Method and products for photochromic marking and/or for securing authenticity of objects
A photochromic and authenticity technology, which is applied to the authenticity inspection of banknotes, chemical instruments and methods, and the printing of special varieties of printed matter, which can solve the problems of no inherent coloring and unusable security features, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0109] Example 1: Detection of low-level security features
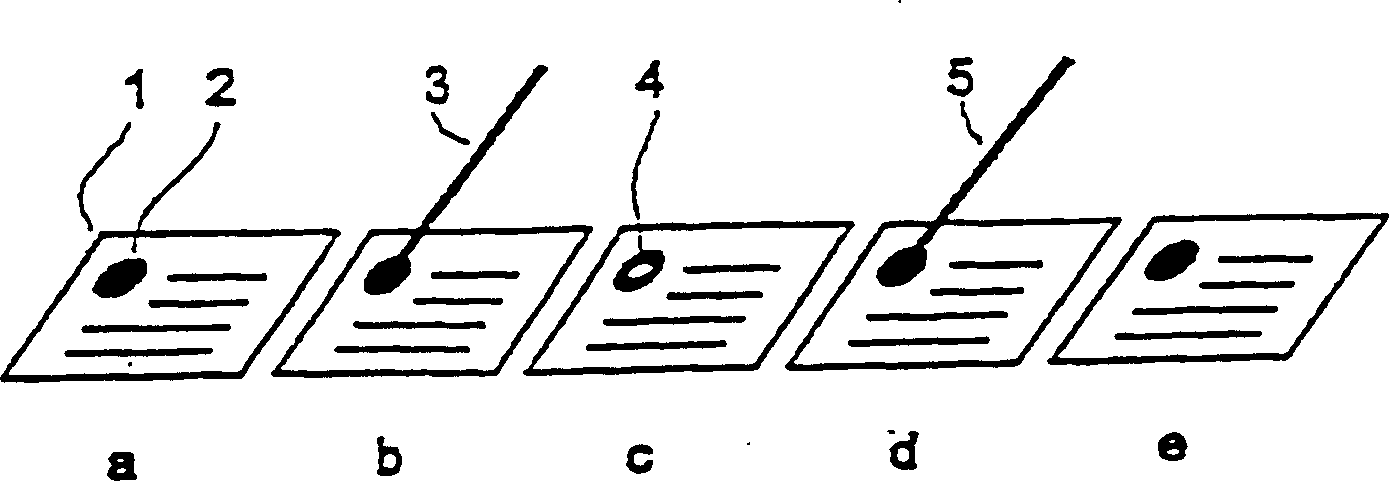
[0110] Users can easily test the photochromic properties of bacteriorhodopsin or BR variants ( figure 1 ). The feature 2 applied to a document 1 (such as a banknote, security, artwork or other valuable object) and prepared with a preparation containing the bacteriorhodopsin variant D96N can be detected, for example, based on the fact that when using the maximum emission in the green When illuminated by light 3 emitted by light-emitting diodes in the light and yellow range, its color changes from purple to yellow. It is especially easy to spot in 4 when the area is not fully illuminated. Without further manipulation, the purple color reappears after a few seconds to a few minutes, depending on the preparation used, and the initial state is reestablished. Alternatively, it can be irradiated with light 5 emitted by a light-emitting diode whose maximum emission is in the blue light range, and the purple color can be r...
Embodiment 2
[0111] Example 2: Preventing copying
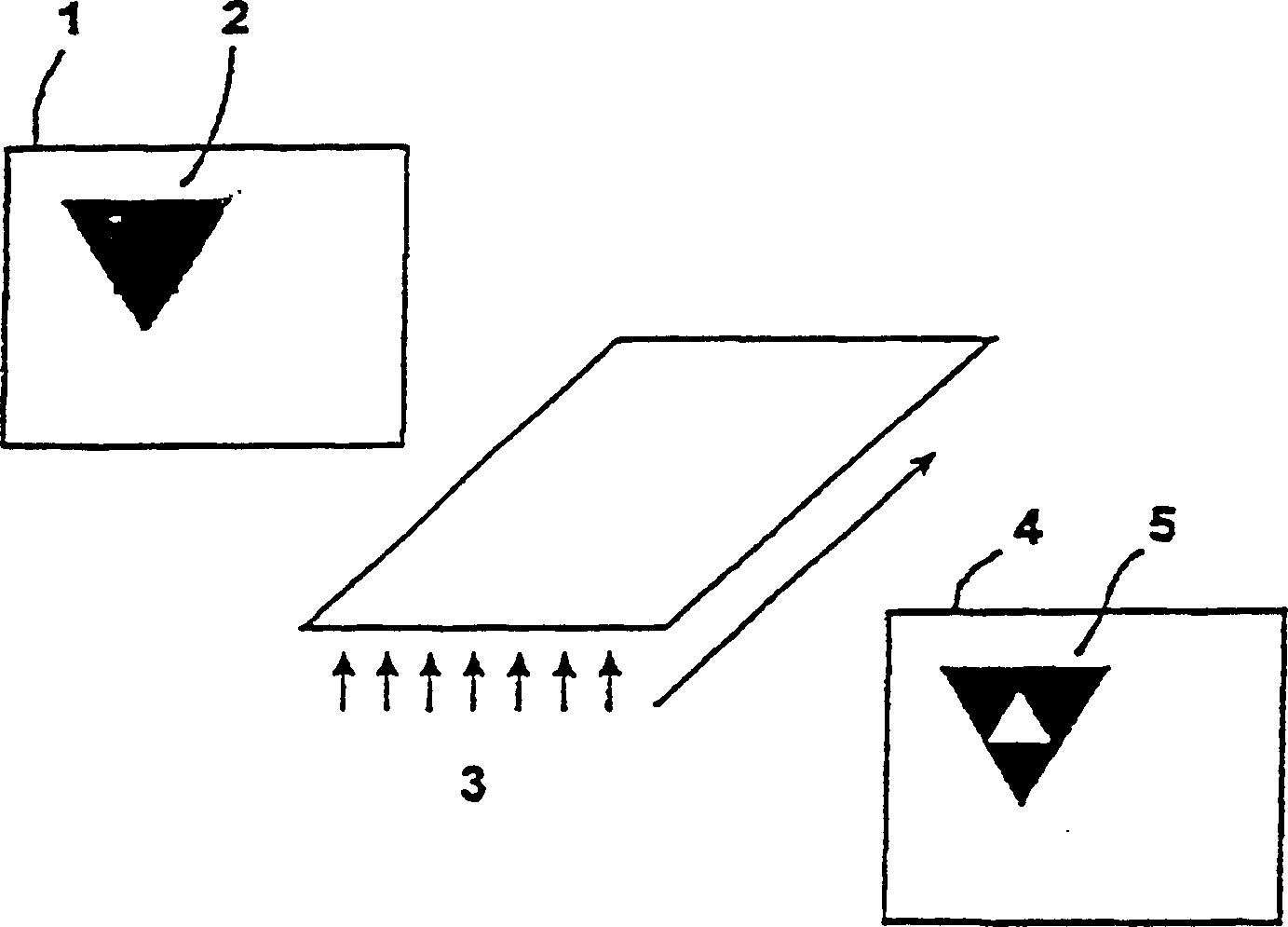
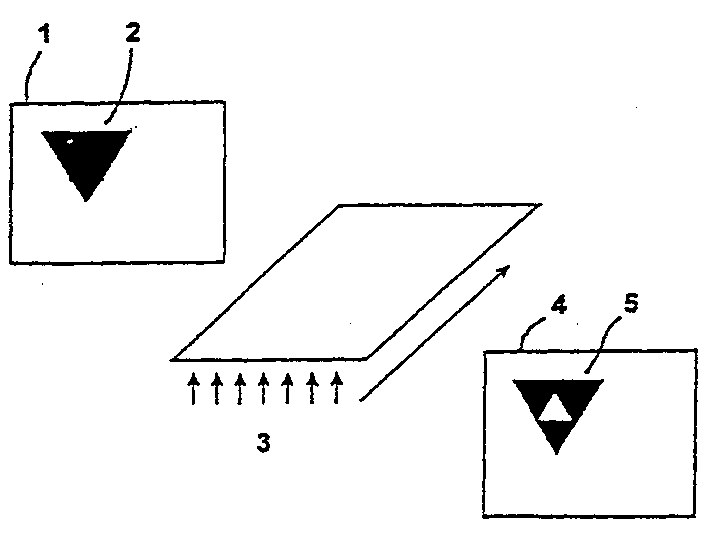
