Solid-state image sensor, manufacturing method for solid-state image sensor, and camera
A technology of a solid-state imaging device and a manufacturing method, which is applied in the direction of electric solid-state devices, semiconductor devices, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as shadows, shortening of the exit pupil distance, and image quality degradation, and achieve the reduction of shadows and shortening of the exit pupil distance. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
[0043]
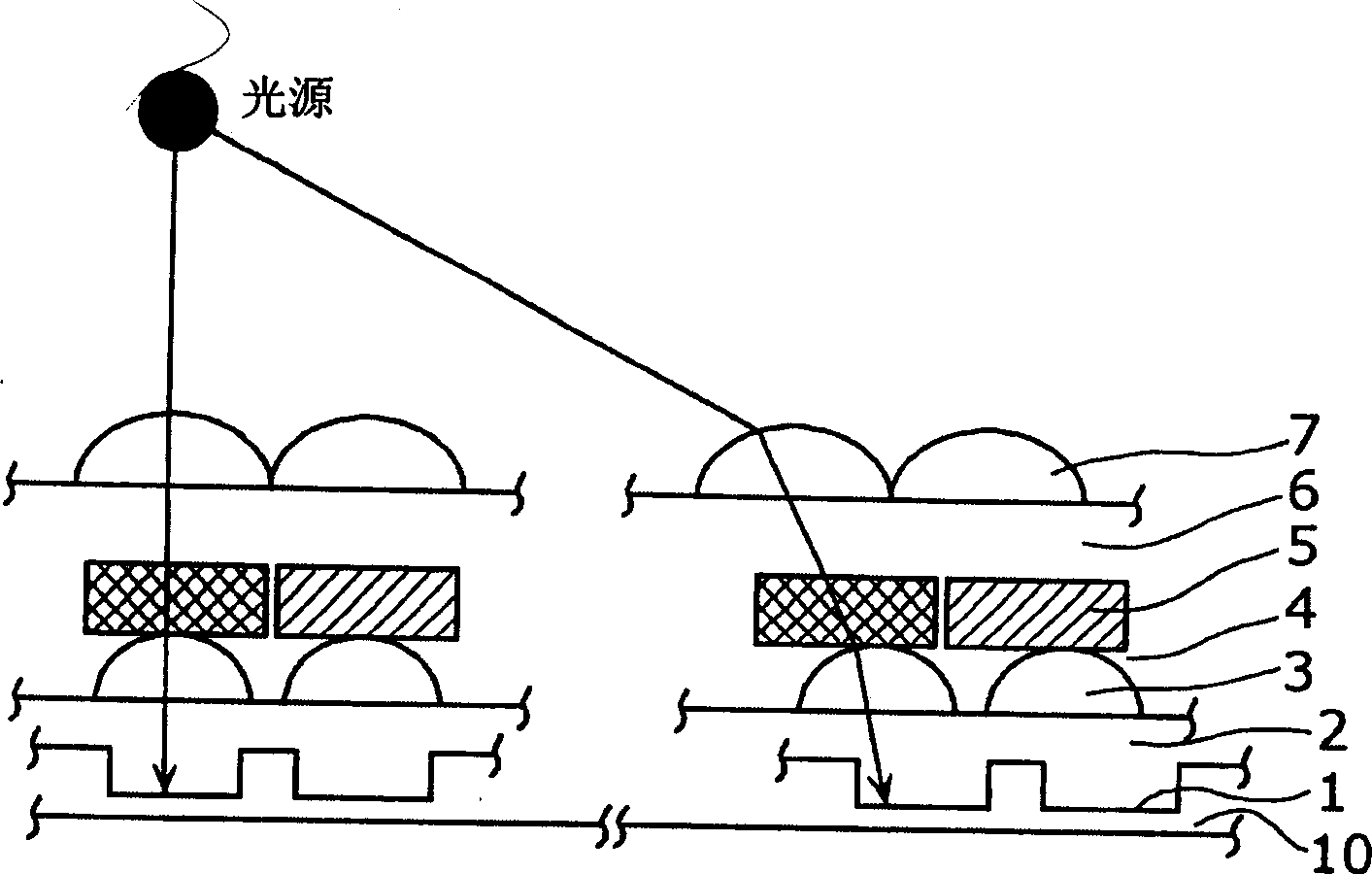
[0044] image 3 It is a cross-sectional view showing the solid-state imaging device according to the first embodiment of the present invention. This solid-state imaging device has a light-receiving surface composed of light-receiving elements (photodiodes) arranged two-dimensionally. This figure shows a cross section of two light receiving elements at the center (the left side of the figure) and a cross section of two light receiving elements at the end (right side of the figure) on the light receiving surface. In addition, the solid line in the figure indicates the source from the light source (equivalent to Figure 18 The incident light pattern of the lens 110) is shown.
