Internal combustion engine for driving propeller shaft
A technology for internal combustion engines and crankshafts, which is applied to motor-driven engines, engine components, sliding contact bearings, etc., and can solve problems such as no thrust bearing bushes and difficulties.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
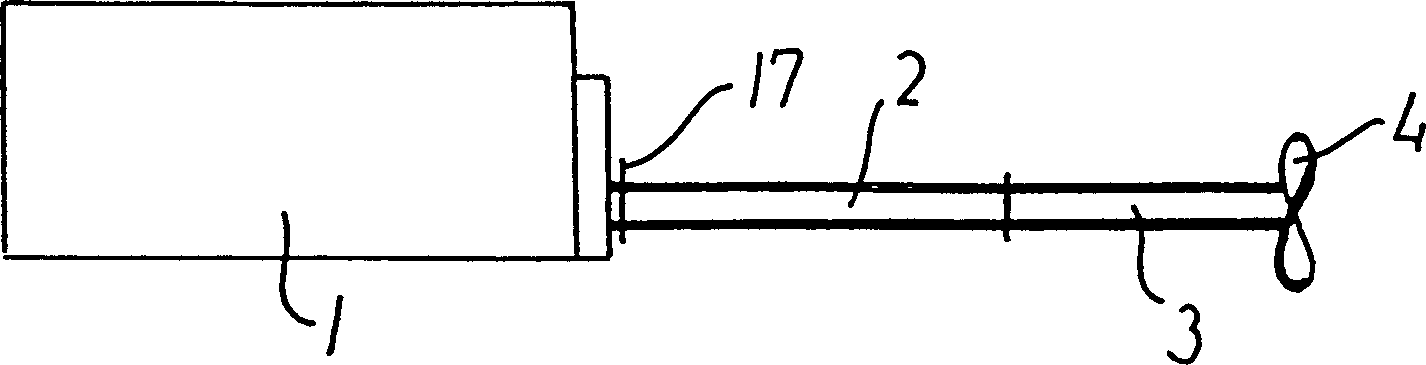
[0024] figure 1 Illustrated is an internal combustion engine 1 connected to a propeller shaft 3 with a propeller 4 through an intermediate shaft 2. The internal combustion engine may be a four-stroke engine or a two-stroke engine, such as the applicant's ME type or MC type two-stroke crosshead engine, and these engines are well known to those skilled in the art. The engine