Evidence right and fractal-based full-moon landing area site selection method
A technology of landing zone and evidence, applied in the field of image processing, can solve the problems of more human factor intervention and heavy workload, and achieve the effect of reducing workload and human factor intervention
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
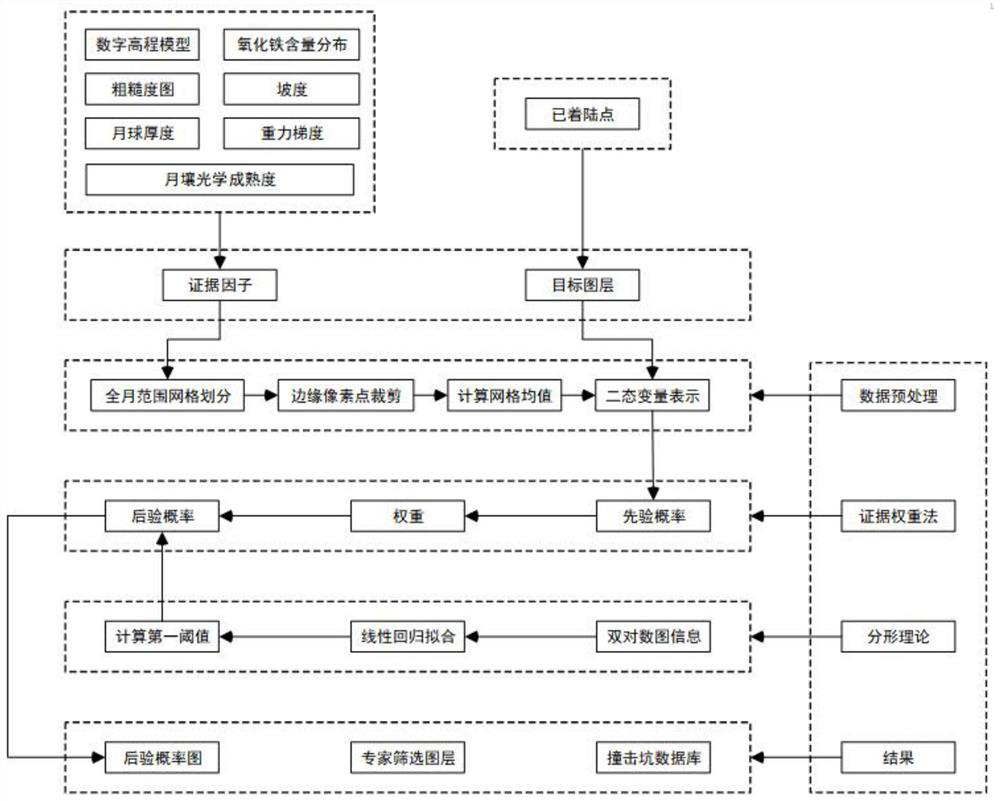
[0073] Embodiment 1 provides a method for selecting the location of the full moon landing zone based on the right of evidence and fractal, according to figure 1 As shown, specifically:
[0074] In specific applications, the evidence factors include lunar shell thickness, roughness map, slope, digital elevation model, gravity gradient, iron oxide content distribution, and lunar soil optical maturity, and the target layer includes the landed point;
[0075] In the specific application, based on data preprocessing, the division of the full-month grid, the clipping of the edge pixels of the evidence layer, the calculation of the network mean, and the binary variables of the evidence layer and the target layer are completed. express;
[0076] In the specific application, the prior probability, the weight of each evidence factor in each cell grid and the posterior probability are calculated based on the weight of evidence method;
[0077] In the specific application, based on the ...
