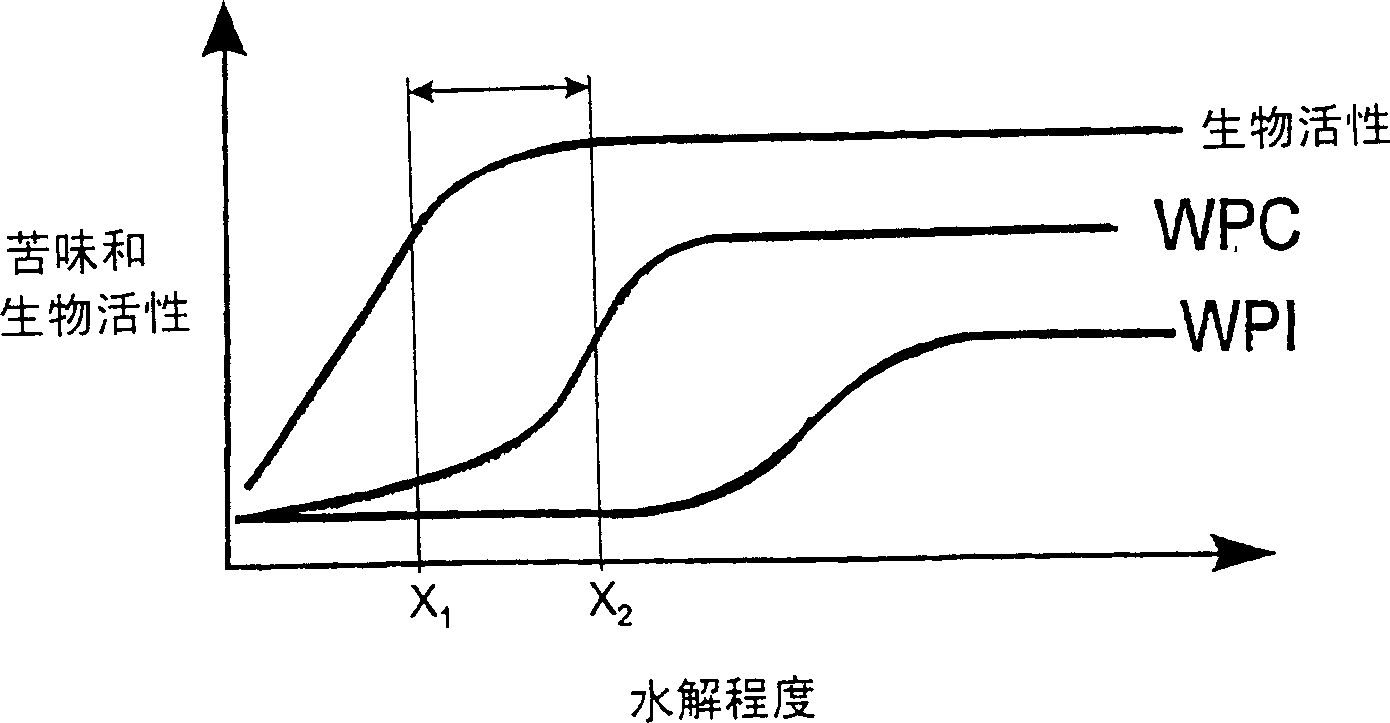
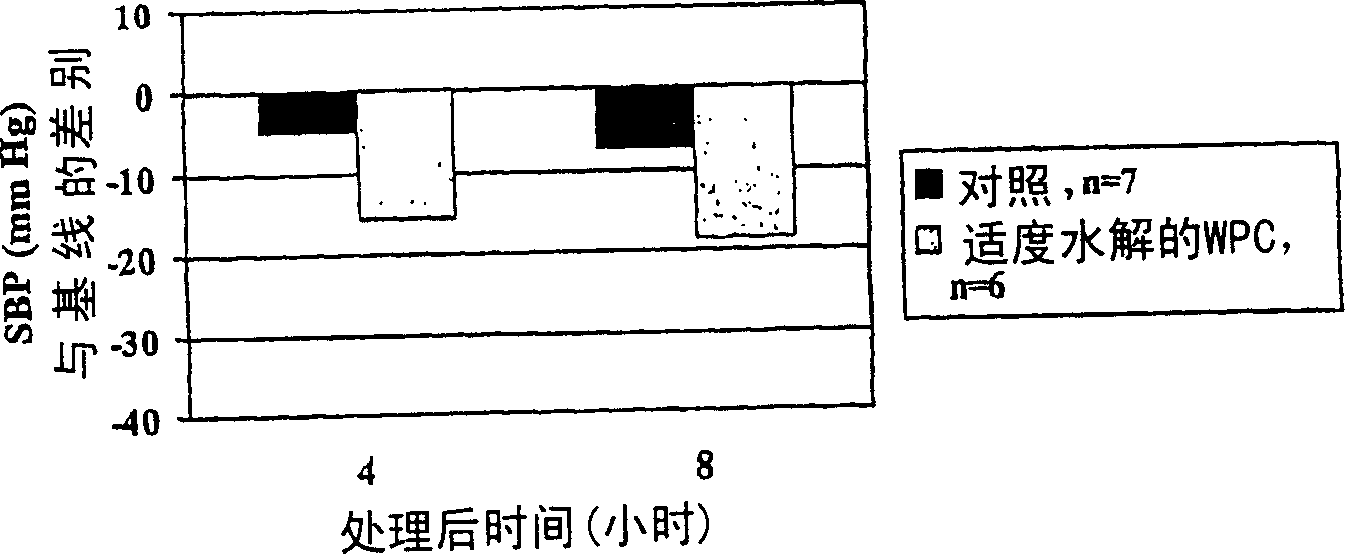
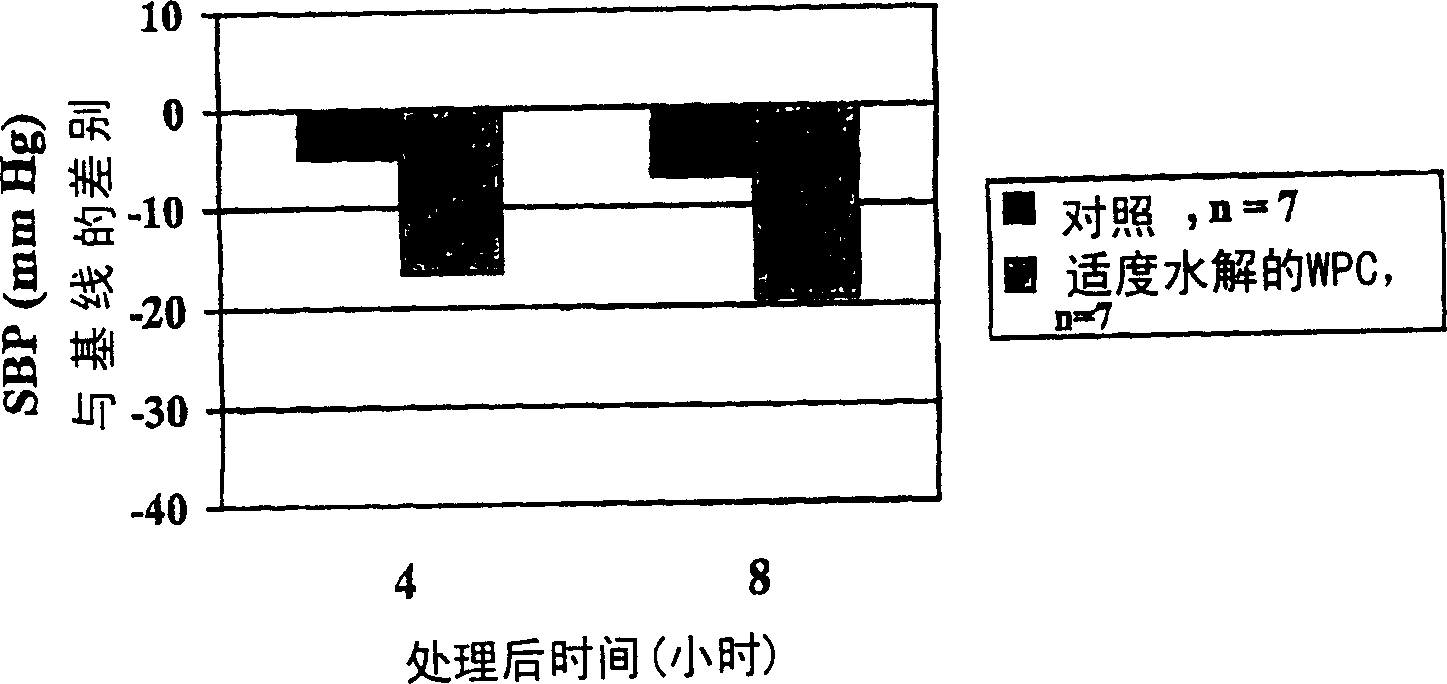
Improved bioactive whey protein hydrolysate
A whey protein hydrolysis and whey protein technology, which is applied in the field of hydrolyzed whey protein products, can solve the problems that can not be used to terminate whey protein, the solubility of the final product decreases, and unfavorable food ingredients, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0110] Trial production of WPI mild hydrolyzate
[0111] Whey protein isolate produced by cationic ion exchange technology with a protein content greater than 90% w / w (ALACEN TM 895) is reconstituted at 20% solid matter in water (50°C). Restoration of ALACEN TM 895 was transferred to a 150 L box at 50°C. Water (50°C) was added to the tank to give a final solids volume of 4%. The solution was stirred and Neutrase (E:S 0.9%) was added.