[0045] In this figure, on a photodiode 1 formed on a silicon semiconductor substrate 10 of a solid-state imaging device, a planarized transparent insulating film (protective film) 2 made of BPSG (borophosphosilicate glass) or the like is sequentially stacked and formed. In-layer lens 3 with co...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0066]
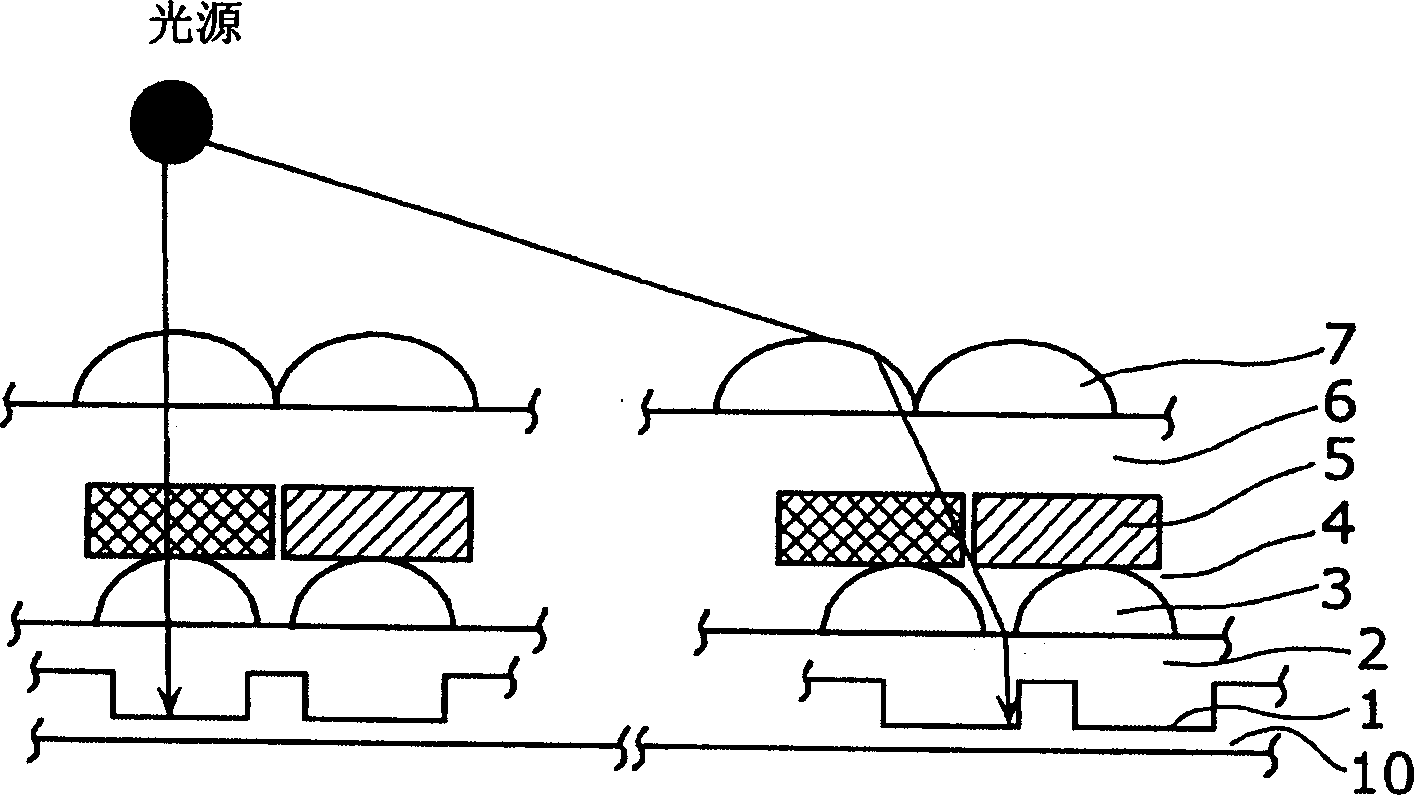
[0067] Figure 7 It is a cross-sectional view of the solid-state imaging device in the second embodiment of the present invention. The graph is structured with image 3 Compared with the above structure, the difference is that the color filter 5 is removed, and the microlens 7 is replaced by a microlens 7a. The description of the same points will be omitted below, and the description will focus on the different points.
[0068] The microlens 7 a is different from the microlens 7 in that it is opaque and doubles as a color filter.