[0112] Receipt 1 contains feature 2 of the invention in which a specific amount of light-sensitive bacteriorhodopsin material (eg wild-type bacteriorhodopsin) is used in combination with a more light-sensitive bacteriorhodopsin material (eg bacteriorhodopsin variant D96N ), the document has uniform areas of the same color in the unexposed state ( figure 2 ). Instead of the insensitive bacteriorhodopsin material, suitable dyes of the same color can also be used. If the document is reproduced by means of a photocopier 3, the photosensitive bacteriorhodopsin material is bleached more strongly than the surrounding material with lower sensitivity due to exposure to light during the reproduction process. The result is that the replica 4 will display the low level security feature 5 in which it will permanently retain its different colour. From this, it can be clearly identified that the replica is a replica.
Embodiment 3
[0113] Example 3: Workup, Auxiliary Substances and Application Methods
[0114] a) Subsequent crosslinking
[0115] A 40% solution of glutaraldehyde was applied to the substrate with a dried photochromic layer consisting of the substrate and bacteriorhodopsin for 15 minutes. The glutaraldehyde solution was then rinsed with water. By such treatment the photochromic layer is rendered water-insoluble.
[0116] b) Photochemical reaction
[0117] 10 mg of purple film (BR-D96N) was finely dispersed in 4 ml of UV-curable ink (IFS3000 from Schmitt Company). After coating the mixture with a doctor blade, it was cured overnight under UV light.
[0118] c) application
[0119] screen printing
[0120] The principle of screen printing is porous printing, which is similar to mask technology. The printing plate consists of a mesh fabric provided with an ink-impermeable barrier. The printed pattern is always open. Printing is done by brushing an ink-filled screen with a squeegee. D...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com