Exhaust denitrification device of engine
An engine and denitrification technology, applied in exhaust devices, engine components, engine control, etc., can solve the problems of large structure, exhaust temperature rise, reduced engine reliability and durability, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
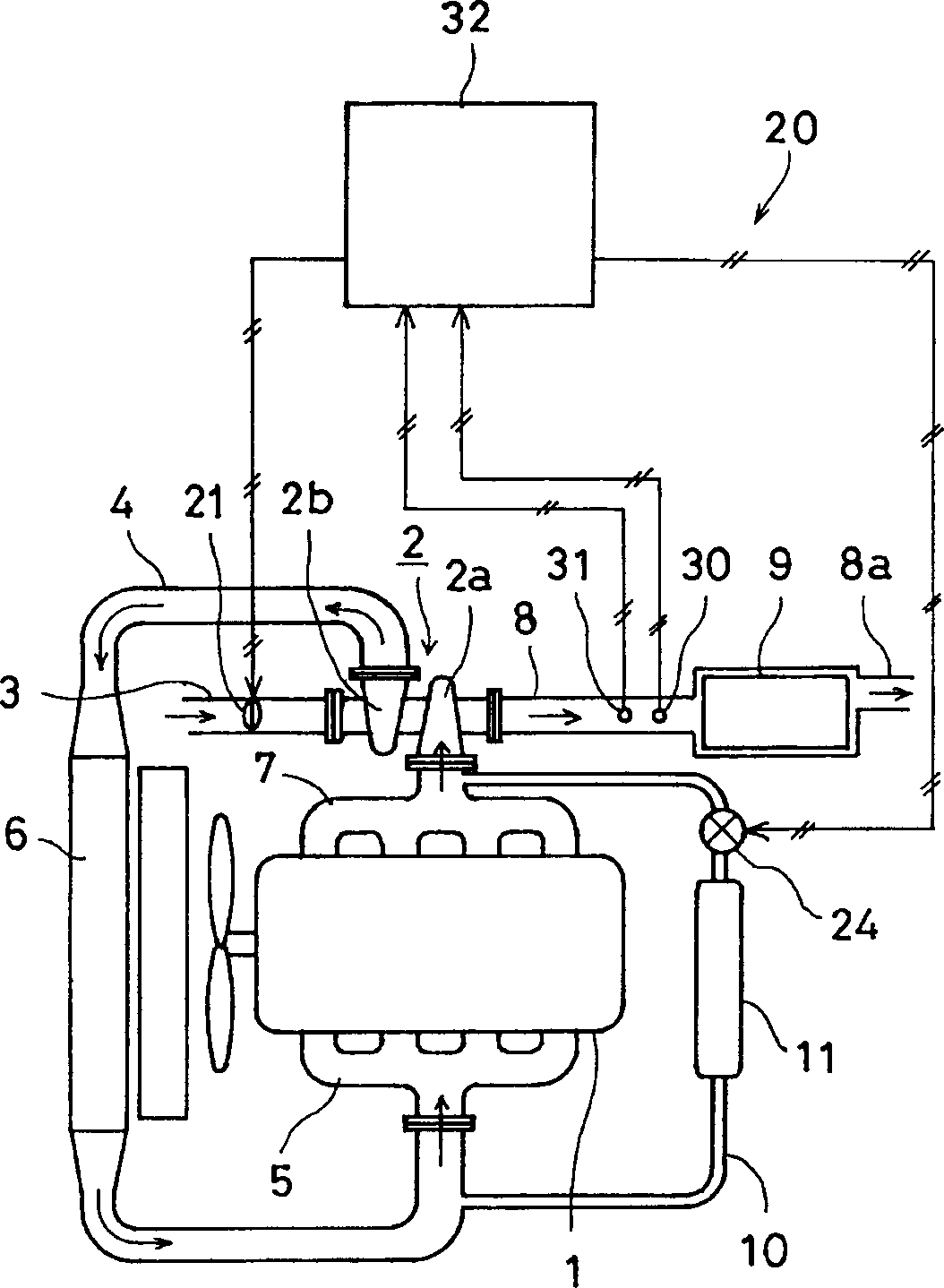
[0047] figure 1 It is a conceptual diagram of an engine exhaust gas denitrification device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. The engine 1 has a turbocharger 2 consisting of an exhaust turbine 2a and a compressor 2b. The exhaust turbine 2a is mounted on an exhaust manifold 7, and its outlet is provided with an exhaust pipe 8. A NOx absorbing catalyst 9 is installed in the exhaust pipe 8, and a tailpipe 8a is installed at the outlet thereof. A suction pipe 3 is installed at the suction port of the compressor 2b connected to the exhaust turbine 2a, and a suction throttle valve 21 with an adjustable opening area is arranged at the suction pipe 3. An air supply pipe 4 is attached to the discharge port of the compressor 2b, and a branch pipe 5 is connected to it, and an intercooler 6 is installed on the air supply pipe 4 .
[0048] The downstream of the intercooler 6 on the air supply pipe 4 and the upstream of the exhaust turbine 2 a in the exhaust branch pipe ...
