A Method for Calculating Orthotropic Material Parameters of Motors
An orthotropic, material parameter technology, applied in computer material science, computer-aided design, calculation, etc., can solve problems such as difficult calculations, and achieve the effect of easy acquisition and error avoidance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
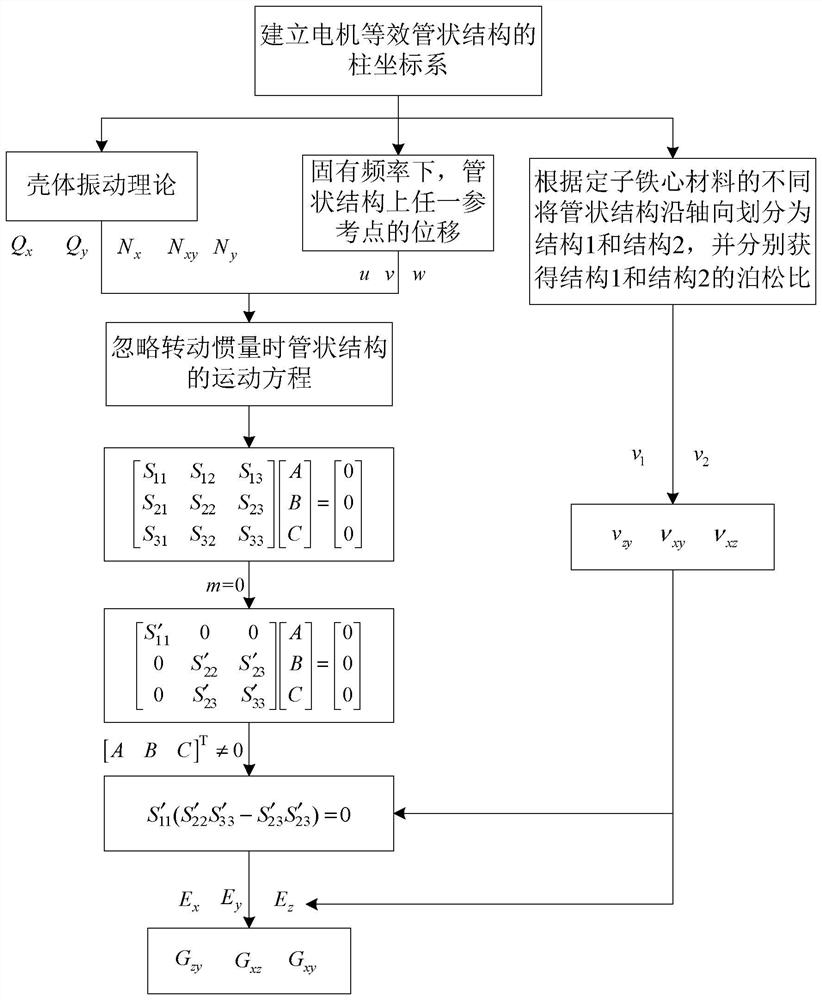
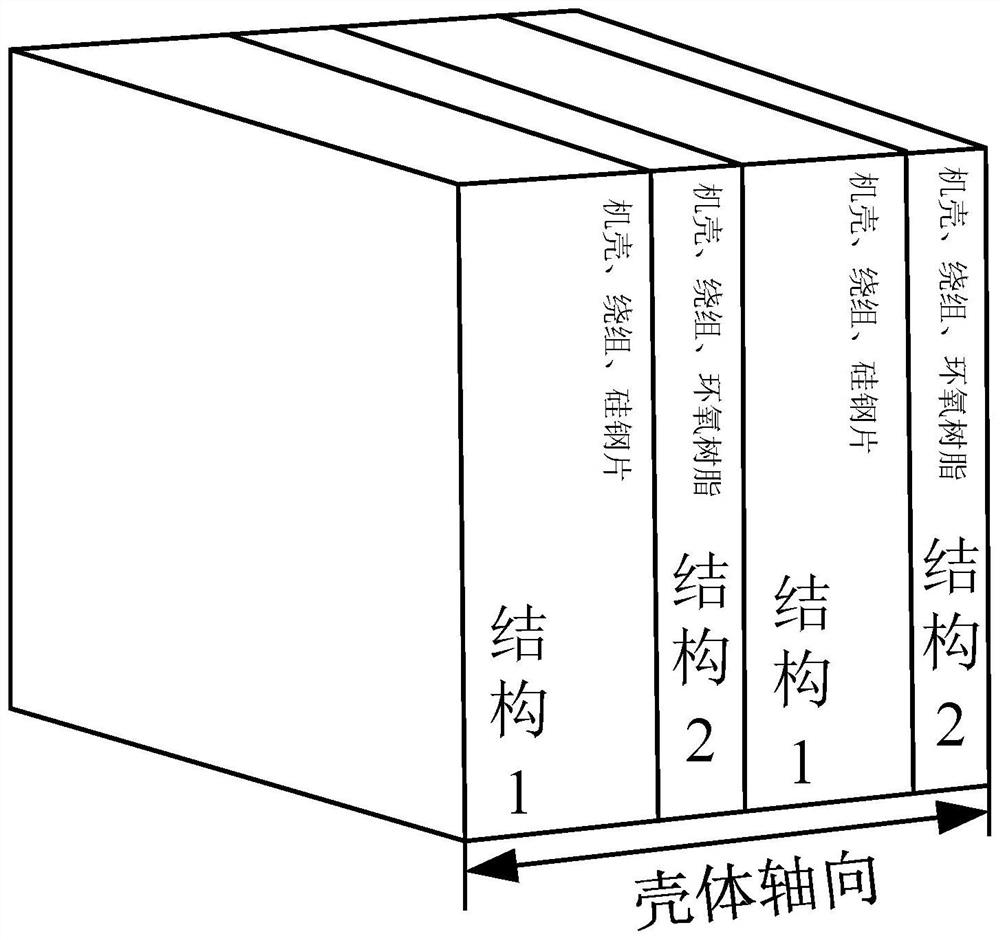
[0088] Specific implementation mode 1: refer to Figure 1 to Figure 4 Describing this embodiment in detail, in the method for calculating the orthotropic material parameters of a motor described in this embodiment, since the rotor and the rotating shaft have little influence on the natural frequency, this embodiment only uses the casing, the stator core, the Windings and end caps are the research objects. Therefore, based on the orthotropic analytical model with the shell theory as the core, the research object needs to be equivalent to a cylindrical shell, that is, the shell, the stator core and the winding are equivalent to the shell, and the end caps at both ends are used as the shell. Support structure, that is, the casing, stator core and winding of the motor are equivalent to a tubular structure.
