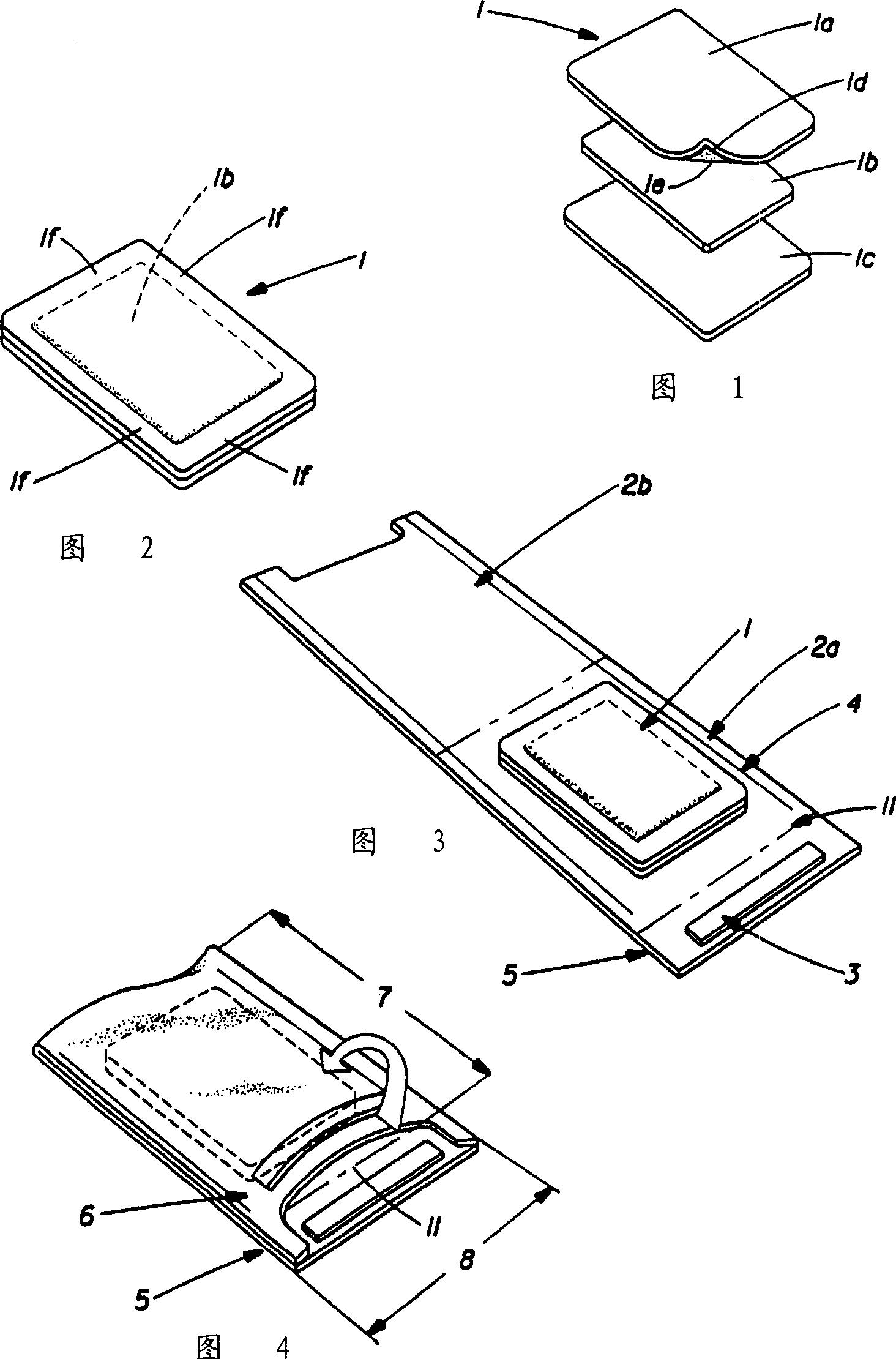
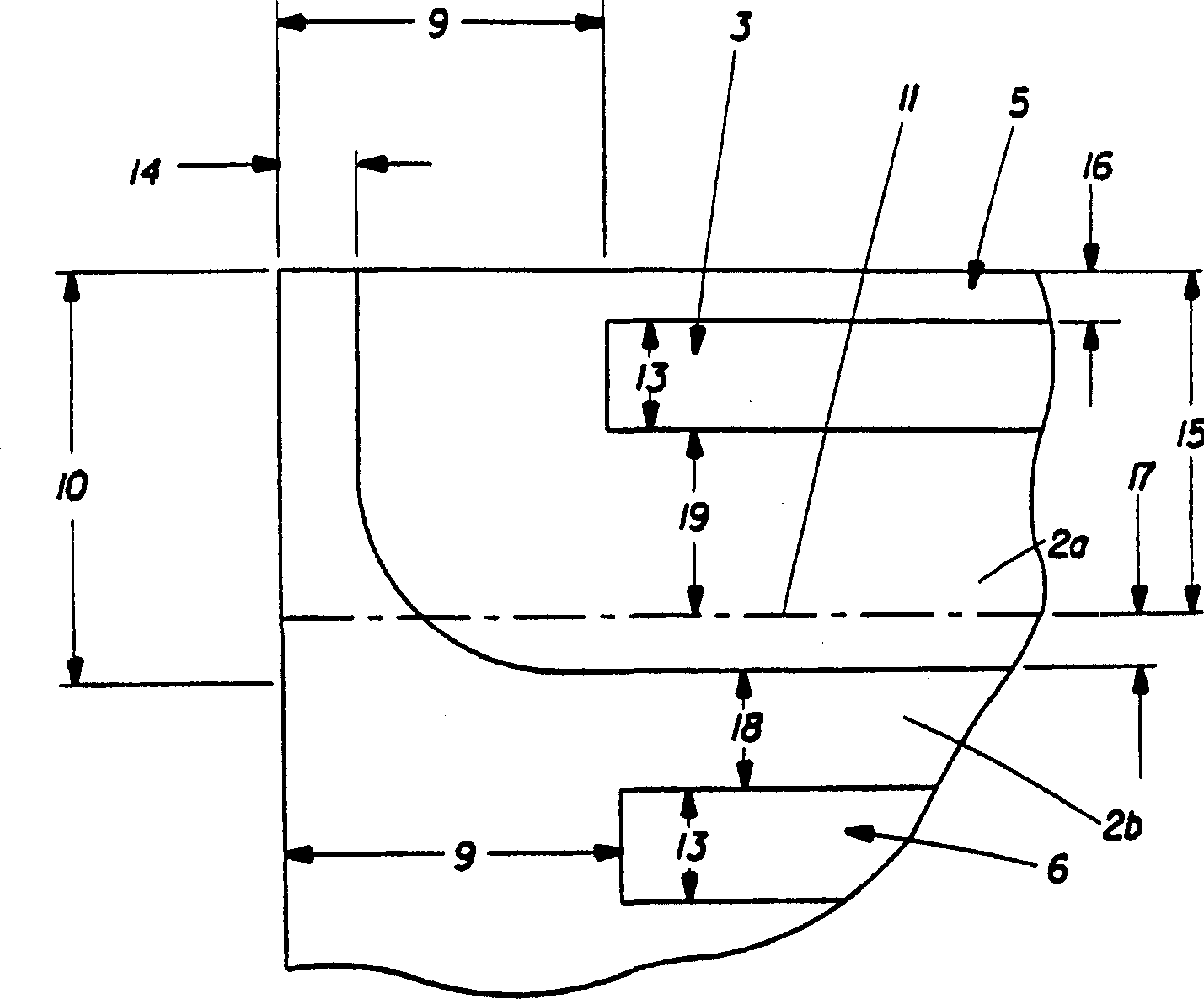
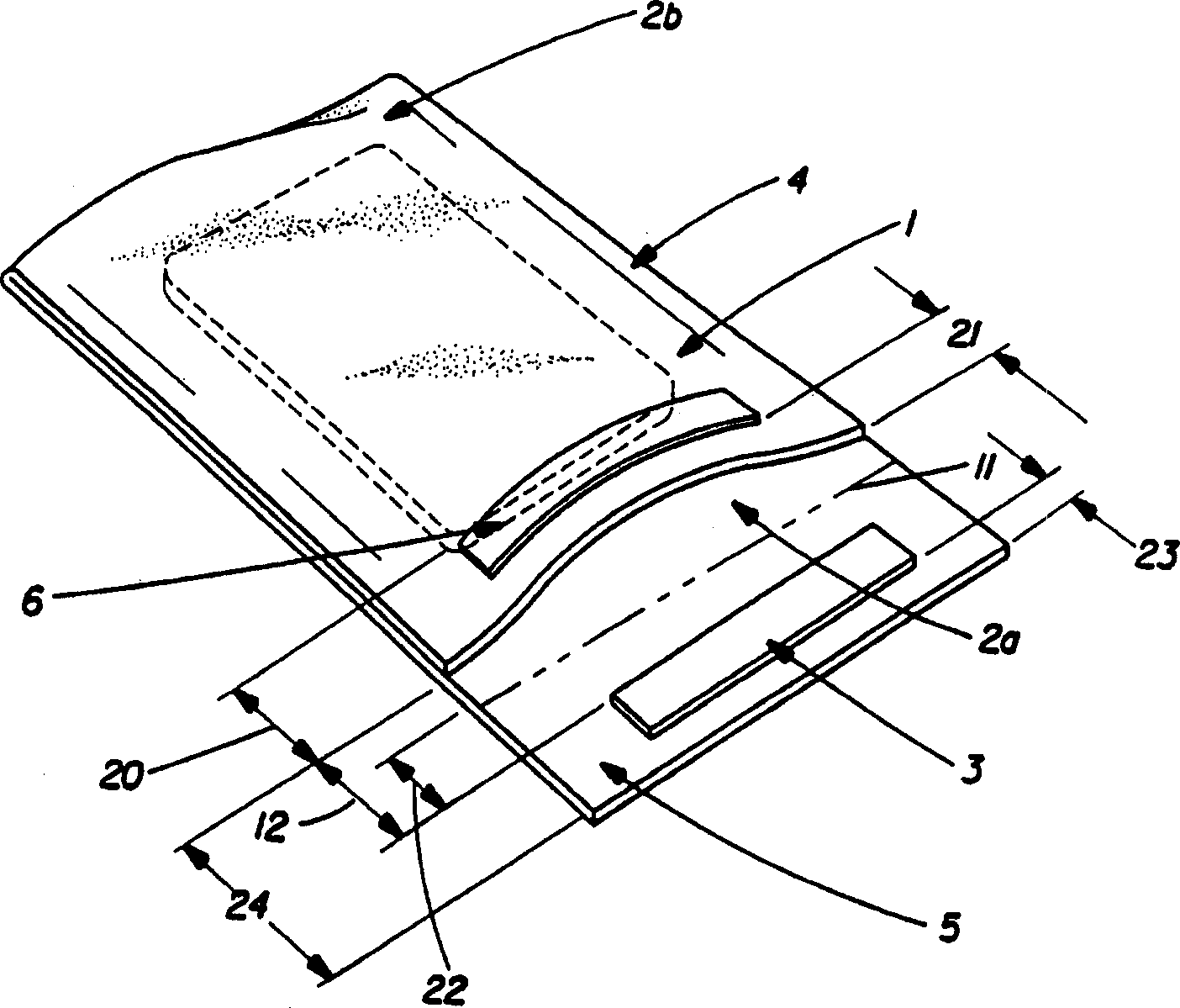
Fabric sanitization treating process
A sanitation treatment and fabric technology, applied in the field of sanitation treatment, can solve the problems of ineffective antifungal treatment, expensive and inconvenient sanitation treatment, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022]The principles of sterilization and disinfection in various environments are well known, and typical methods can be referred to in standard textbooks. Examples of various microorganisms hereinafter collectively referred to as "microorganisms" include: microorganisms, bacteria; viruses; parasites, fungi / spores, and mixtures thereof. It is well known that various disinfectants can be used to kill or inactivate microorganisms. Dead microorganisms are often classified as "cidal" and inactivated microorganisms as "static". In this context, this distinction is not important because dead and inactivated microorganisms are collectively referred to herein as "killed" and all disinfectants that "kill" microorganisms are collectively referred to herein as "antimicrobial agents". ". The activity of microorganisms can be affected by other factors including, but not limited to, concentration, pH, time of exposure to antimicrobial agents, etc.
[0023] "Bacteria" is used herein to m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com