Adjustable extemal cavity laser
A technology of lasers and beams, applied in lasers, laser components, semiconductor lasers, etc., can solve the problems of adjustable external cavity laser size, cost, complexity, and increased sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
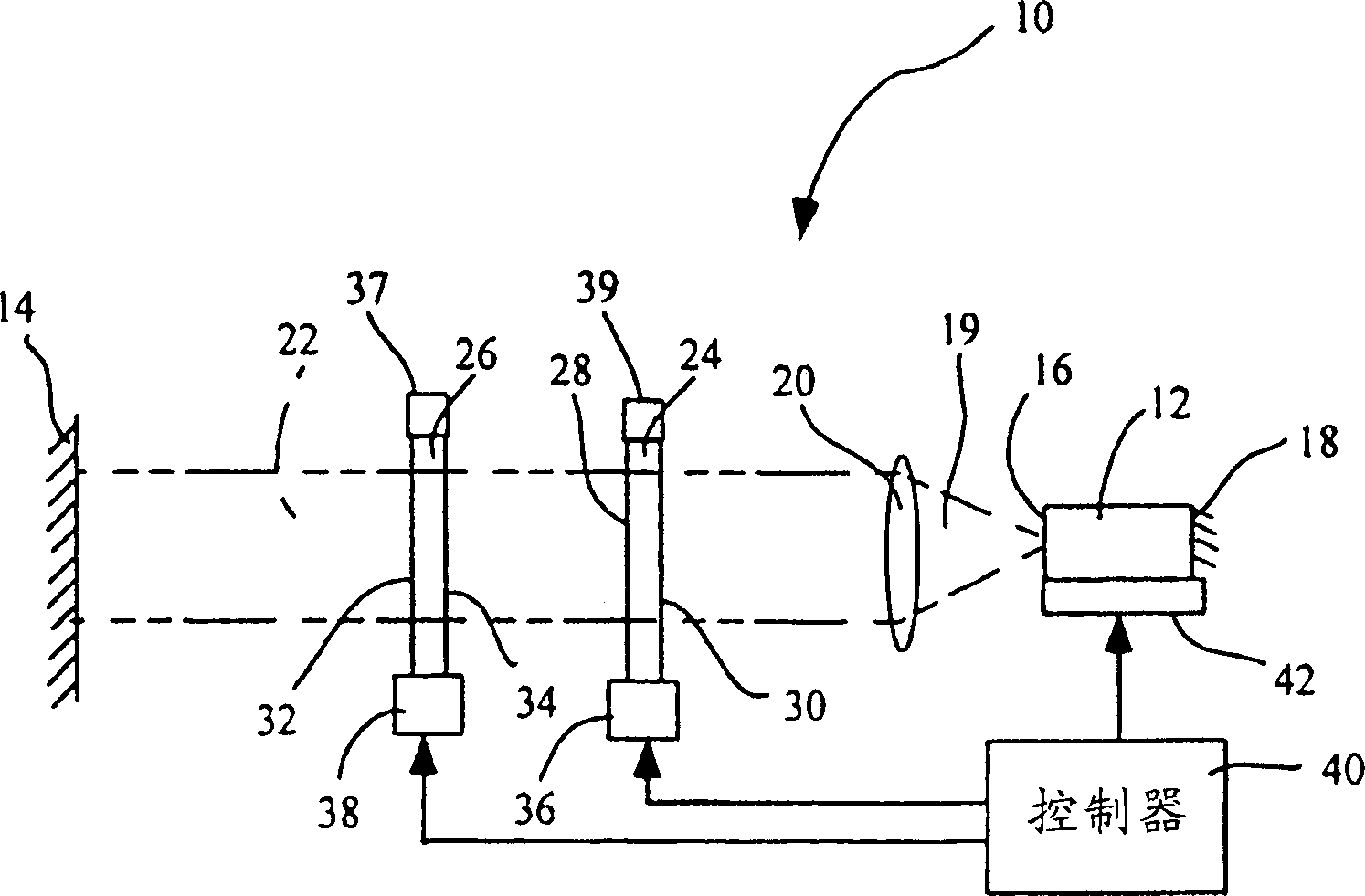
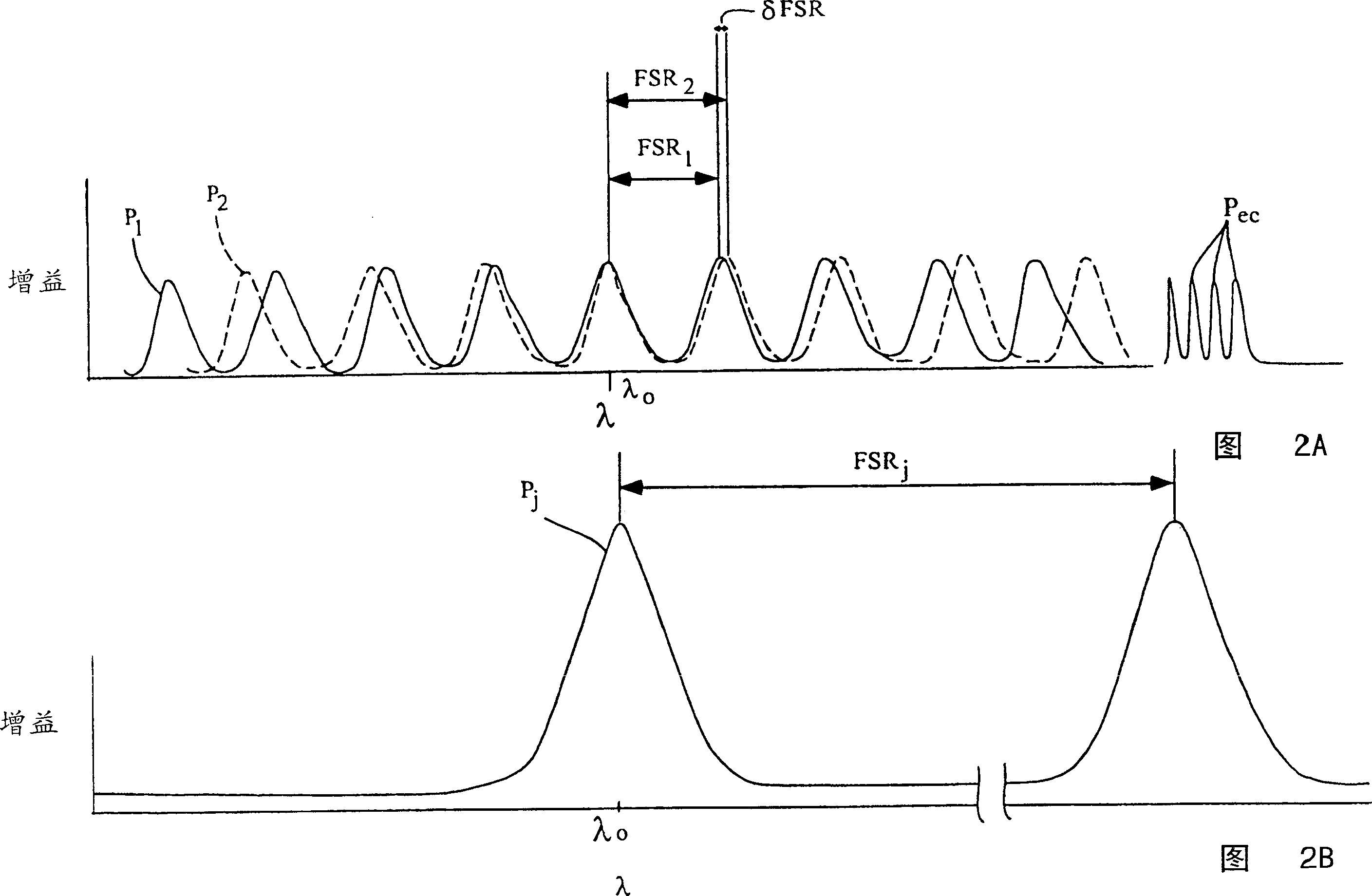
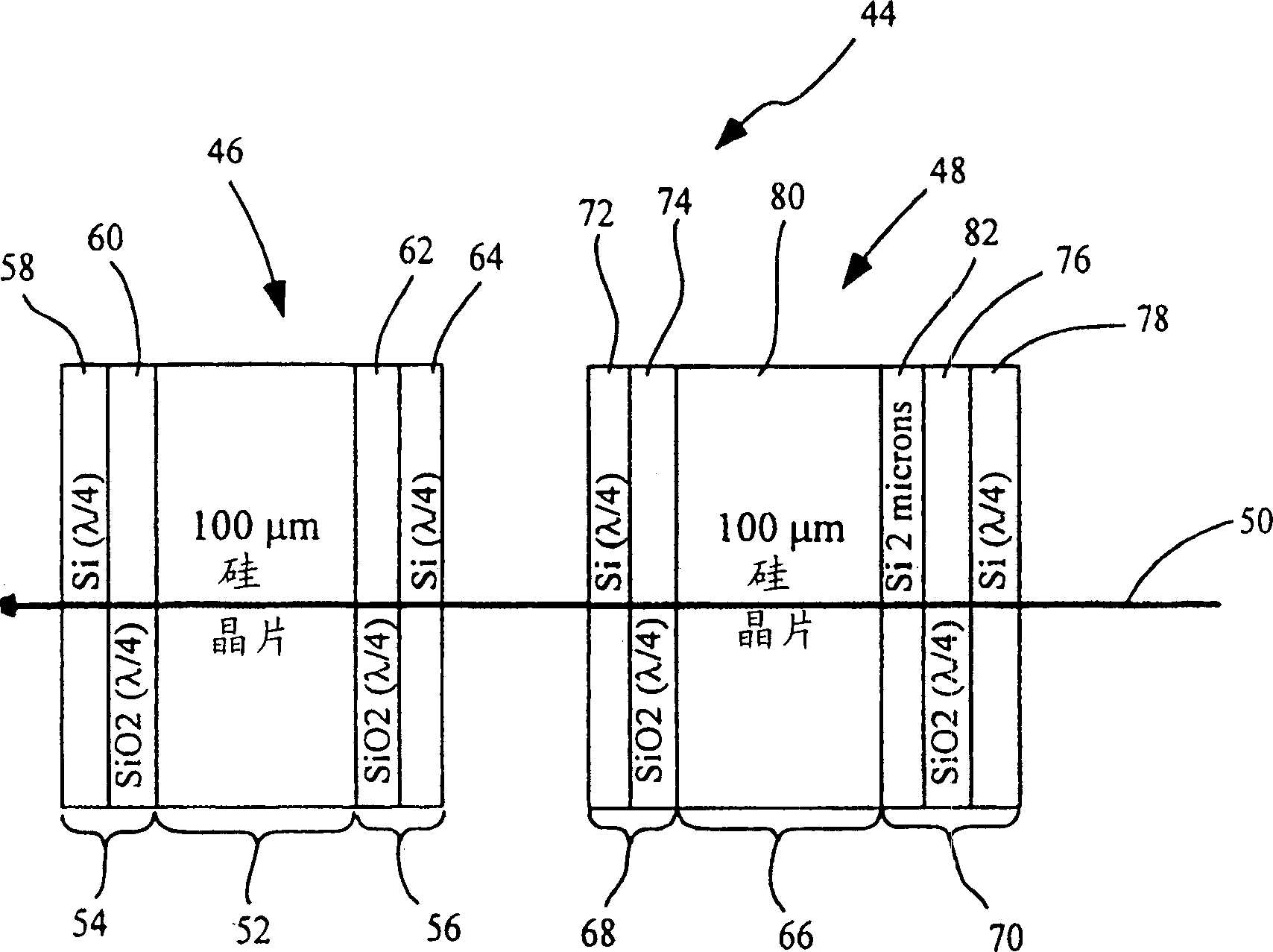
[0040] More particular reference to the drawings is to illustrate the Figure 1 to Figure 1 The invention is embodied in the apparatus shown in 7. It should be understood that the device may vary in configuration and detail of components, and the method may vary in detail and order of actions without departing from the basic concept disclosed. The invention is primarily disclosed in terms of the use of external cavity lasers. However, the invention can be used with various types of laser devices and optical systems. It is to be understood that the terminology used herein is for the purpose of describing particular embodiments only and is not limiting, since the scope of the present invention is defined only by the claims. The relative sizes of components, as well as the distances between them, shown in the figures are of many examples exaggerated for clarity and therefore should not be considered limiting.
[0041] see figure 1 , which shows a laser device 10 of the presen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com