Noise reduction pre-preocessor for digital video using previously generated motion vecotrs and adaptive spatial filering
An adaptive, motion vector technology, used in digital video signal modification, image data processing, television, etc., to solve problems such as interfering with compression system performance, reducing image quality, and reducing apparent focus.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
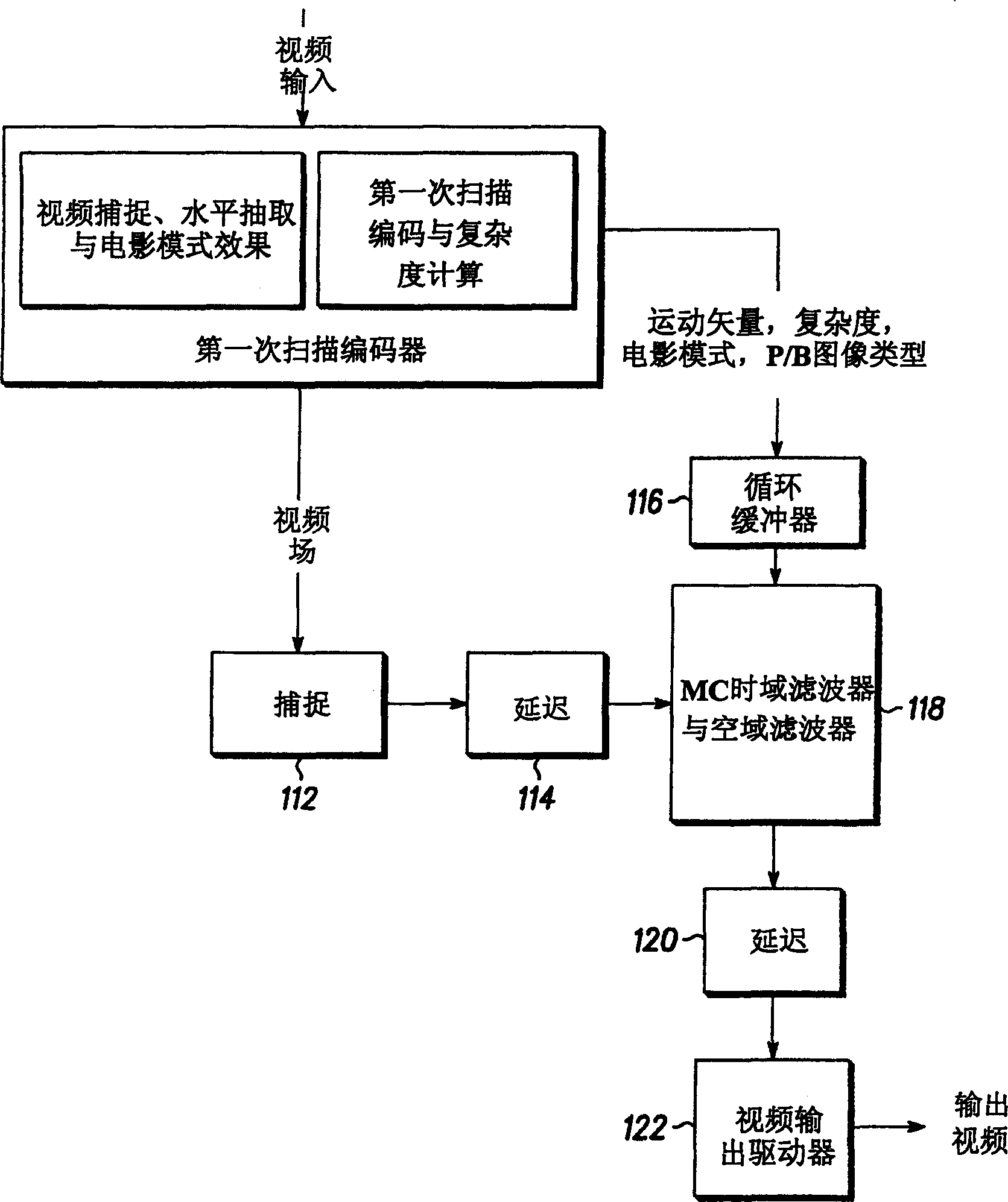
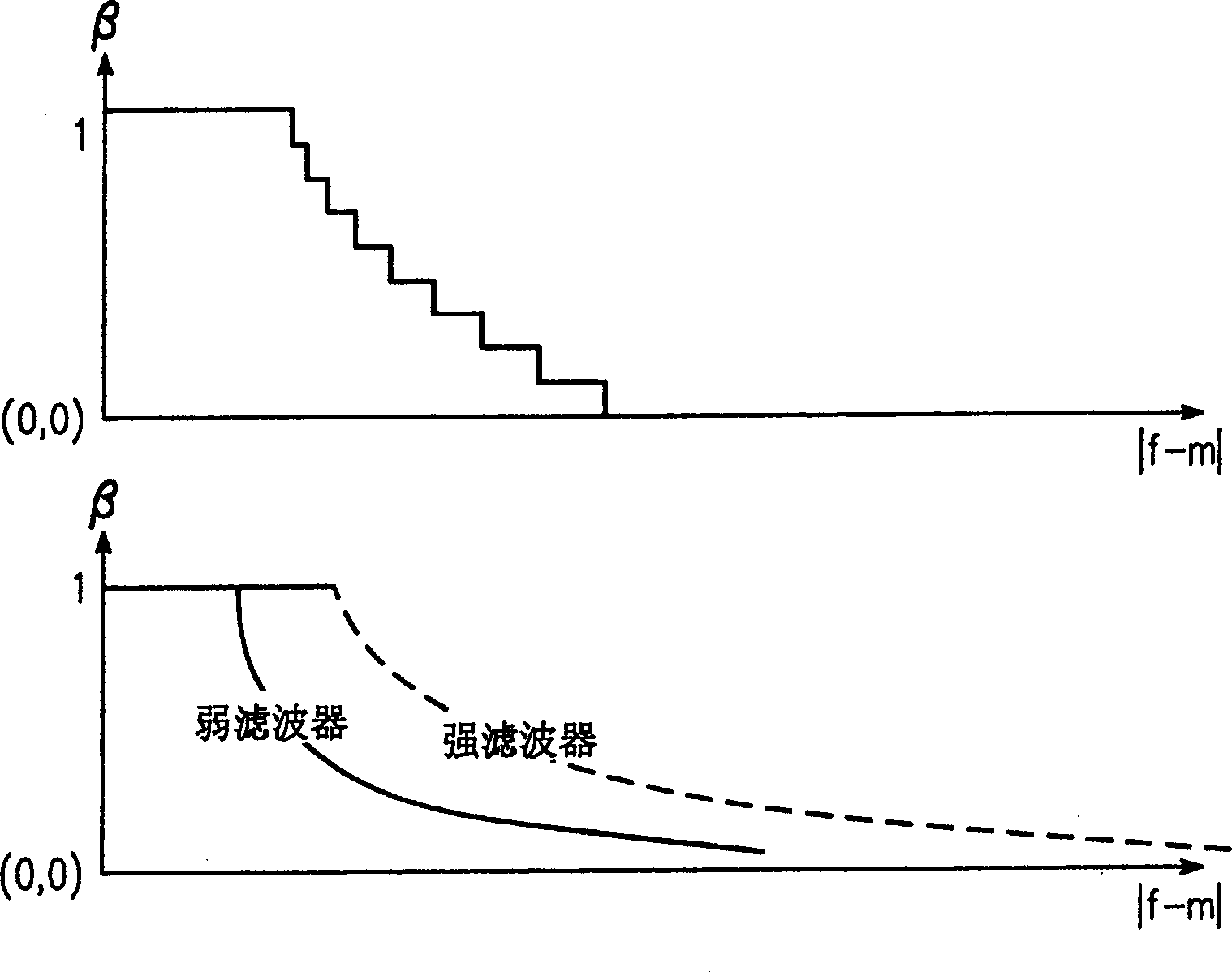
[0017] The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for noise reduction in video systems by utilizing pregenerated motion vectors to apply motion compensated temporal filtering and applying adaptive spatial filtering.
