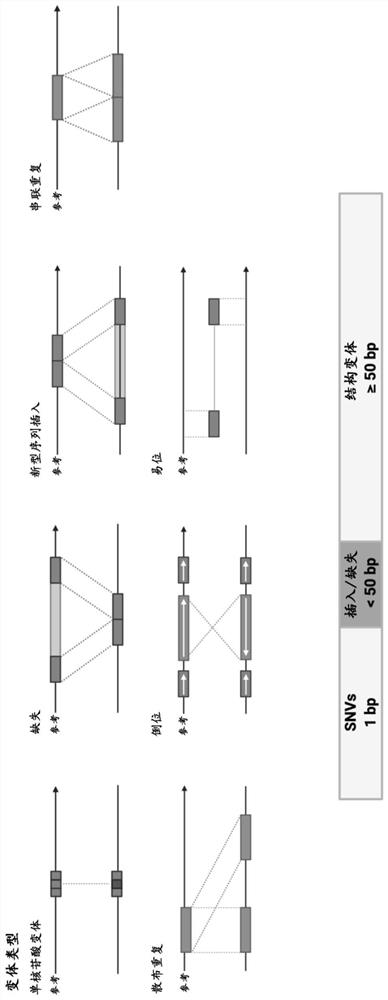
Identification of genomic structural variants using long read sequencing
A genome and variant technology, applied in genetic engineering, microbial measurement/inspection, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of expensive whole genome sequencing and difficulty in analyzing structural variants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
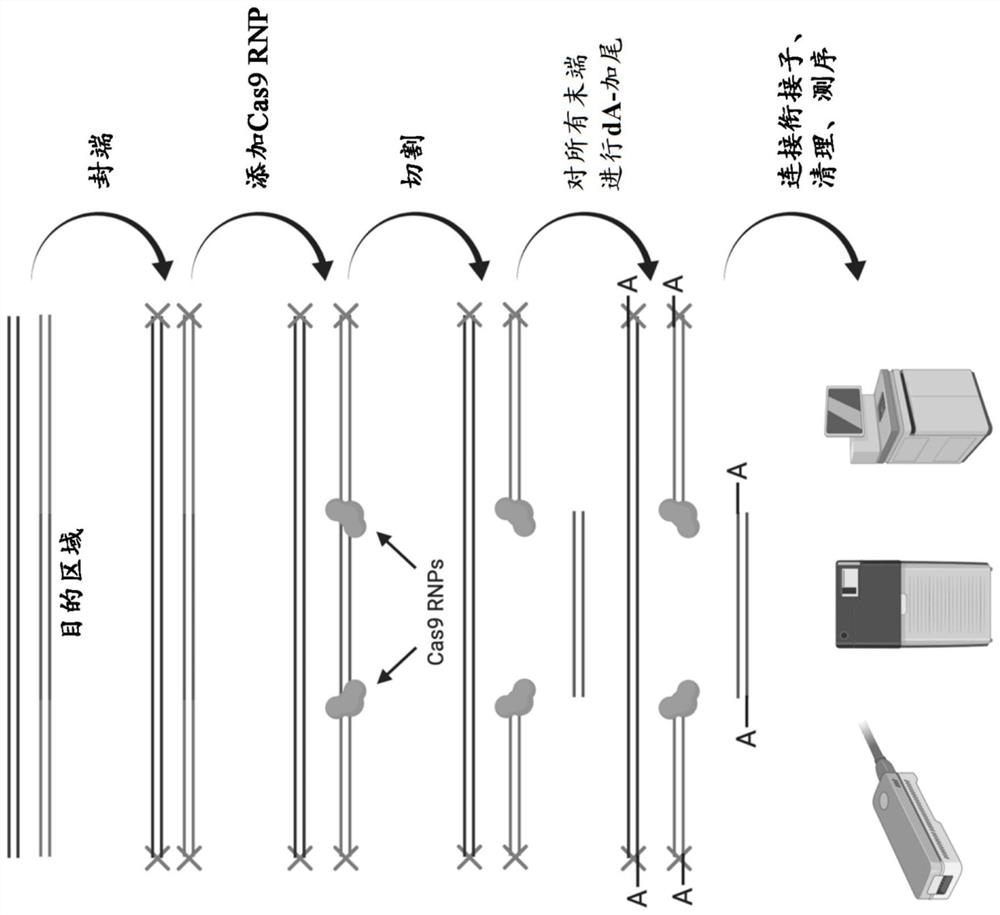
[0404] Example 1: Target enrichment protocol
[0405] An exemplary target enrichment protocol begins with the preparation of the Cas9 ribonucleoprotein complex (RNP). All crRNAs were pooled into an equimolar mixture at a total concentration of 50-100 μM prior to guide RNA assembly. The crRNA mixture and tracrRNA were then combined so that both the tracrRNA concentration and the total crRNA concentration were 5-10 μM. The gRNA duplexes were formed by denaturation at 95°C followed by cooling to room temperature. Ribonucleoprotein complexes (RNPs) were constructed by combining gRNA duplexes with Cas9 nuclease followed by incubation at room temperature.