[0112] Two hours after enzyme addition, the first hydrolyzate was pumped through the UHT unit. Enzymes were inactivated by heating the hydrolyzate to 88°C using direct steam injection, and the hydrolyzate was held at this temperature for 1.5 seconds. The hydrolyzate is cooled instantaneously to ambient temperature by a shell and tube heat exchanger.
[0113] The hydrolyzate is then dehydrated and dried.
[0114] The hydrolyzate prepared by the method of embodiment 1 has the following characteristics:
[0115] Solubility: 95%
[0116] ...
Embodiment 2
[0125] The hydrolysis reaction was repeated as described above in Example 1 (10% total solids, E:S 0.9%, 150 L). After inactivation, the hydrolyzate is immediately dehydrated and dried.
[0126] The hydrolyzate prepared by this method has the following characteristics, which are determined by the elaboration of said Example 1:
[0127] Solubility: 97%
[0128] Thermal stability: 120°C for 10 minutes @ TS solubility 96%
[0129] In vitro ACE-I activity: 503mg / L IC50
[0130] Foaming ability: significantly increased than non-hydrolyzed WPI
[0131] Gelling property: significantly increased than non-hydrolyzed WPI
[0132] Flavor: Significantly better than WPC-based mild hydrolysates
[0133] Appearance: transparent yellowish
Embodiment 3
[0135] The hydrolysis reaction of Example 1 was repeated as described above (4% total solid matter, E:S0.9%, 150 L). Four hours after enzyme addition, the first hydrolyzate was pumped through the UHT apparatus using the same conditions as in Example 1.
[0136] The hydrolyzate prepared by this method has the following characteristics, which are determined by the elaboration of said Example 1:
[0137] In vitro ACE-I activity: 230mg / L IC50
[0138] Foaming ability: significantly increased than non-hydrolyzed WPI
[0139] Gelling property: significantly increased than non-hydrolyzed WPI
[0140] Flavor: Significantly better than WPC-based mild hydrolysates
[0141] Appearance: transparent yellowish
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com