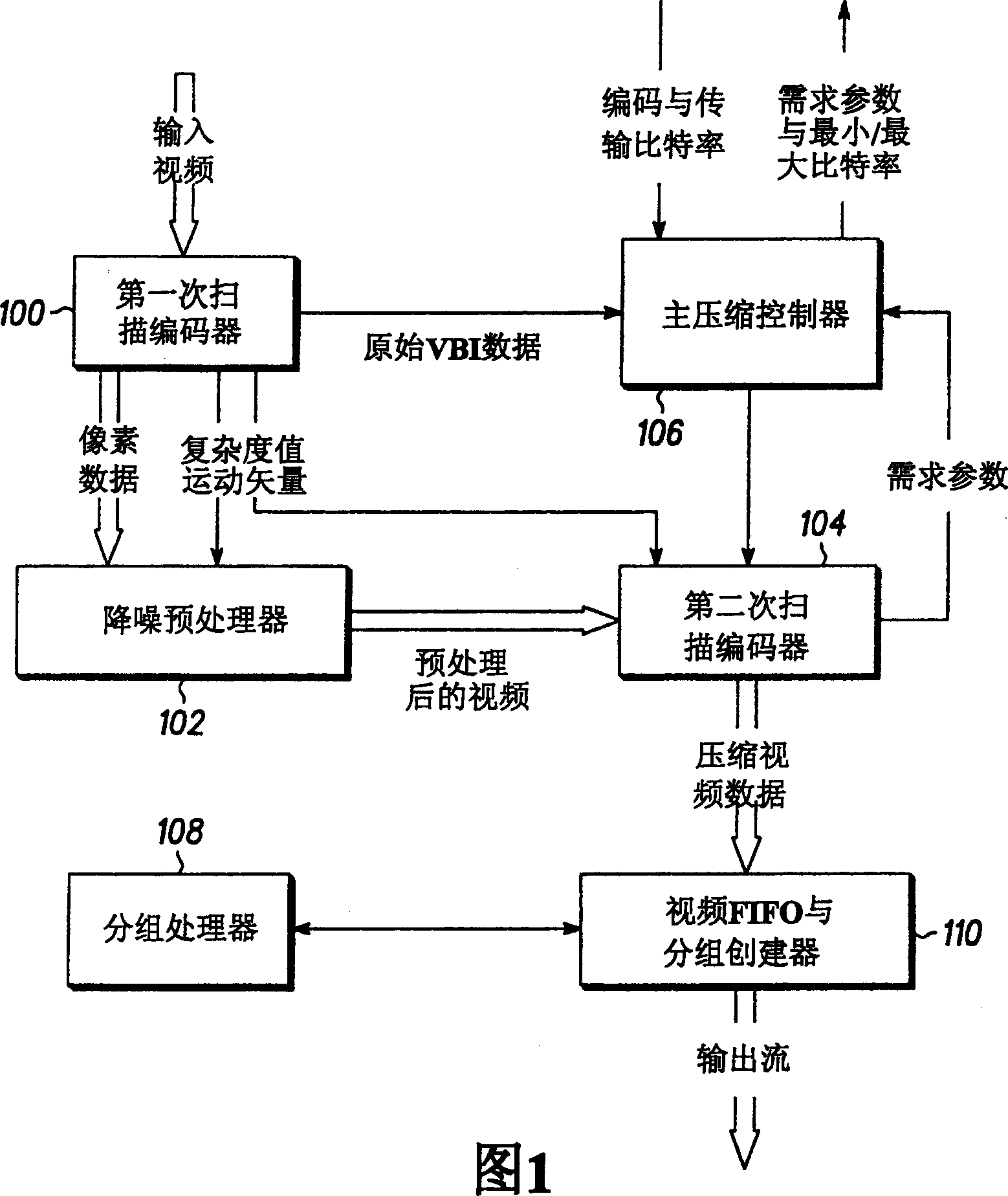
[0018] FIG. 1 depicts a block diagram of an example processing architecture of a video frame encoding subsystem in accordance with the present invention. This subsystem is part of a larger digital video encoding system.
[0019] This subsystem consists of the following components:
[0020] scan the encoder 100 for the first time;
[0021] Noise reduction preprocessor 102;
[0022] scan the encoder 104 for the second time;
[0023] Master Compression Controller (MCC) 106;
[0024] packet processor 108; and
[0025] Video FIFO queue and packet creator 110.
[0026] System overview
[0027] The first pass encoder 100, the noise reduction preprocessor 102 and the second pass encoder 104 jointly operate to estimate the complexity of the input vide...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com