calculation result .
[0042] First, use out_clk to synchronize VSync_in (frame synchronization signal) to the out_clk domain (latched twice in a row, not shown in the above figure), and each VSync_in (frame synchronization signal) arrives, which means that the video input module has input a new frame,...
Embodiment 3
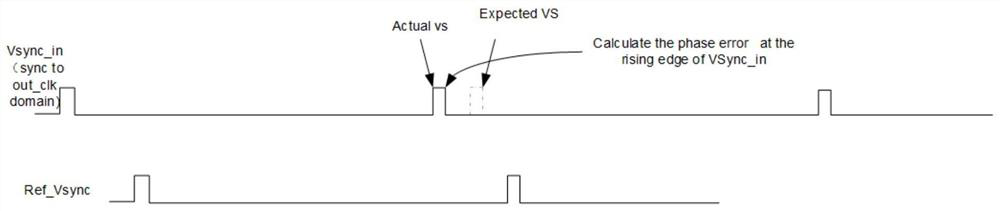
[0045] see image 3 , image 3 It is a schematic diagram of the calculation process of the CAL_DELTA module for a method of dynamically adjusting video timing.
[0046] The CAL_DELTA module works as follows:
[0047] Wherein, there is a locally generated Vsync signal inside the CAL_DELTA module: Ref_VSync; this signal is generated by the output timing controller Refdtime_GEN module. Here, the idea of negative feedback of the PLL is used.
[0048] Ref_Vsync is initially set to lag behind VSync_in (frame sync signal) with a fixed phase. And Ref_Vsync works in the out_Clk clock domain. From the perspective of the out_clk clock domain, Ref_vsync is constant (two adjacent Ref_vsyncs calculate the number of out_clk, and its value remains unchanged), but because the out_clk clock cycle will drift, the absolute time length of two adjacent Ref_Vsyncs changes.
[0049] Therefore, when the relative frequency and phase of the input clock and out_clk are drifted due to various facto...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com