Split doses of phospholipid ether analogs for treatment of cancer
A cancer and dose technology, applied in preparations for in vivo experiments, drug combinations, in vivo radioactive preparations, etc., can solve problems such as reducing the therapeutic effect of radiopharmaceuticals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
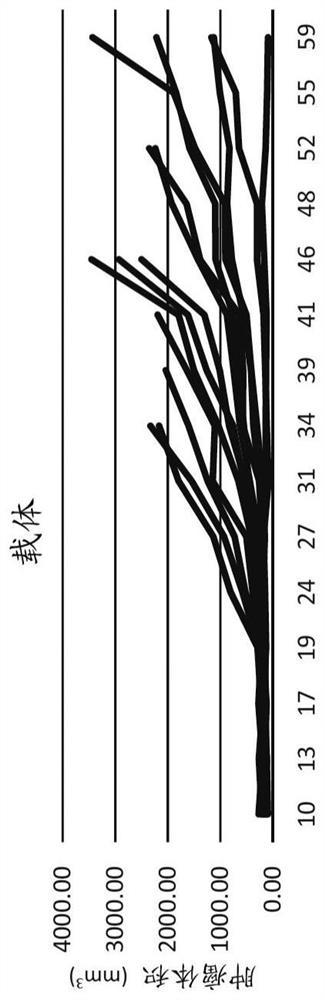
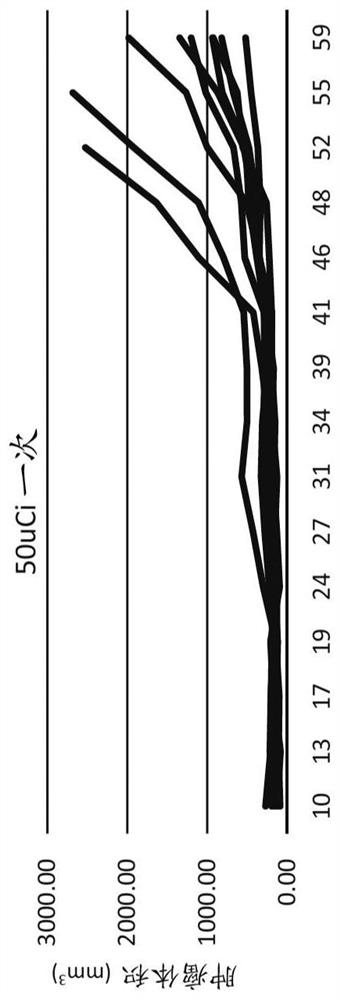
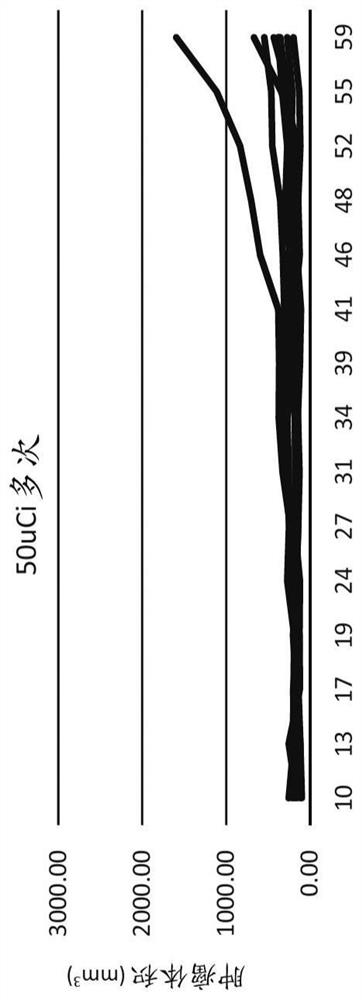
[0088] The OPM-2 cell line (human multiple myeloma) was purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Rockville, MD) and maintained in McCoy's 5a medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum. Female CB17 SCID mice, approximately 5-7 weeks old, were injected subcutaneously with 1 × 10 7 Viable cells (in -100 [mu]L Dulbecco's PBS). When the tumor size reaches a predetermined size (approximately 150-200 mm 3) to start the study. Potassium iodide concentration 0.1% potassium iodide in drinking water was administered to mice 3 days before injection and for 2 weeks after injection to block free iodide that may be present in the drug formulation. Mice were randomized into multiple dose groups. During the study, tumor volumes were measured using calipers. Tumor doubling time is calculated as TDT = D x log(2) / log(1 + r / 100), where D is the number of days between measurements and r = growth rate; r / 100 = (V2 - V1 / V1) x 100% . Statistical analysis: One-way ANOVA, Du...
Embodiment 2
[0093] Repeated / fractionated doses of CLR131 were well tolerated and better tolerated than a single equivalent dose. All CLR131 doses exhibited significant antitumor activity in this multiple myeloma model. Single-dose infusion yielded similar MM inhibition results to bortezomib. Fractionation of the dose resulted in a statistically significant reduction in tumor volume after 26 days compared to the control group. The split dose resulted in a statistically significant reduction in tumor volume at 52 days (p<0.05) compared to all other treatments. Tumor doubling time was significantly increased with fractionated doses compared to all other treatments. Fractional doses resulted in a statistically significant survival benefit.
Embodiment 3
[0095] As shown in Table 2, the split dose (cohort 5) delivered 18% more drug compared to the single bolus dose (cohort 4), as measured by the actual millicurie dose delivered to the patient. However, the mean magnitude of adverse events decreased and the median magnitude remained unchanged despite giving patients more medication. In addition, efficacy assessments also demonstrated improvement between single bolus doses and split-dose regimens. Median overall survival improved from 6.5 months (single bolus dose) to 7.4 months (fractionated dose), and the assessment of median overall survival in the split-dose group is still ongoing. Mean progression-free survival increased from 2.8 months to 2.9 months, respectively, reassessed in the split-dose group. The mean reduction in surrogate measures of efficacy was greater between cohorts, with a mean reduction of 29% in the cohort of patients who received a single bolus dose and a mean reduction of 40% in the cohort of patients who...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com