Embodiment 2
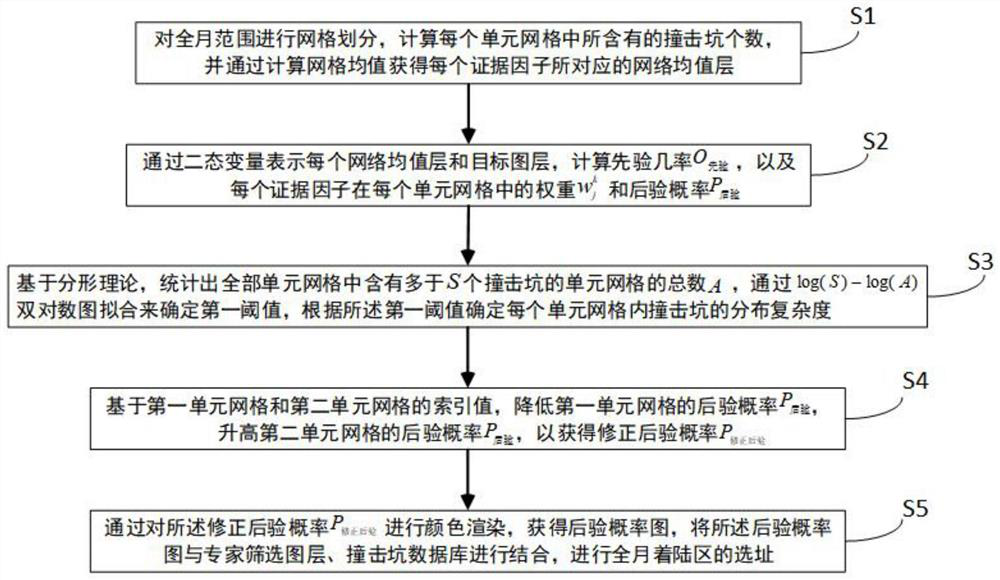
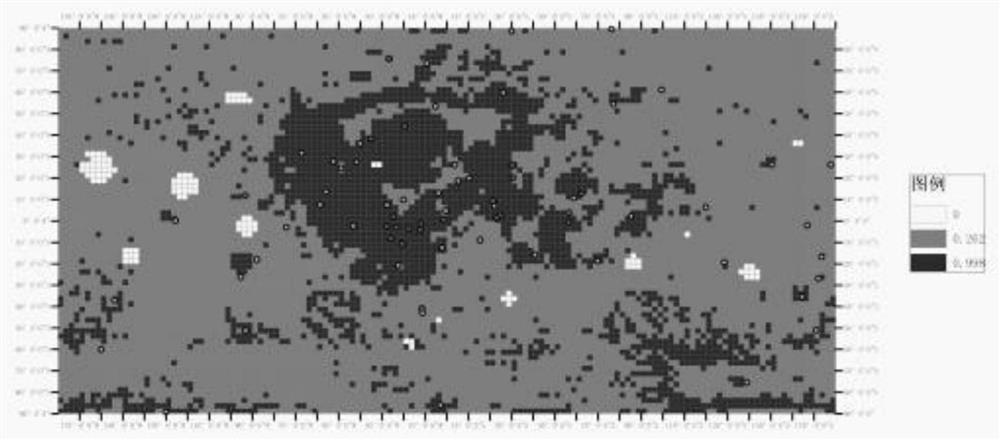
[0081] Embodiment 2 provides a method for selecting the location of the full moon landing area based on the right of evidence and fractal, according to figure 2 As shown, the specific steps are as follows:
[0082] S1. Carry out grid division for the whole month, calculate the number of impact craters contained in each unit grid, and obtain the network mean layer corresponding to each evidence factor by calculating the grid mean value;
[0083] In this embodiment, the full moon range used is 20037.4km*40074.4km, which is divided into 72*144 grids, that is, the size of each grid is set to 278.3km*278.3km.
[0084] In this embodiment, the grid mean value is the mean value of the pixel points in the unit grid, and the evidence factors include lunar shell thickness, roughness map, slope, digital elevation model, gravity gradient, iron oxide content distribution, and lunar soil optics. maturity;
[0085] Based on the aforementioned step S1, in the specific processing process, fi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com