Embodiment 2
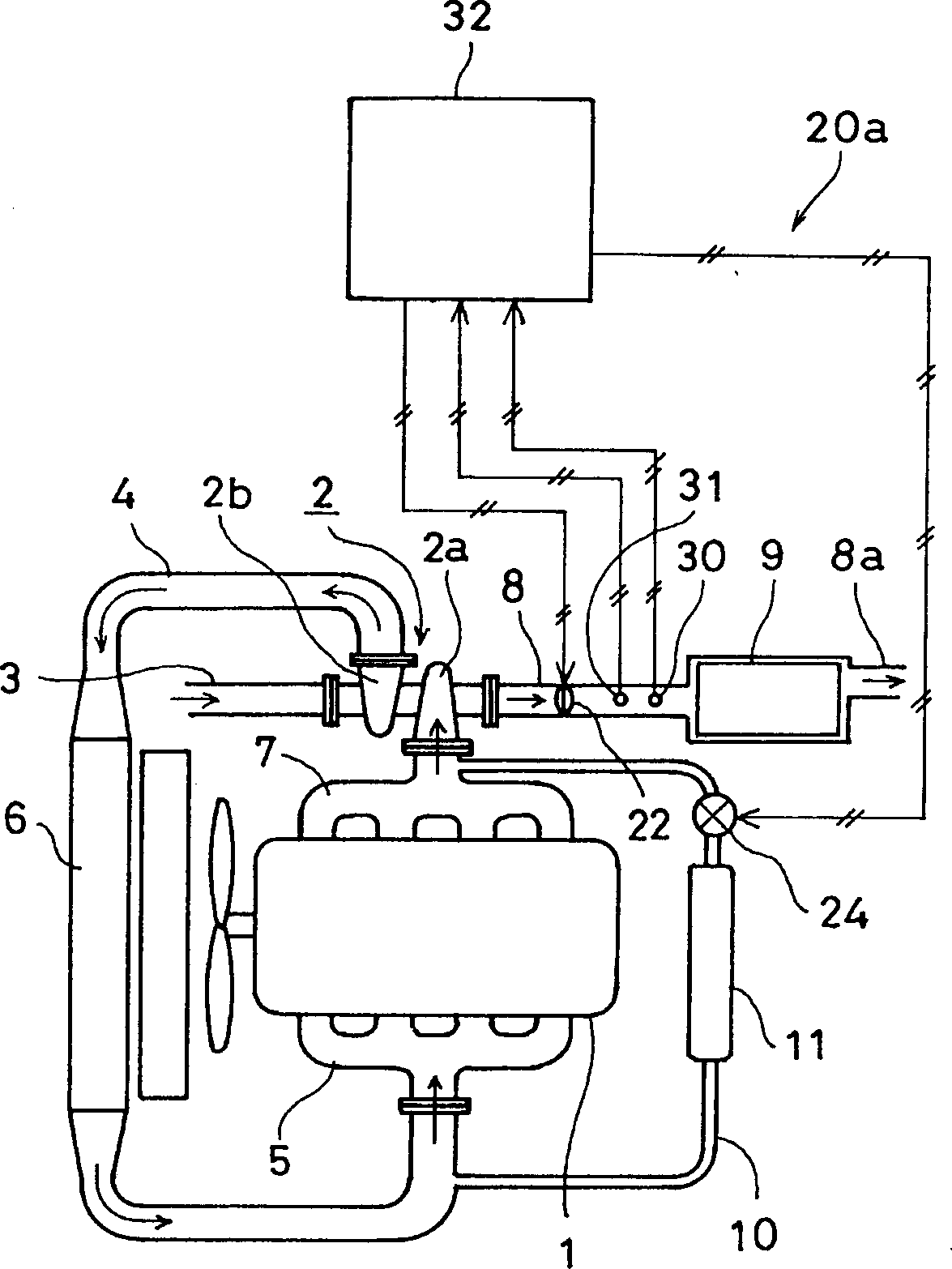
[0060] image 3 It is a conceptual diagram of the exhaust gas denitrification device of the second embodiment. Components that are the same as those in Embodiment 1 are denoted by the same symbols and their descriptions are omitted, and only the different parts will be described. exist image 3 In this embodiment, an exhaust throttle valve 22 is installed in the exhaust pipe 8 instead of the intake throttle valve 21, and is connected with the control device 32 to form an exhaust gas recirculation amount control mechanism 20a. When the air-fuel ratio of the exhaust gas is brought into a rich state, the control device 32 outputs a control signal to throttle the exhaust throttle valve 22 and open the EGR valve 24 . In this way, the pressure on the exhaust side rises and creates a large pressure difference with the supply air. Its action and effect are the same as those of Embodiment 1, so its description is omitted.
Embodiment 3
[0062] Figure 4 It is a conceptual diagram of the exhaust gas denitrification device of the third embodiment. Components that are the same as those in Embodiment 1 are denoted by the same symbols and their descriptions are omitted, and only the different parts will be described. exist Figure 4 In this embodiment, the suction throttle valve 21 is removed, and the air supply pipe 4 and the tail pipe 8a are connected with the air extraction pipe 12, and the air extraction valve 23 is provided in the air extraction pipe 12. The extraction valve 23 is connected with the control device 32 to form an exhaust gas recirculation amount control mechanism 20b. When the air-fuel ratio of the exhaust gas becomes rich, the control device 32 outputs a control signal to open the exhaust valve 23 to release a part of the supplied air to the outside. This reduces the supply air volume to make the exhaust gas rich, while keeping the supply air pressure to exhaust pressure ratio very small to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com