may have a cylinder diameter of 30 to 120 cm, and the number of cylinders may be, for example, 5 to 20. For a crosshead engine, the rotation speed may be 60 to 300 rpm. The output power of the engine may be 3000 to 130,000 kW, for example. The engine preferably has a relatively large output power, such as at least 30,000 kW, a cylinder number of at least 8, and a cylinder diameter of at least 70 cm.
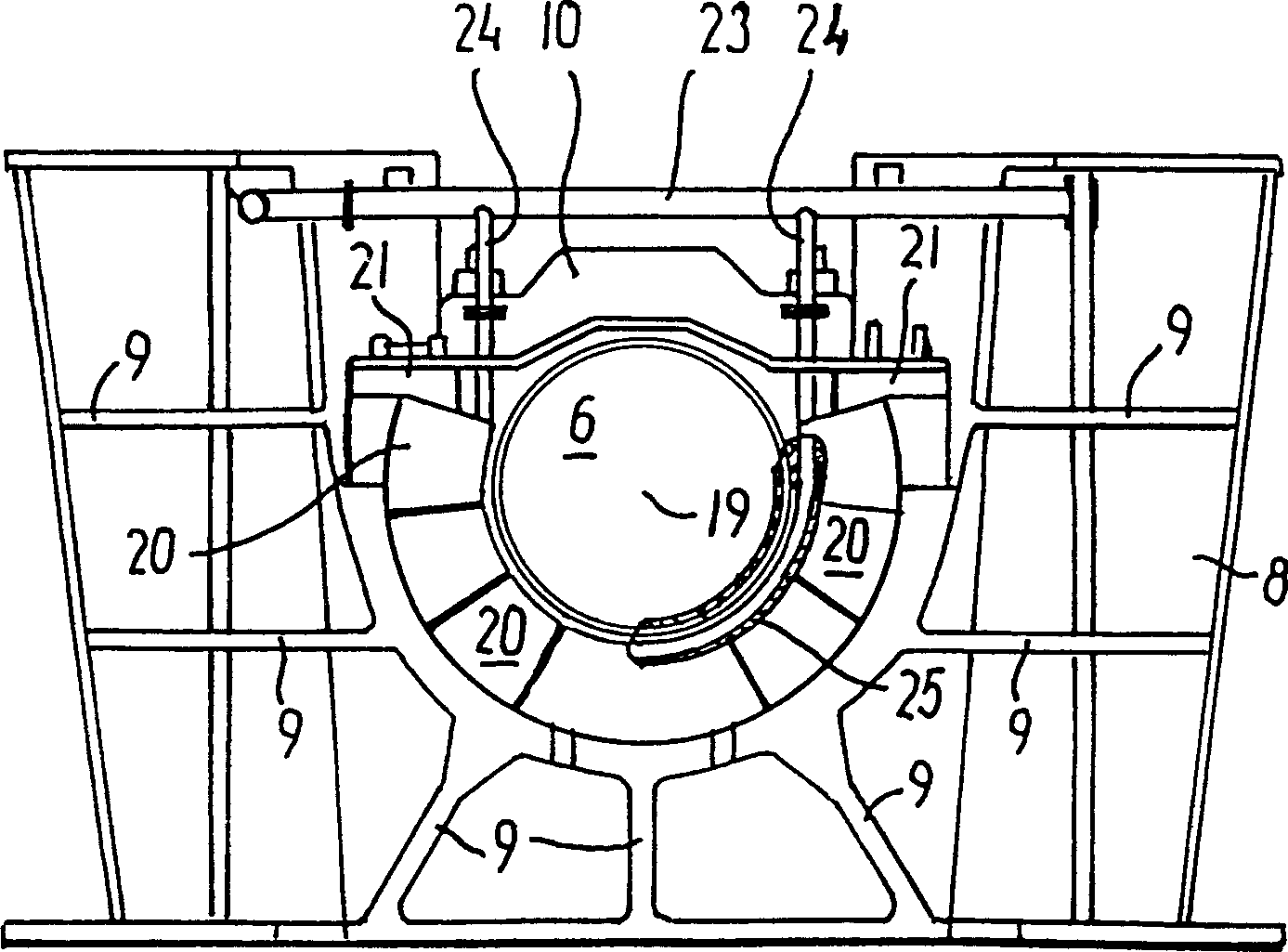
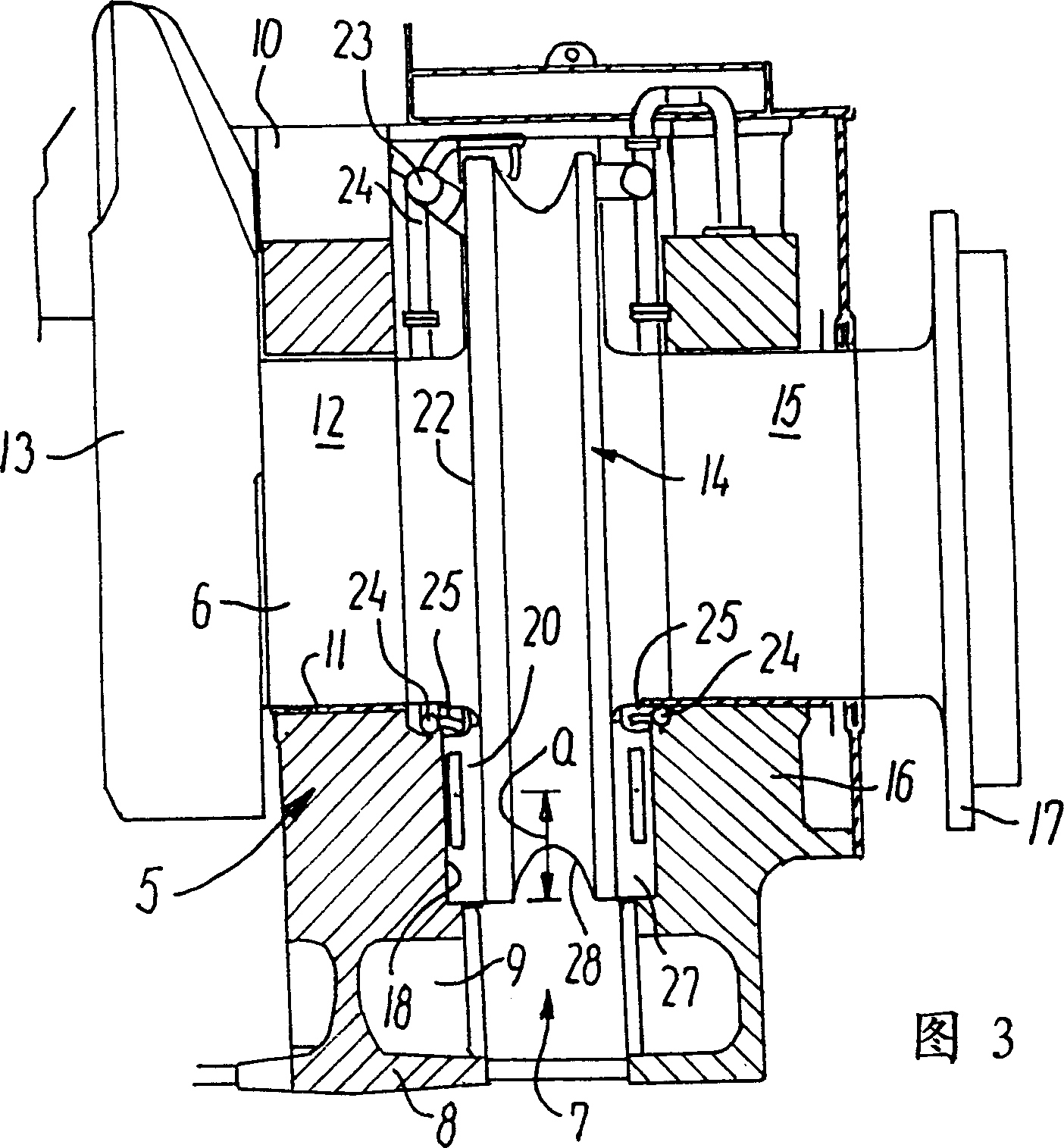
[0025] In the rearmost main bearing 5 of the crankshaft 6, the internal combustion engine 1 has a figure 2 The thrust bearing 7 in the rear view, the longitudinal section of the thrust bearing is shown in FIG. 3...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com