Solar energy semiconductor air conditioning system
An air-conditioning system and semiconductor technology, applied to semiconductor devices, photovoltaic modules, lighting and heating equipment, etc., can solve the problems of low cooling capacity, poor practicability, and low cooling efficiency, and achieve the effect of reasonable structure, simple structure, and flexible adjustment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Example Embodiment
[0010] The specific structure, working process and best implementation mode of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
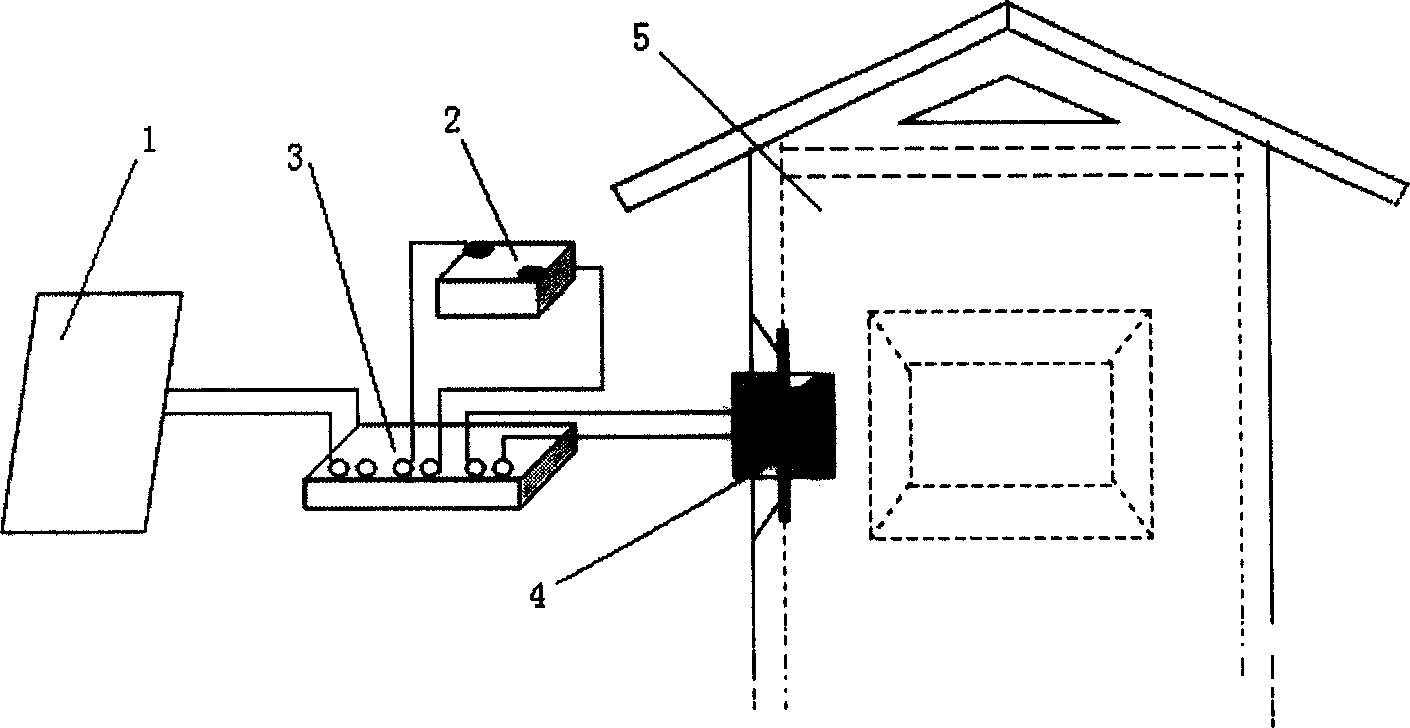
[0011] figure 1 The structural diagram of the solar semiconductor air-conditioning system provided by the present invention. The air conditioning system includes a semiconductor refrigeration / heating module 4 arranged in a cooling / heating space 5, a solar photoelectric converter 1 for supplying DC power to the semiconductor refrigeration / heating module, an energy storage device 2 for storing excess electricity, and A numerical control matcher 3 electrically connected with the solar photoelectric converter, the energy storage device and the semiconductor refrigeration / heating module. The solar photoelectric converter is composed of a plurality of polycrystalline silicon battery panels, which are installed outdoors; the battery panels are connected in series or in parallel to provide different charg...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com