[0069] According to this configuration, similar to the first embodiment, the exit pupil distance can be shortened and shadow shadows can be simulated. In addition, since the microlens 7a also serves as a color filter, the film thickness of the solid-state imaging device can be reduced by an amount equivalent to the thickness of the color filter layer. For example, in the solid-state imaging device in the first embodiment, when the dist...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0086]
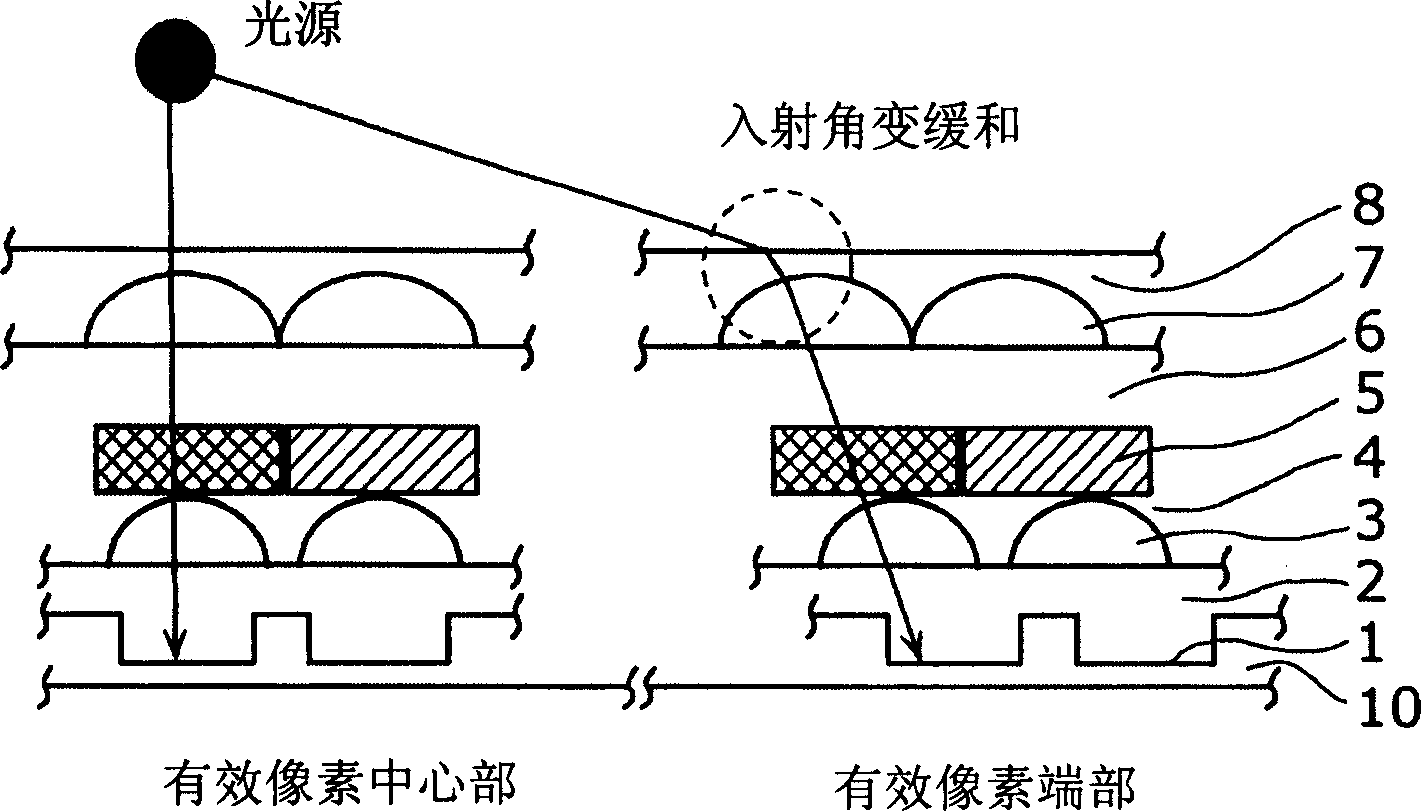
[0087] Figure 11 It is a cross-sectional view of the solid-state imaging device in the third embodiment of the present invention. The graph is structured with image 3 Compared with the above structure, the difference is that the color filter 5 is removed, and the inner lens 3 is replaced by the inner lens 3a. Hereinafter, the description of the same content is omitted, and the different content is mainly explained.
[0088]The in-layer lens 3 a is different from the in-layer lens 3 in that it is opaque and doubles as a color filter.
[0089] According to this configuration, similar to the first embodiment, the exit pupil distance can be shortened and shadow shadows can be simulated. In addition, since the in-layer lens 3a also serves as a color filter, the film thickness of the solid-state imaging device can be reduced by an amount equivalent to the thickness of the color filter layer. For example, in the solid-state imaging device in the first embodiment, whe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com