Evaporation phase change heat transfer component based on gel decoupling driving and application thereof
A technology of heat transfer components and gel, which is applied in the field of heat transfer, can solve the problems of limiting the capillary material's liquid absorption capacity and maximum heat flux, and achieve the effects of improving liquid absorption and heat transfer capacity, large evaporation area, and expanding the scope of application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
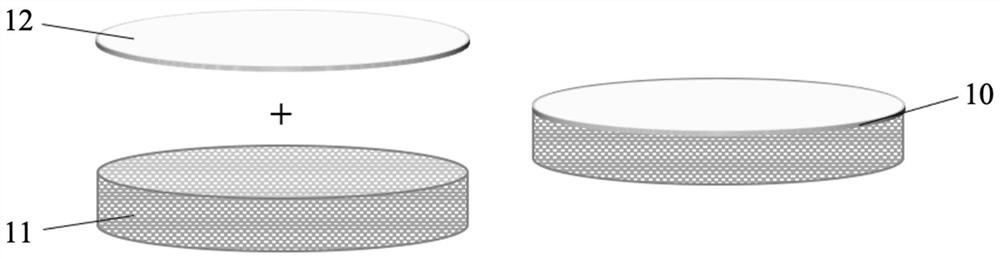
[0033] The preparation method of the evaporative phase change heat transfer member 10 is as follows:
[0034] 1) The surface of the capillary core 11 is modified with a functional group that can be chemically bonded to the hydroxyethyl methacrylate hydrogel 12, and the functional group can be a functional group with an unsaturated chemical bond, such as a methacrylate functional group;
[0035] 2) Pour the hydroxyethyl methacrylate hydrogel 12 stock solution into the mold, and adopt the optical method, thermal method or other method to make the hydrogel stock solution semi-crosslinking;
[0036] 3) The semi-solidified hydroxyethyl methacrylate hydrogel 12 is attached to the capillary core 11 , and after lamination, the hydrogel is completely cross-linked to obtain the evaporative phase change heat transfer member 10 .
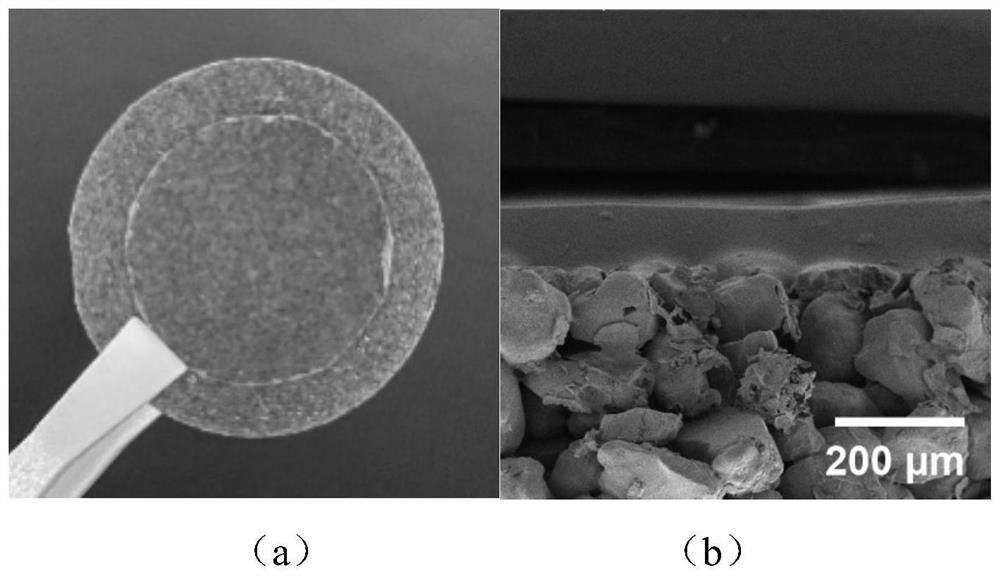
[0037] An example of the obtained evaporative phase change heat transfer member 10 is shown in the figure figure 2 As shown in (a), the upper layer is the hy...
Embodiment 3
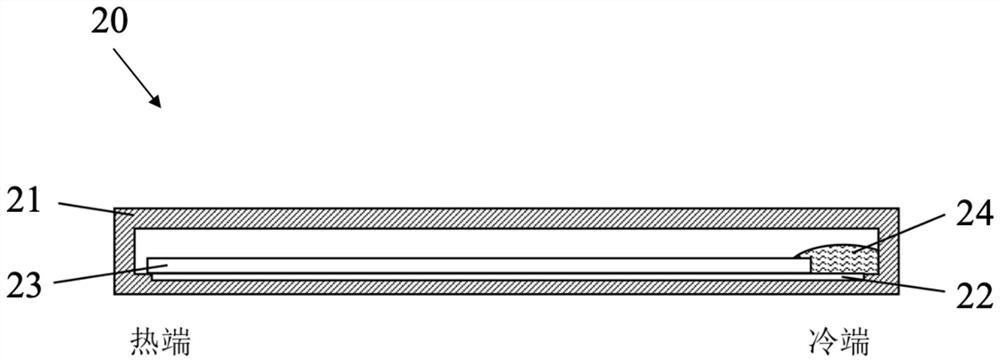
[0043] like Figure 4 As shown, the evaporative phase change heat transfer member 30 based on gel decoupling driving provided in the third embodiment includes a substrate 31 , a group of microgrooves 32 , and a hydrogel film 33 . The microgroove group 32 is formed on the base 31 and extends from the cold end to the hot end, and includes a plurality of elongated channels parallel to each other. The microgroove group 32 is located at the return inlet of the cold end and communicates with the heat transfer medium 34 (water). The hydrogel film 33 covers all the micro-grooves 32 except for the return inlet, and closely adheres to other parts (outer surfaces) of the substrate 31 except for the grooves.
[0044] When the evaporative phase change heat transfer member 30 is used for heat dissipation, the hydrogel film 33 absorbs water 34 from the microgroove group 32, the water 34 absorbs heat and evaporates into the environment mainly at the hot end, and then the water vapor condenses...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com