Unfrozen water model based on adsorption and capillary coupling effect
A coupling effect and unfrozen water technology, applied in the field of permafrost engineering, can solve problems such as lack of universal expressions, complex theoretical models, and difficulty in application, and achieve simplified model expressions, simple expressions, and fewer input parameters Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] An unfrozen water model based on adsorption and capillary coupling effects, including the following steps:
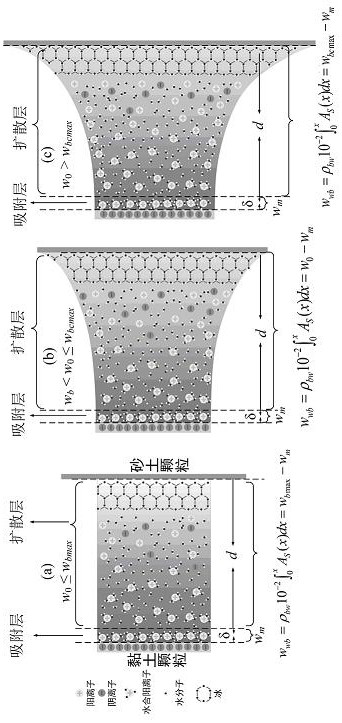
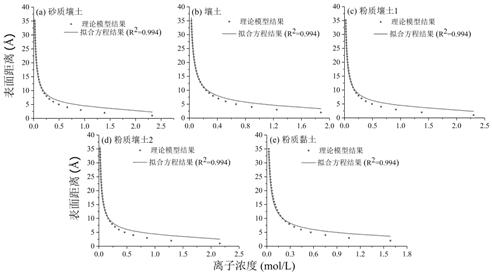
[0022] (1) Collect soil samples and measure the specific surface area of the soil A S and humidity at room temperature, and the soil moisture at room temperature as the initial water content w 0 .
[0023] Among them: the clay content in the soil is less than 20%, and its specific surface area A S At 60.5~6.22g / cm 3 between.
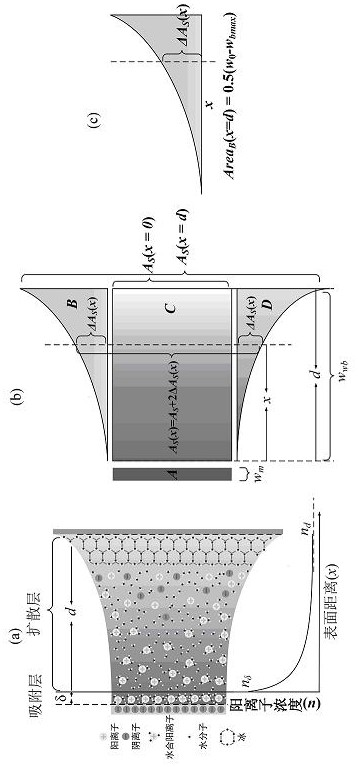
[0024] (2) Establish the following unfrozen water content model and calculate the unfrozen water content w u :
[0025]
[0026] In the formula: w m is the strongly bound water content, and w m =0.036 A S ; w bm is the residual bound water content, and w bm =0.027 A S ; w bmax is the maximum bound water content, and w bmax =0.38 A S ; w bcmax is the maximum carrying water content of clay particles and sand or silt particles, and w bcmax =0.608 A S ; w m , w bmax and w bcmax Both are mass moisture ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com