A method for making a 3D printing bio-ink material with controllable distribution of materials and a method for making a three-dimensional biomimetic hydrogel scaffold
A bio-ink and 3D printing technology, applied in the field of bio-3D printing, can solve the problems of difficult regulation of cell behavior and preparation of functional tissues, and achieve the effect of personalized customization, controllability and simple production process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
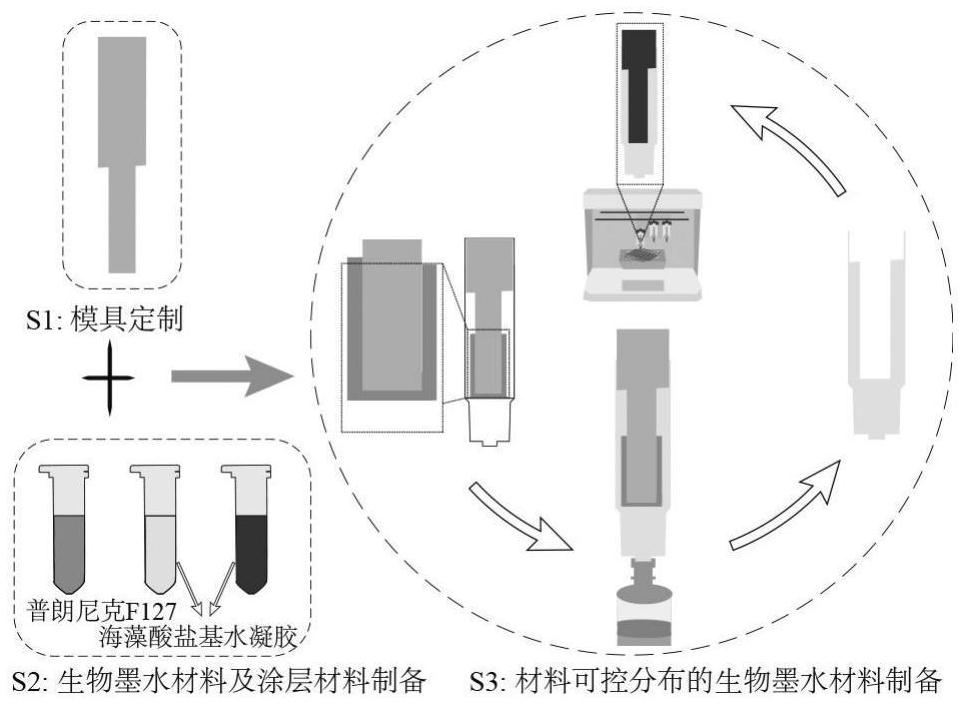
[0028] Embodiment 1: This embodiment describes a method for making a 3D printing bio-ink material with controllable distribution of materials. The method includes the following steps:
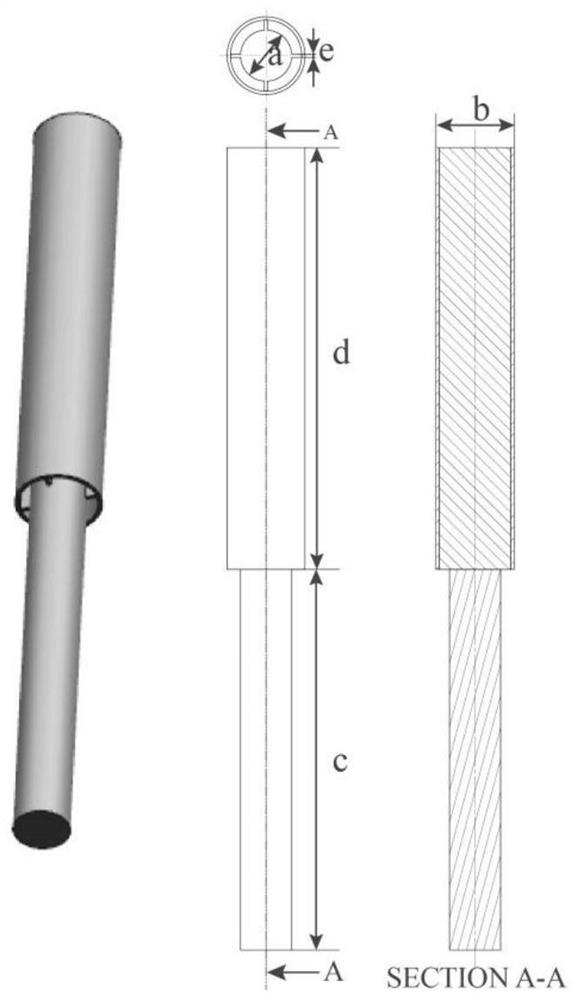
[0029] Step 1: 3D printing a customized high-precision mold, in which the mold fits with the inner surface of the barrel (not close fit, there are some random gaps);
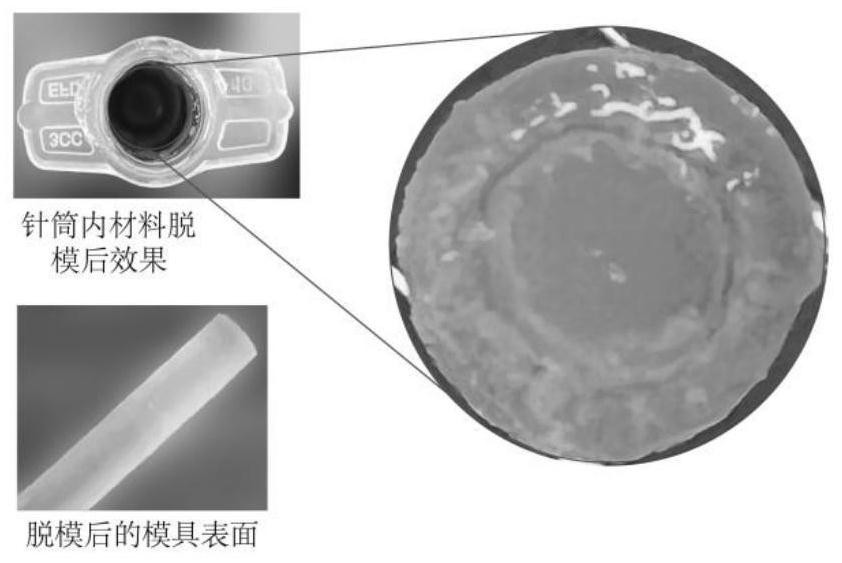
[0030] Step 2: Prepare a cold hydrogel with a temperature-sensitive characteristic and a dynamic viscosity of 3000-25000 Pa.s at room temperature and a thermo-induced hydrogel of 1-500 Pa.s, and use the thermo-induced hydrogel as the surface of the mold. Layer material; the surface coating of the mold means that not all surfaces are coated, in fact only a partial coating. The realization of the fit is to use the uncoated mold surface to produce a clearance fit with the inner surface of the barrel. This clearance fit is used to fix the mold, not for demolding between the outer layer of cold hydrogel and the coating material. Afte...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0032] Embodiment 2: In Embodiment 1, a method for producing a 3D printing bio-ink material with controllable distribution of materials, in step 1, the shape of the mold directly affects the material distribution of the 3D printing bio-ink material. The printing uses a high-precision resin 3D printer with a printing accuracy of not less than 0.05mm.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0033] Embodiment 3: In Embodiment 1, a method for producing 3D printing bio-ink material with controllable distribution of materials, in step 1, the 3D-printed mold pattern is adjusted according to the preset pattern of bio-ink material distribution And personalized customization; the clearance of the clearance fit is +0.01~+0.1mm, to ensure the fixation of the mold on the inner surface of the syringe and the mold placement and removal during the bio-ink material production process.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com