[0406] The next stage involves dephosphorylation of genomic DNA. From 1 to 4 genomic DNA samples can be combined into dephosphorylation reactions for a total of 1-5 μg gDNA per phosphorylation reaction. Input DNA was dephosphorylated using calf intestinal phosphatase or shrimp alkaline phosphatase.
[0407] The next stage in...
Embodiment 2
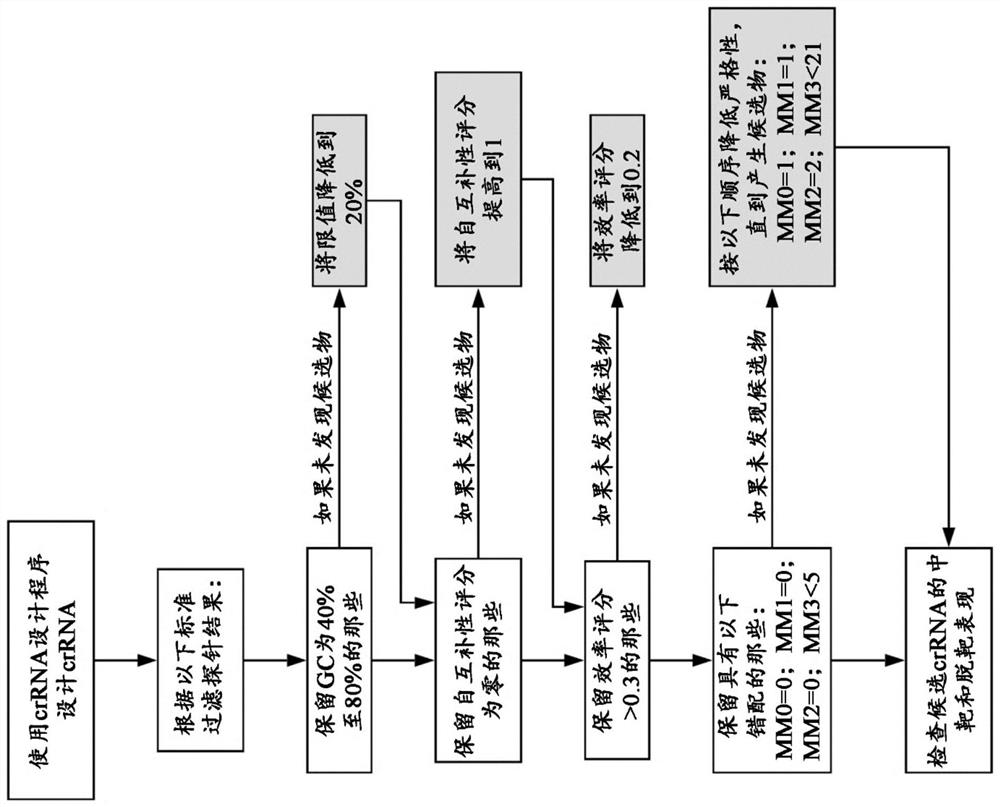
[0410] Example 2: BRCA1 crRNA probe design
[0411] In the case of BRCA1, the CHOPCHOP design program generated a total of 5567 possible crRNA probes along the entire length of the BRCA1 genomic locus. These crRNA sequences were then filtered using the filtering scheme described in [0041], reducing the number to 233 crRNA probes. The crRNA sequences are then checked using a second design checker tool such as the IDT CRISPR-Cas9 Guide RNA Design Checker Tool. The number of candidate crRNA probes was reduced to 86 probes. The final set of crRNA probes was selected based on the position of the target site.
[0412] like Figure 4A As shown, successful Cas9 cleavage and sequencing resulted in increased sequencing coverage of target regions, with little or no sequencing coverage of non-target regions. In samples with known deletions in exons 15 and 16, a sharp drop in sequencing coverage was observed where the deletions occurred ( Figure 4B ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com