Actively guiding robot for endoscopic inspection
An active guidance, robotic technology, applied in manipulators, surgery, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems such as not comprehensive consideration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
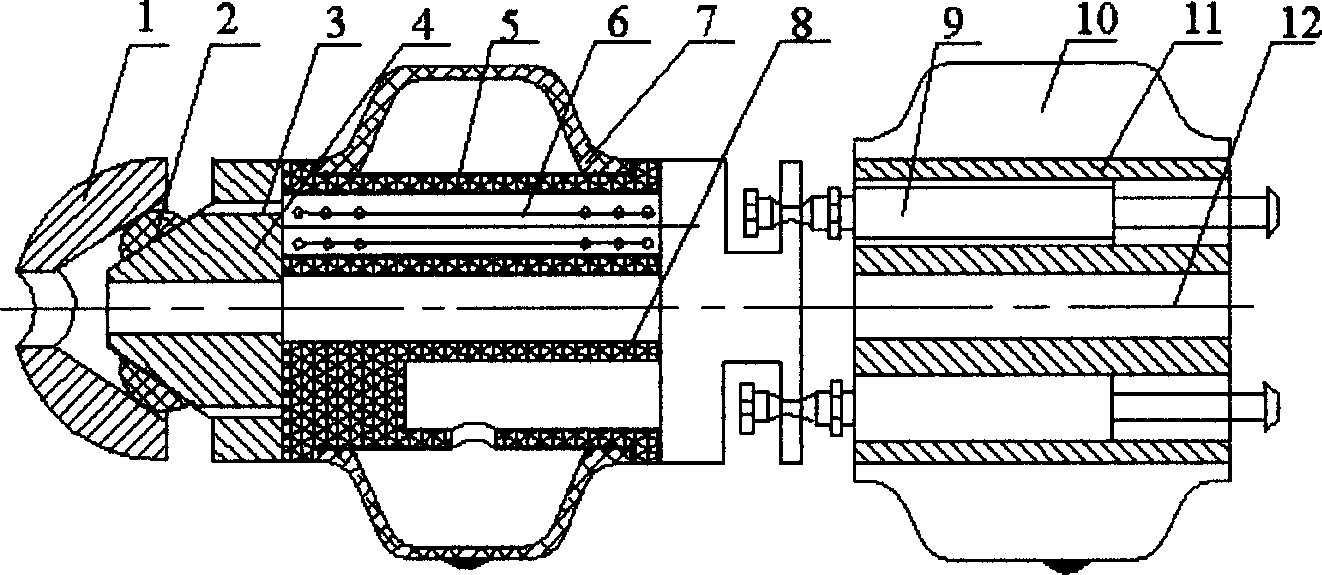
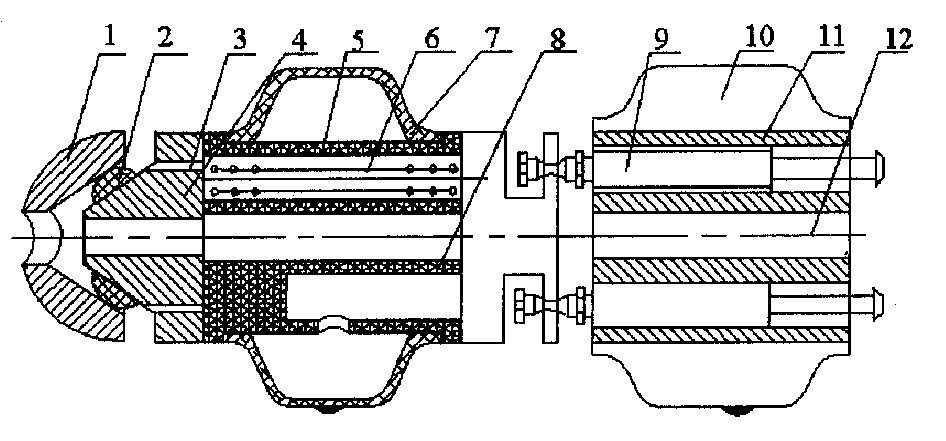
[0011] An active-guided endoscopic inspection robot suitable for inspecting the cavity of a human body is composed of a pressure sensor 3, a steering mechanism 8 and a peristaltic flexible moving mechanism. The central hole 12 runs through the head and tail of the active guiding endoscopic inspection robot, and the fiber endoscope or CCD camera is arranged in the central hole 12 . The pressure sensor 3 is located at the front of the robot. When the endoscopic inspection robot is actively guided into the cavity of the human body, the force between the robot and the cavity wall of the human body can be detected at any time, and the steering mechanism 8 and the peristaltic flexible moving mechanism can be guided to follow up. The body cavity turns or moves. The middle part is the steering mechanism 8 with the rubber cylindrical ring 5 as the main body, and the peristaltic flexible moving mechanism with gas as the power source is located at the tail. When the endoscopic inspectio...
Embodiment 2
[0013] The actively guided endoscopic inspection robot composed of a pressure sensor 3, a steering mechanism 8, and a peristaltic flexible moving mechanism capable of moving and turning is suitable for the inspection of the cecum and other distal intestinal tracts. The central hole 12 runs through the head and tail of the active guiding endoscopic inspection robot, and has a built-in endoscopic fiberscope or CCD camera. The pressure sensor 3 is composed of a guide head 1, a sensor sensitive element 2 and a conical sensor seat 4, and is located at the front end of the endoscopic inspection robot. The sensor sensitive elements 2 are evenly distributed on the tapered sensor seat 4 to form an array sensor distributed at equal intervals. In order to improve flexibility and reduce volume, the sensitive element 2 of the sensor can adopt pressure-sensitive conductive rubber. The steering mechanism 8 is located behind the pressure sensor 3, and its main body is a rubber cylindrical ri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com