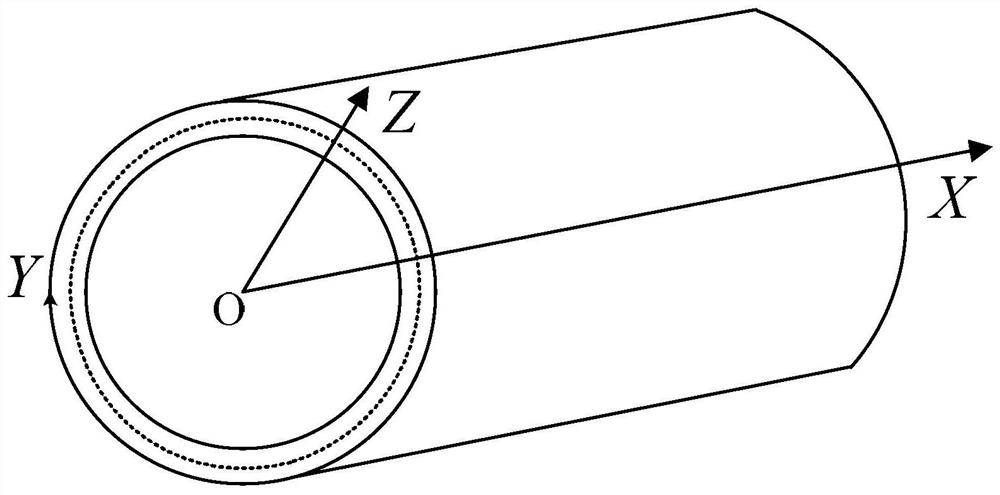
[0089] In order to facilitate the analysis, a cylindrical coordinate system is established with the center of one end face of the tubular structure as the origin O. The X-axi...
specific Embodiment
[0193] In this example, a three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor with a model of YT-3000-8 is selected as the experimental motor, the rotor and bearings are removed, and only the assembly structure of the casing, stator core, winding and end caps at both ends is selected as the experiment Prototype, hang it with a soft rope, try to ensure that it is in a free state. The excitation point is selected along the prototype body, and the low-order natural frequency is measured by the hammer method. In order to improve the correlation between the acceleration signal and the hammer signal, and reduce the error caused by the interference signal. Using the same point for multiple taps and averaging the transfer function to obtain accurate experimental data (m,n,f 实验 ). Due to the limitation of experimental equipment, only two cases of axial order m=0, 1 can be measured, while the radial order is not limited. In this embodiment, n=2, 3, 4, and 5 are selected.
[0194] Set (0,n,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com